预约演示
更新于:2025-10-21

Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd.
更新于:2025-10-21
概览
标签
肿瘤
皮肤和肌肉骨骼疾病
血液及淋巴系统疾病
小分子化药
生物类似药
单克隆抗体
疾病领域得分
一眼洞穿机构专注的疾病领域
暂无数据
技术平台
公司药物应用最多的技术
暂无数据
靶点
公司最常开发的靶点
暂无数据
| 排名前五的药物类型 | 数量 |
|---|---|
| 小分子化药 | 45 |
| 蛋白水解靶向嵌合体(PROTAC) | 31 |
| 生物类似药 | 9 |
| 单克隆抗体 | 6 |
| 化学药 | 4 |
关联
96
项与 Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. 相关的药物靶点 |
作用机制 HK2抑制剂 [+2] |
最高研发阶段批准上市 |
首次获批国家/地区 印度 |
首次获批日期2021-05-01 |
靶点 |
作用机制 PD-1抑制剂 |
在研机构 |
原研机构 |
最高研发阶段批准上市 |
首次获批国家/地区 中国 |
首次获批日期2018-12-17 |
作用机制 5-HT1A receptor拮抗剂 |
非在研适应症- |
最高研发阶段批准上市 |
首次获批国家/地区 英国 |
首次获批日期2018-09-20 |
505
项与 Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. 相关的临床试验CTRI/2024/12/078285
A randomised, double-blind, multicentre study to compare the immunogenicity and safety of proposed abatacept biosimilar (DRL_AB) with Reference abatacept (Orencia®) administered subcutaneously as an add-on to methotrexate in patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis. - NIL
开始日期2025-12-01 |
CTRI/2025/06/088798
Evaluation of the potential of a Test Product (Sunscreen) to induce phototoxicity (photo irritation) in adult participants, using a photo patch test technique. IS 4011 2018 Guidelines. - NIL
开始日期2025-06-25 |
CTRI/2025/06/089158
Evaluation of efficacy and in use tolerance of a test product (Facewash) in men and or women. - NIL
开始日期2025-06-23 |
100 项与 Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
1,202
项与 Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. 相关的文献(医药)2025-08-01·SYNTHESIS-STUTTGART
Quality by Design Driven Improved Process of Abiraterone Acetate
作者: Bandichhor, Rakeshwar ; Reddy, B Ramalinga ; Komati, Shravan Kumar ; Annapurna, Sasikala Cheemalapati Venkata ; Bathini, Pavan Kumar ; Gaddameedhi, Prashanth Reddy ; Manda, Amarendhar ; Annapragada, Ratnamala ; Rao, Srinivas Talasila ; Nahide, Pradip D. ; Madhra, Mukesh Kumar
Abstract:
Abiraterone is an antiandrogen and selective inhibitor of 17α-hydroxylase/C17,20-lyase (CYP17) and is currently used in the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer and metastatic high-risk castration-sensitive prostate cancer. Here an improved kilogram scale synthesis of Abiraterone is presented, starting from commercially available dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) by employing Quality by Design (QbD) principles, statistical design of experiments (DoE), and green metrics parameters to evaluate the environmental impact and efficiency. This article focuses on identifying critical quality attributes (CQAs), exploring the relationship between CQAs and material attributes (MAs), and determining the critical process parameters (CPPs) for synthesizing hydrazone, vinyl iodide intermediates, and the final product, Abiraterone acetate. The presented approach effectively managed critical impurities and achieved impressive yields of 98, 84, and 78% with purity >99% in the hydrazone, vinyl iodide intermediate, and final API, respectively. The improved synthesis was optimized and scaled for multi-kilogram batches, addressing challenges from previous methods and yielding ICH quality material in 65% overall yield.
2025-07-29·Cureus Journal of Medical Science
Retrospective Electronic Medical Records Study to Understand the Usage Patterns and Patient Profiles of Those Prescribed Amlodipine and Its Combinations
Article
作者: Lhila, Sunil ; Kumar, Rohit ; Sanghavi, Arti ; Shah, Jay ; Bhureddy, Swathi ; Katare, Sagar ; Shah, Snehal ; Pande, Arindam ; Verma, Garima
BACKGROUND:
Hypertension is a lifestyle disorder with a target blood pressure (BP) <140/90 mmHg. Amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker (CCB), is the first-line choice of treatment. This study aims to assess the effectiveness, tolerability, and treatment pattern of amlodipine or its combinations in patients with hypertension.
METHODOLOGY:
This retrospective, electronic medical records (EMR)-based longitudinal study analyzed anonymized data of hypertensive patients with prescriptions for amlodipine or its combinations. The primary aim was to understand the usage patterns, while the secondary goals were to assess effectiveness and tolerability. Outcome measures included changes in mean systolic BP (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP), and the incidence of pedal edema.
