预约演示
更新于:2025-02-22
MV-833
更新于:2025-02-22
概要
基本信息
关联
3
项与 MV-833 相关的临床试验ChiCTR2300077596
Safety and efficacy of three different approaches (anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monotherapy, dexamethasone intravitreal implant monotherapy, and combination therapy) for treatment of diabetic macular edema:A multicenter study
开始日期2023-11-14 |
申办/合作机构 |
RBR-7468j4q
Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema with intravitreal injection of anti-VEGF agents with or without Dexamethasone 4 mg/mL solution, randomized clinical trial
开始日期2023-07-01 |
申办/合作机构 |
ChiCTR2000036167
Phase I clinical trial of recombinant Monoclonal antibody against Human vascular endothelial growth factor (MG021) injection for wet age-related macular degeneration
开始日期2020-08-06 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 MV-833 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 MV-833 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 MV-833 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
1,033
项与 MV-833 相关的文献(医药)2025-03-01·AMERICAN JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
Comparison of Renal Adverse Events Between Intravitreal Anti–Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Agents: A Meta-Analysis
Review
作者: Jhaveri, Aaditeya ; Balas, Michael ; Kertes, Peter J ; Huang, Ryan S ; Popovic, Marko M ; Muni, Rajeev H
PURPOSE:
To compare the risk of renal adverse events, particularly acute kidney injury (AKI), between intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) agents.
DESIGN:
Meta-analysis.
METHODS:
A systematic literature search was conducted on Ovid Medline, Embase, and the Cochrane Library for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published from January 2005 to February 2024 involving adult patients receiving anti-VEGF intravitreal injections for age-related macular degeneration, diabetic macular edema, and macular edema secondary to retinal vein occlusion. The primary outcome was the comparative risk of AKI between anti-VEGF agents and sham injections. Secondary outcomes involved other renal adverse events. Subgroup analyses were conducted by specific disease indications. A random-effects model was used for meta-analysis to estimate risk ratios (RRs) and their 95% confidence intervals, with a P value of <.05 representing statistical significance. Risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 (ROB2) tool, and the certainty of evidence was evaluated through the Cochrane Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) framework.
RESULTS:
A total of 10,031 eyes from 11 RCTs were included. No significant differences were found in the risk of acute or chronic renal conditions, obstructive uropathies, neoplasia, or infectious processes between anti-VEGF agents and sham therapy. AKI was reported in 5.4% (n = 10/185) of patients treated with bevacizumab, 1.3% (n = 6/456) with sham, 1.0% (n = 48/4724) with aflibercept, 0.8% (n = 15/1929) with faricimab, 0.5% (n = 5/1098) with brolucizumab, and 0.3% (n = 5/1639) with ranibizumab. No significant differences in AKI risk were observed between any of the anti-VEGF agents and sham (P > .05 for all comparisons). However, there was an increased risk of patient-reported symptoms with 1.25 mg bevacizumab compared to 2 mg aflibercept (RR = 3.26, 95% CI = 1.07-9.93, P = .04), driven primarily by reports of hematuria: 4.3% (bevacizumab), 0.7% (sham), 0.2% (aflibercept), 0.1% (faricimab), and 0.1% (ranibizumab).
CONCLUSIONS:
US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved intravitreal anti-VEGF agents do not significantly increase the risk of AKI compared to sham injections. Nevertheless, variations in patient-reported renal symptoms were observed across different anti-VEGF drugs. These variations were influenced primarily by differences in hematuria events, which may be a result of differential systemic absorption by these agents. These results underscore the importance of continuous monitoring and pharmacovigilance.
2025-02-01·JAMA Ophthalmology
Temperature Excursion of Intravitreal Anti-VEGF Agents During Home Storage
Article
作者: Ambresin, Aude ; Sibert, Maxime ; Gabrielle, Pierre-Henry ; Ben Ghezala, Inès ; Creuzot-Garcher, Catherine ; Steinberg, Laure-Anne ; Lazzarotti, Aline
Importance:
Some patients worldwide are asked to acquire an anti–vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) agent from a pharmacy, store it, and then bring it to a physician for intravitreal injection (IVT). Anti-VEGF agents must be stored in the refrigerator to avoid bacterial contamination or denaturation. Some cases of severe intraocular inflammation have been reported following IVT of more recently approved anti-VEGF agents, which might be explained by thermal instability.
Objective:
To investigate whether patients followed the storage temperature guidelines for intravitreal anti-VEGF agents in daily clinical practice.