RESULTS:
Most of the participants were aged 40 to 64 years (65.47%) and were predominantly male (52.85%). Dyslipidemia and diabetes mellitus (DM) were the most common comorbidities. There was a statistically significant reduction in SBP and DBP from visit 1 to visit 2 with amlodipine or its combination therapies (p < 0.001), irrespective of any comorbid condition. Pedal edema occurred in 0.91% of patients, notably lower than the reported 1.7%-32%.
CONCLUSION:
Amlodipine or its combinations demonstrated a significant reduction in BP with a very low incidence of pedal edema. Hence, amlodipine shows good tolerability and effectiveness in the Indian population.
2025-07-01·The Journal of the Association of Physicians of India
Prospective Real-World Study Comparing the Safety and Effectiveness of Nimesulide with Available Antipyretic and Analgesics for Treatment of Fever or Fever with Pain—ENDEVER
Article
作者: Pebbili, Kranthi Kiran ; Shejole, Vivek Samadhan ; Katare, Sagar Shivanand ; Yadagiri, Sunil Kumar Yadav ; Kotak, Bhavesh Prabhudas ; Kondiba Toke, Sahebrao ; Kadam, Neelam Ramakant ; Chandrappa, Ambrish M ; Bhagat, Seema ; Banerjee, Ritwik ; Ashraf, Syed Mustafa ; Sanghavi, Arti Pradip
INTRODUCTION:
Fever and pain are natural body responses to infections and inflammation. This study aims to collect real-world data and compare the safety and effectiveness of nimesulide (100 mg), ibuprofen (400 mg) + paracetamol (325 mg), and paracetamol (650 mg) in individuals with fever or fever-related pain.
METHODS:
A prospective, multicenter, comparative, and observational study was conducted in four centers across India with male and female subjects aged 18-60 years with fever or fever with pain. Fever reduction was assessed using a thermometer, and pain intensity was measured with the visual analog scale (VAS) at multiple intervals, up to 10 days.
RESULTS:
The study enrolled 303 subjects, divided into three groups: (1) group I (nimesulide), (2) group II (ibuprofen + paracetamol), and (3) group III (paracetamol). Remarkable fever and pain reduction were exhibited in the nimesulide group. Its effect on fever reduction was observed within 15 minutes of administration, with a significant improvement in VAS scores. Patients on nimesulide showed greater fever reduction at 1, 2, 4, and 6 hours, continuing through day 8, and greater improvements in VAS, especially by day 1 (p < 0.0001). No serious adverse events or deaths were reported.
CONCLUSION:
Nimesulide (100 mg) was superior to ibuprofen (400 mg) + paracetamol (325 mg) and paracetamol (650 mg) in managing fever or fever with pain, with a comparable safety profile.
455
项与 Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. 相关的新闻(医药)2025-10-16
·复星医药
10月16日,2025可持续全球领导者大会在上海举行。大会以“携手应对挑战:全球行动、创新与可持续增长”为主题,包括诺贝尔奖得主、图灵奖得主、全球500强企业负责人等在内的约500位中外嘉宾参会。
复星国际联席董事长汪群斌应邀作题为《以创新驱动:复星全球化攀登之路》的演讲,分享了复星如何在全球化征程中,以创新为核心驱动力,实现商业价值与社会价值的双赢。
汪群斌表示:
作为一家创新驱动的全球家庭消费产业集团,复星成立三十余年来始终秉持‘助天下’的初心,将全球化视野与本地化深耕相结合,将科技创新与社会责任相融合,走出一条创新驱动、责任引领的可持续发展之路。
“创新的最高境界,是让生命不留遗憾。”汪群斌表示,“在健康领域,创新不是论文上的数字,而是患者眼中的希望。每一个未被满足的医疗需求背后,都是一个渴望健康的家庭。”
他以复星自主研发的创新型抗PD-1单抗H药汉斯状为例,进一步阐释复星对创新的理解。
肺癌是全球发病率和死亡率最高的恶性肿瘤,而小细胞肺癌是其中侵袭性最强的亚型,约80%的患者首次确诊时已处于广泛期阶段,临床病情恶化快,总体预后不良。
面对这一严峻挑战,复星的科学家团队成功研发出H药——全球首个获批用于一线治疗小细胞肺癌的抗PD-1单抗。截至目前,H药已在中国、欧盟、英国、新加坡、印度等近40个国家和地区获批上市,惠及全球逾11万名患者。
H药是首个且目前唯一在欧盟获批用于广泛期小细胞肺癌治疗的抗PD-1单抗。“作为中国企业,我们感到很自豪,这意味着中国创新药成功进入了全球药品审批最严格的市场。”汪群斌说。
值得一提的是,10月9日,H药胃癌围手术期III期临床研究达到了主要终点,支持提前申报上市。这意味着,未来,胃癌患者在术前和术后有望不再需要进行辅助化疗。
今年以来,复星在创新药领域实现多点破局。HLX43是一款靶向PD-L1的抗体偶联药物(ADC),正在中、美、日、澳等国家开展非小细胞肺癌、胸腺癌等实体瘤的临床研究。目前,全球范围内尚无PD-L1 ADC获批上市,HLX43有潜力成为高效、安全的“广谱抗癌药”。此外,在小分子创新药方面,复星自研的靶向药物复迈宁获批两项罕见病适应症,填补了相关罕见病肿瘤领域的治疗空白。
汪群斌认为,在创新药赛道,从“跟跑”到“并跑”再到“领跑”,中国企业正在经历一次伟大的转型,“就复星而言,我们将继续以源头创新为目标,聚焦未满足的临床需求,携手全球合作伙伴共同推动医疗健康事业发展。”
作为最早“出海”的中国民营企业之一,复星在全球超过40个国家和地区持续深耕。汪群斌表示:“我们深刻体会到,全球化能力的核心是创新能力,是价值链整合的能力。”
在医药领域,复星始终瞄准全球化进行布局。经过十多年积累,逐步构建起全球化的研发、注册、BD(业务发展)和营销能力。截至目前,复星旗下生物药创新产品已触达近60个国家和地区,惠及全球超85万患者。其中,乳腺癌治疗核心产品汉曲优,是中国、欧盟、美国获批的“中国籍”单抗生物类似药,累计在全球50多个国家和地区获批上市。
▲截止至2025年7月,汉曲优全球发货750多万支,惠及全球超过26万患者
在全球研发方面,复星打造了领先的小分子创新药平台,抗体、ADC等大分子技术平台,细胞治疗技术平台,并前瞻布局核药技术平台。专注于大分子的复宏汉霖已在全球范围内完成800余项药政注册申请,并获得600余项批准。
在全球BD方面,复星长期与Abbott、Dr. Reddy's、Lotus、Sandoz等通过战略合作,加速拓展全球主要市场。今年上半年,复宏汉霖BD合同现金流入超10亿元,同比增长280%。今年8月,复星医药两款自研的小分子抑制剂也连续实现对外授权,将携手海外合作伙伴,惠及更多全球患者。
复星的全球化创新不止于医药领域。汪群斌介绍,在文旅消费领域,复星旅文Club Med地中海俱乐部持续深化AI数字化升级,G.M Copilot对话助手提供7x24小时即时响应的个性化服务,目前已覆盖巴西、法国、比利时、新加坡、马来西亚等全球12个国家市场。今年8月,复星旅文与阿里云达成全栈AI合作,基于通义千问模型共同开发文旅智能体“AI G.O”,全球客户的度假全流程体验将得到大幅提升。
在金融服务领域,复星葡萄牙保险依托AI应用,全面提升业务全流程效率,并提高数据准确性,推动保险业务快速发展。目前,车险自动理赔率从2023年末的48%提升至66%。
此外,豫园灯会走出国门,相继在法国巴黎、泰国曼谷举办,为海外朋友了解中国文化、爱上中国文化,打开了新的窗口。舍得酒业也承载着“舍与得”的中国智慧,扬帆出海,登陆40个国际和地区。
“创新是价值创造的源动力。我们始终相信,依托创新不断实现价值创造,是中国企业出海最重要的锚。”汪群斌说。
“企业不仅是商业主体,更是社会公民。我们相信,商业向善是企业可持续发展的基石,创新不仅是技术突破,更是社会问题解决方案的重新设计。”汪群斌表示,在30多年的发展历程中,复星始终高度重视ESG(环境、社会、治理)责任。
在抗击全球疟疾方面,复星持续贡献“中国方案”,将诺贝尔奖得主屠呦呦团队发现的青蒿素,研发成为中国001号(青蒿琥酯)、002号(注射用青蒿琥酯)创新药。截至2025年6月底,复星已累计向全球供应超过4.2亿支注射用青蒿琥酯,累计救治全球超8400万重症疟疾患者。