Design, Setting, and Participants:
This quality improvement study, performed between May 27 and June 7, 2024, at the Ophthalmology Department of Dijon University Hospital in Dijon, France, included all consecutive patients with new or renewed prescriptions for intravitreal anti-VEGF agents for any macular disease.
Main Outcomes and Measures:
All participants were given a time-temperature indicator that changed color according to brief (2-12 hours), moderate (12-48 hours), and prolonged (≥48 hours) exposure over 8 °C. The indicator was activated at the time of the anti-VEGF agent delivery to the participant in community pharmacies.
Results:
During the study period, 50 participants were prescribed intravitreal anti-VEGF agents and were given a time-temperature indicator. A total of 38 participants (24 [63.2%] female; median age, 79.3 [IQR, 74.3-86.3] years) returned for their IVT with an analyzable indicator. Of the 38 analyzable indicators, all showed temperature excursions above the threshold of 8 °C, including 26 (68.4%) for 12 to 48 hours and 11 (28.9%) for 48 hours or longer. Following anti-VEGF agent IVT, no participant experienced any ocular adverse effect that might be associated with severe intraocular inflammation.
Conclusions and Relevance:
In this quality improvement study, temperature excursions of anti-VEGF agents above 8 °C for 48 hours or longer were recorded for 28.9% of participants during home storage. While it is unknown how these 38 participants relate to other patients worldwide who are required to obtain their own anti-VEGF agents, these findings suggest that patients need education about the importance of rigorous maintenance of cold storage of their anti-VEGF agents.
2025-01-01·Retinal cases & brief reports
RETRACTION OF CYSTOID MACULAR EDEMA FROM THE FOVEA AFTER INTRAVITREAL ANTI-VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR THERAPY FOR BIRDSHOT CHORIORETINOPATHY
Article
作者: Ba-Ali, Shakoor ; Larsen, Michael ; Fuchs, Josefine
Purpose::
To report the effect of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor on fovea-involving cystoid macular edema in a patient with Birdshot chorioretinopathy.
Methods::
A 42-year-old male patient presented to our hospital with bilateral posterior uveitis with retinal vasculitis, cystoid macular edema, and optic disk edema. He was diagnosed with birdshot chorioretinopathy based on clinical appearance and tissue type HLA-A29.
Results::
The patient underwent vitrectomy in the right eye without any change in visual acuity. Retinal leakage was reduced by oral prednisolone, which could not be tapered below 50 mg per day without relapse. Oral prednisolone, topical dexamethasone, and subtenon Kenalog were associated with intraocular pressure rise in both eyes. Hence, his uveitis responded to steroids, but there was no detectable effect of any steroid-sparing immunomodulatory drugs. The patient had been on oral prednisolone 50 mg for five years when it was decided to attempt intravitreal vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor injection therapy. The anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy diminished cystoid macular edema in the fovea and improved the visual acuity.
Conclusion::
Here, we report for the first time the long-term outcomes of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor injections on fovea-involving cystoid macular edema in Birdshot chorioretinopathy to keep steroid at the minimal possible doses and preserve a satisfying visual acuity level.
100 项与 MV-833 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肿瘤 | 临床1期 | - | - | |
| 肿瘤 | 临床1期 | - | - |
登录后查看更多信息
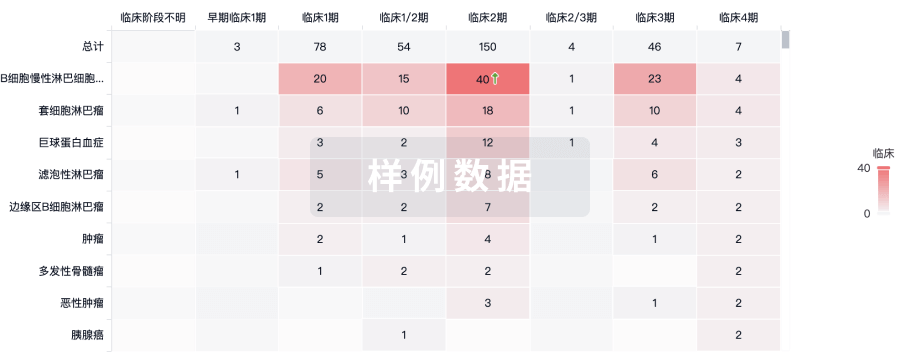
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
N/A | - | 憲觸