过去数十年间,尽管全球抗疟取得了重大进展,疟疾仍然是全球主要公共卫生问题之一,特别是在撒哈拉以南非洲,疟疾每分钟就夺走一个人的生命。根据世界卫生组织《2024年世界疟疾报告》,2023年全球83个国家估计有2.63亿新发疟疾病例,全球疟疾死亡人数达到59.7万人。
面对这一严峻挑战,复星持续创新,尽最大努力提升药品可及性。2023年6月,复星自主研发的第二代注射用青蒿琥酯Argesun获世界卫生组织预认证,成为首个通过该预认证的一步配制青蒿琥酯注射剂。与第一代产品相比,第二代产品极大提升了临床使用的便利性,特别适用于医疗条件相对落后的非洲偏远地区,被当地医护人员称为“来自中国的救命药”。
▲复星医药子公司Tridem Pharma首个非洲区域性药品分销中心已在科特迪瓦投入运营,为医疗健康产品在非洲地区的持续可及性提供保障。
同样围绕“健康”这个全球公共议题,在中国乡村,复星于2017年发起了乡村医生项目。秉持“我们守护村医,村医守护大家”理念,经过8年坚持,乡村医生项目已覆盖16个省、市、自治区的78个县,守护着2.5万名村医,惠及300万户农村家庭、超1600万农村人口。
今年9月,“健康中国·2025全国暖心乡村医生及乡镇卫生院院长”发布仪式在清华大学举行。会上推出了AI村医助手(1.0),它依托阿里巴巴通义大模型打造,把专家们共同编写的《乡村医生诊疗口袋书》转化为数字数据库,村医可以通过简洁的窗口,一问一答,随时查阅口袋书中权威、普惠的基层医疗问诊方案,高效辅助日常工作。
“当每位中国村医、每位非洲儿童都能享受到这个时代最重要的创新红利,我们的创新就有了最大价值。”汪群斌表示,“‘助天下’是复星成立之初就确立的企业价值观,无论青蒿琥酯援非抗疟,还是乡村医生项目,都是这一理念的具体实践。”
凭借多年来的持续努力,复星MSCI ESG评级保持为AA,连续入选标普全球《可持续发展年鉴》,并在中国企业中名列最佳1%,富时罗素ESG评分也持续领先全球同业。
汪群斌表示,在可持续发展道路上,商业向善的力量正在推动企业与社会、中国与世界,在命运共同体的理念下发生深刻变革,“未来,复星将携手全球合作伙伴,以创新为梯,以责任为缆,继续攀登可持续发展的新高峰,为人类命运共同体贡献中国企业的智慧与力量。”
抗体药物偶联物
2025-10-12
·信狐药迅
本周药品注册受理数据,分门别类呈现,一目了然。(10.1-10.12)
新药上市申请
药品名称
企业
注册分类
受理号
瑞西奇拜单抗注射液
上海华奥泰生物药业股份有限公司
1
CXSS2500106
新药临床申请
药品名称
企业
注册分类
受理号
ICP-332
广州诺诚健华医药科技有限公司
1
CXHL2501074
注射用HSK55718
上海海思盛诺医药科技有限公司
1
CXHL2501078
注射用HSK55718
上海海思盛诺医药科技有限公司
1
CXHL2501077
RTX-117片
溪砾科技(深圳)有限公司
1
CXHL2501076
RTX-117片
溪砾科技(深圳)有限公司
1
CXHL2501075
HRS-5041片
江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司
1
CXHL2501068
HSK45019片
上海海思盛诺医药科技有限公司
1
CXHL2501073
HSK45019片
上海海思盛诺医药科技有限公司
1
CXHL2501072
HRL1101散
北京华睿鼎信科技有限公司
1
CXHL2501071
LPM6690176胶囊
烟台创和生物科技有限公司
1
CXHL2501064
LPM6690176胶囊
烟台创和生物科技有限公司
1
CXHL2501063
LPM6690176胶囊
烟台创和生物科技有限公司
1
CXHL2501062
DII235注射液
诺华(中国)生物医学研究有限公司
1
CXHL2501061
HSK36357胶囊
上海海思盛诺医药科技有限公司
1
CXHL2501060
HSK36357胶囊
上海海思盛诺医药科技有限公司
1
CXHL2501059
注射用硼[10B]法仑
深圳市中核海得威生物科技有限公司
2.2
CXHL2501079
1861B
普照国康(湖北)药业有限公司
2.2
CXHL2501070
注射用左炔诺孕酮微球
上海市生物医药技术研究院
2.2
CXHL2501065
泽美妥司他片
江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司
2.4
CXHL2501069
瑞维鲁胺片
江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司
2.4
CXHL2501067
注射用多西他赛(白蛋白结合型)
石药集团中奇制药技术(石家庄)有限公司
2.4
CXHL2501066
YF-3注射液
苏州永心生物科技有限公司
1
CXSL2500865
人前/中脑神经前体细胞注射液
浙江泉生生物科技有限公司
1
CXSL2500864
注射用SHR-4394
江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司
1
CXSL2500863
重组人源化抗HER2双特异性抗体注射液
上海津曼特生物科技有限公司
1
CXSL2500862
注射用ISH0688
盛禾(中国)生物制药有限公司
1
CXSL2500868
IBI363
信达生物制药(苏州)有限公司
1
CXSL2500860
IBI363
信达生物制药(苏州)有限公司
1
CXSL2500859
注射用ISH0613
盛禾(中国)生物制药有限公司
1
CXSL2500858
IBNI617肠溶胶囊
合肥瀚微生物科技有限公司
1
CXSL2500867
IBNI617肠溶胶囊
合肥瀚微生物科技有限公司
1
CXSL2500866
XLS-103注射液
香雪生命科学技术(广东)有限公司
1
CXSL2500857
XLS-103注射液
香雪生命科学技术(广东)有限公司
1
CXSL2500856
注射用YB-01
元本(珠海横琴)生物科技有限公司
1
CXSL2500855
仿制药申请
药品名称
企业
注册分类
受理号
枸橼酸西地那非口溶膜
合肥华方医药科技有限公司
3
CYHS2503629
枸橼酸西地那非口溶膜
合肥华方医药科技有限公司
3
CYHS2503628
硫代硫酸钠注射液
成都诺和晟鸿生物制药有限公司
3
CYHS2503624
呋塞米注射液
亚邦医药股份有限公司
3
CYHS2503622
多索茶碱片
合肥合源药业有限公司
3
CYHS2503631
对乙酰氨基酚片
瑞阳制药股份有限公司
3
CYHS2503606
对乙酰氨基酚片
瑞阳制药股份有限公司
3
CYHS2503605
色甘酸钠滴眼液
武汉新瑞医药科技有限公司
3
CYHS2503616
美索巴莫注射液
山东益健药业有限公司
3
CYHS2503609
呋塞米注射液
河南普瑞药业有限公司
3
CYHS2503598
盐酸利多卡因注射液
广州瑞尔医药科技有限公司
3
CYHS2503595
盐酸决奈达隆片
浙江众延医药科技有限公司
4
CYHS2503637
氢溴酸替格列汀片
杭州和泽坤元药业有限公司
4
CYHS2503636
注射用磷酸左奥硝唑酯二钠
石家庄四药有限公司
4
CYHS2503627
西格列汀二甲双胍片(II)
多多药业有限公司
4
CYHS2503626
硝苯地平控释片
山东宜岛康制药有限公司
4
CYHS2503625
卡泊三醇软膏
南京海融制药有限公司
4
CYHS2503623
糠酸莫米松鼻喷雾剂
浙江致新医药科技有限公司
4
CYHS2503621
阿达帕林过氧苯甲酰凝胶
江苏盈科生物制药有限公司
4
CYHS2503635
溴芬酸钠滴眼液
海南斯达制药有限公司
4
CYHS2503634
克立硼罗软膏
佑华医药科技有限公司
4
CYHS2503633
盐酸氨溴索口服溶液
四川森科制药有限公司
4
CYHS2503632
阿奇霉素干混悬剂
广东方盛健盟药业有限公司
4
CYHS2503630
苯磺顺阿曲库铵注射液
山东威智百科药业有限公司
4
CYHS2503648
丙酸氟替卡松乳膏
浙江华海制药科技有限公司
4
CYHS2503638
阿达帕林凝胶
国药控股鑫烨(湖北)医药有限公司
4
CYHS2503608
枸橼酸莫沙必利片
四川依科制药有限公司
4
CYHS2503607
蛋白琥珀酸铁口服溶液
华润紫竹药业有限公司
4
CYHS2503604
盐酸乐卡地平片
吉林天衡英睿制药有限公司
4
CYHS2503620
盐酸乐卡地平片
吉林天衡英睿制药有限公司
4
CYHS2503619
氯沙坦钾氢氯噻嗪片
翎耀生物科技(上海)有限公司
4
CYHS2503618
盐酸头孢卡品酯颗粒
杭州和泽坤元药业有限公司
4
CYHS2503617
卡贝缩宫素注射液
武汉九珑医药有限责任公司
4
CYHS2503615
氢溴酸伏硫西汀片
云鹏医药集团有限公司
4
CYHS2503614
盐酸尼卡地平注射液
吉林敖东药业集团延吉股份有限公司
4
CYHS2503613
盐酸尼卡地平注射液
吉林敖东药业集团延吉股份有限公司
4
CYHS2503612
多替诺雷片
山东朗诺制药有限公司
4
CYHS2503611
多替诺雷片
山东朗诺制药有限公司
4
CYHS2503610
达格列净二甲双胍缓释片(I)
江苏亚邦爱普森药业有限公司
4
CYHS2503603
达格列净二甲双胍缓释片(III)
江苏亚邦爱普森药业有限公司
4
CYHS2503602
阿帕他胺片
昆山龙灯瑞迪制药有限公司
4
CYHS2503601
夫西地酸乳膏
浙江核力欣健药业有限公司
4
CYHS2503600
亚叶酸钙注射液
山西普德药业有限公司
4
CYHS2503599
比卡鲁胺片
杭州和泽坤元药业有限公司
4
CYHS2503597
依折麦布阿托伐他汀钙片
浙江恒研医药科技有限公司
4
CYHS2503596
依折麦布阿托伐他汀钙片
浙江恒研医药科技有限公司
4
CYHS2503594
精氨酸布洛芬颗粒
白云山东泰商丘药业有限公司
4
CYHS2503593
盐酸赛洛唑啉鼻用喷雾剂
四川普锐特药业有限公司
4
CYHS2503592
瑞舒伐他汀钙片
山西汾河制药有限公司
4
CYHS2503591
瑞舒伐他汀钙片
山西汾河制药有限公司
4
CYHS2503590
酮洛芬贴剂
海南合瑞制药股份有限公司
3
CYHL2500179
马沙骨化醇注射液
南京泽恒医药技术开发有限公司
3
CYHL2500178
尿素[14C]胶囊
成都欣科医药有限公司
3
CYHL2500177
倍氯米松福莫特罗吸入气雾剂
鲁南贝特制药有限公司
4
CYHL2500176
抗五步蛇毒血清
江西生物制品研究所股份有限公司
3.4
CXSL2500869
静注人免疫球蛋白
广东卫伦生物制药有限公司
3.4
CXSL2500861
进口申请
药品名称
企业
注册分类
受理号
萘普生钠片
Bayer(Schweiz)AG
5.1
JXHS2500117
注射用A型肉毒毒素
Daewoong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
3.4
JXSS2500130
PF-07328948片
Pfizer Inc.
1
JXHL2500311
PF-07328948片
Pfizer Inc.
1
JXHL2500310
BMS-986519肠溶胶囊
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
2.2
JXHL2500308
BMS-986519肠溶胶囊
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
2.2
JXHL2500307
BMS-986519肠溶胶囊
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
2.2
JXHL2500306
BMS-986519肠溶胶囊
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
2.2
JXHL2500305
Entrectinib胶囊
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
2.4
JXHL2500309
Pasritamig注射液
Janssen Research & Development, LLC
1
JXSL2500194
AZD2936
AstraZeneca AB
1
JXSL2500193
Pasritamig注射液
Janssen Research & Development, LLC
1
JXSL2500195
中药相关申请
药品名称
企业
注册分类
受理号
复方南藤胶囊
南京中医药大学
1.1
CXZL2500094
TQA凝胶贴膏
赛灵药业科技集团股份有限公司
2.2
CXZL2500093
荆防合剂
鲁南厚普制药有限公司
2.3
CXZL2500092
注:绿色字体部分为潜在首仿品种;
不包含原料药、医用氧、注射用水、氯化钠或葡萄糖注射液等申请,不包含再注册、一次性进口、技术转移、复审申请。
申请上市
2025-10-09
Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment (TED) Treatment is not exclusive to adults. Children with graves’ disease are also susceptible, which create a possible market
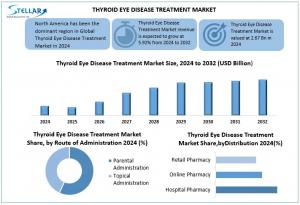
“Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market is set to soar from USD 2.67B in 2024 to USD 4.23B by 2032 at 5.92% CAGR, driven by Teprotumumab, biologics, pediatric therapies, and innovative treatments.”
”
— Dharti Raut
WILMINGTON, DE, UNITED STATES, October 9, 2025 /
EINPresswire.com
/ -- Explore the
Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market
, valued at USD 2.67B in 2024, projected to reach USD 4.23B by 2032 at a CAGR of 5.92%. Key drivers include Teprotumumab, biologics, pediatric therapies, and global market growth.
Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market Overview:
Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) Treatment Market is poised for explosive global growth, projected to surge from USD 2.67B in 2024 to USD 4.23B by 2032 at a 5.92% CAGR, driven by rising thyroid disorders, including Graves’ disease affecting over 750 million people worldwide. Innovative biologics, Teprotumumab, pediatric therapies, and personalized treatment options are accelerating market adoption, while early diagnosis and advanced imaging expand patient access. North America leads with FDA-approved therapies, Europe thrives on strong R&D and regulatory support, and Asia-Pacific emerges as a high-growth hub with cost-effective treatments. Key players like Amgen, Pfizer, Roche, Novartis, and Sanofi intensify competition, with strategic investments offering high ROI and unlocking untapped opportunities in ocular care, targeted biologics, and advanced TED management.
𝐔𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐜𝐤 𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐞 𝐢𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐭𝐬—𝐫𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐚 𝐟𝐫𝐞𝐞 𝐬𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐫𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐧𝐨𝐰 :
https://www.stellarmr.com/report/req_sample/thyroid-eye-disease-treatment-market/2767
Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market Poised for Explosive Growth as Graves’ Disease Cases Skyrocket Globally
Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market is set to surge as the global prevalence of thyroid disorders, particularly Graves’ disease, rises dramatically. With over 750 million people affected worldwide and 1% of the U.S. population living with hyperthyroidism, demand for cutting-edge TED therapies, including Teprotumumab, biologics, and personalized treatments, is accelerating. Growing awareness and innovative treatment options are driving the market toward unprecedented growth, unlocking exciting opportunities in ocular care and advanced thyroid eye disease management.
Pediatric Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market Set to Soar as Childhood Graves’ Cases Reveal Untapped Opportunities
Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) treatments have traditionally focused on adults, emerging data reveal a growing need for pediatric-specific therapies. With 0.02% of U.S. children diagnosed with hyperthyroidism annually and increasing awareness of TED in adolescents, demand for child-friendly biologics, Teprotumumab, and personalized therapies is set to soar. This untapped segment presents an exciting opportunity for pharmaceutical companies to innovate, develop age-appropriate treatments, and shape the future of pediatric thyroid eye disease care.
Regulatory Hurdles Threaten Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market, but Innovative TED Therapies Could Turn Risks into Opportunities
Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) Treatment Market faces significant headwinds as FDA drug approvals remain a lengthy and costly process. On average, new TED therapies take 8–12 years for approval, with only 10% of investigational drugs successfully reaching the market. Regulatory hurdles, including strict Phase III trials and rigorous safety assessments, can stall the introduction of innovative TED therapies, biologics, and Teprotumumab treatments, sometimes costing over USD 2.6 billion per drug. To navigate these challenges, pharmaceutical companies should prioritize early regulatory engagement and adaptive clinical strategies, turning potential risks into opportunities for pioneering therapies in thyroid eye disease care.
Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market Soars as Parental Biologics and Hospital-Led Care Drive Unprecedented Growth
Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market is driven by both route of administration and end-use industry, with parental administration, including intravenous biologics like Teprotumumab, leading due to rapid symptom relief and targeted action for severe TED cases, while topical treatments support milder symptoms. Hospitals dominate as end users, providing advanced therapies and surgical care, supported by clinics and other providers, with distribution via hospital, online, and retail pharmacies expanding patient access. These segments collectively highlight the growing demand for innovative TED therapies, biologics, and personalized treatment options, making the market dynamic and full of opportunities.
Key Trends Driving Innovation in the Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market
Development of Biologics: Monoclonal antibodies like Teprotumumab are transforming the Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market by targeting the IGF-1 receptor to modulate immunity and reduce inflammation.
Increased Awareness and Early Diagnosis: Growing awareness and advanced imaging tools enable earlier Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) detection and faster treatment initiation.
Key Development: Amgen Secures TEPEZZA
®
Approval in Japan, Expanding Global Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market Leadership
September 24, 2024 – Amgen (NASDAQ: AMGN) gains Japan MHLW approval for TEPEZZA
®
to treat active Thyroid Eye Disease (TED), boosting its leadership in the TED Treatment Market.
Innovative Biologics and FDA Approvals Drive North America’s Leadership in Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market
North America dominates the Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, high prevalence of thyroid disorders, and rapid adoption of innovative biologics like Teprotumumab. With 1 in 8 U.S. women at risk of thyroid issues and strong R&D investment, major pharmaceutical players are fuelling market expansion. Ongoing awareness campaigns and FDA-approved targeted therapies position the region for sustained growth and leadership in the global TED treatment landscape.
𝐈𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐝 𝐢𝐧 𝐝𝐞𝐭𝐚𝐢𝐥𝐞𝐝 𝐢𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐭𝐬? 𝐈𝐧𝐪𝐮𝐢𝐫𝐞 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐚 𝐬𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐫𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 :
https://www.stellarmr.com/report/req_sample/thyroid-eye-disease-treatment-market/2767
Global Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market Heats Up: Biologics, Teprotumumab, and Biosimilars Fuel Fierce Competition
Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market is dominated by leading drug and biotech companies focusing on biologics and monoclonal antibody therapies. In North America, major players like Magen, Viridian Therapeutics, and Physics leverage FDA-approved drugs such as Teprotumumab. Europe thrives on strong R&D investment and regulatory support, with Novartis, Sanofi, and GlaxoSmithKline driving innovation. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific emerges as a high-growth hub, led by HanAll Biopharma and Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, offering cost-effective treatments and expanding patient awareness. Rising competition from targeted biologics, biosimilars, and personalized medicine is reshaping the market, though regulatory hurdles and high development costs remain key challenges, creating opportunities for strategic innovation.
Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market Key Players:
North America
Horizon Therapeutics (United States)
Amgen (United States)
Pfizer (United States)
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals (United States)
Bristol-Myers Squibb (United States)
Novartis (United States)
Bausch Health (Canada)
Europe
Roche (Switzerland)
Novartis International (Switzerland)
Merck KGaA (Germany)
Sanofi (France)
AstraZeneca (United Kingdom)
GlaxoSmithKline (United Kingdom)
Swedish Orphan Biovitrum - Sobi (Sweden)
LEO Pharma (Denmark)
Asia Pacific
Takeda Pharmaceutical (Japan)
Daiichi Sankyo (Japan)
Fosun Pharma (China)
Sun Pharma (India)
Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories (India)
Samsung Bioepis (South Korea)
CSL Limited (Australia)
Middle East & Africa
Teva Pharmaceutical (Israel)
Aspen Pharmacare (South Africa)
South America
Eurofarma (Brazil)
Aché Laboratórios (Brazil)
Elea Phoenix (Argentina)
Analyst Perspective:
Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) Treatment Market is set for rapid global growth, fueled by rising thyroid disorders and Graves’ disease affecting 750M+ people. Biologics, Teprotumumab, and personalized therapies are driving adoption and revenue potential. North America leads with FDA-approved biologics, Europe excels via R&D and regulatory support, and Asia-Pacific grows through cost-effective treatments. Key players like Amgen, Pfizer, and Roche intensify competition, while pediatric treatments and early diagnosis offer untapped opportunities. Strategic investments promise strong ROI, making TED a high-potential, innovation-driven sector.
𝐅𝐨𝐫 𝐟𝐮𝐥𝐥 𝐚𝐜𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬 𝐭𝐨 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐝𝐚𝐭𝐚, 𝐫𝐞𝐪𝐮𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐚 𝐬𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞 𝐫𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭 𝐧𝐨𝐰 :
https://www.stellarmr.com/report/req_sample/thyroid-eye-disease-treatment-market/2767
FAQ
Q1: What is the expected growth of the Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market?
A1: The market is projected to grow from USD 2.67B in 2024 to USD 4.23B by 2032 at a 5.92% CAGR.
Q2: Which therapies are driving the Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market?
A2: Teprotumumab, biologics, pediatric therapies, and personalized treatments are key growth drivers.
Q3: Who are the major players in the global Thyroid Eye Disease Treatment Market?
A3: Leading companies include Amgen, Pfizer, Roche, Novartis, Sanofi, Horizon Therapeutics, and Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories.
Maximize Market Research is launching a subscription model for data and analysis in the
Dental Materials market
https://www.mmrstatistics.com/markets/461/healthcare
About Stellar Market Research
Established in 2018, Stellar Market Research is India Based consulting and advisory firm focused on helping clients to reach their business transformation objectives with advisory services and strategic business. The company’s vision is to be an integral part of the client’s business as a strategic knowledge partner. Stellar Market Research provides end-to-end solutions that go beyond key research technologies to help executives in any organization achieve their mission-critical goals.
Contact Us :
Address
Phase 3, Navale IT Zone, S.No. 51/2A/2, Office No. 202, 2nd floor, Near, Navale Brg, Narhe, Pune, Maharashtra 411041
Email
sales@stellarmr.com
Mobile
+91 9607365656
Lumawant Godage
Stellar Market Research
+ +91 98606 63688
email us here
Visit us on social media:
LinkedIn
Instagram
Facebook
X
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability
for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this
article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
临床3期上市批准
100 项与 Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
组织架构
使用我们的机构树数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

管线布局
2025年11月06日管线快照
管线布局中药物为当前组织机构及其子机构作为药物机构进行统计,早期临床1期并入临床1期,临床1/2期并入临床2期,临床2/3期并入临床3期
药物发现
3
49
临床前
临床申请
1
11
临床1期
临床2期
3
2
临床3期
申请上市
3
23
批准上市
其他
77
登录后查看更多信息
当前项目
| 药物(靶点) | 适应症 | 全球最高研发状态 |
|---|---|---|
利妥昔单抗生物类似药(Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories) ( CD20 ) | 类风湿关节炎 更多 | 批准上市 |
阿扎胞苷 ( DNMT1 ) | 骨髓增生性疾病 更多 | 批准上市 |
环磷酰胺 ( DNA ) | 卵巢腺癌 更多 | 批准上市 |
贝伐珠单抗生物类似药(Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories) ( VEGF-A ) | 晚期肺非鳞状非小细胞癌 更多 | 批准上市 |
卡培他滨 ( TYMS ) | 结肠癌 更多 | 批准上市 |
登录后查看更多信息
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

营收
使用 Synapse 探索超过 36 万个组织的财务状况。
登录
或

科研基金(NIH)
访问超过 200 万项资助和基金信息,以提升您的研究之旅。
登录
或

投资
深入了解从初创企业到成熟企业的最新公司投资动态。
登录
或

融资
发掘融资趋势以验证和推进您的投资机会。
登录
或

生物医药百科问答
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用


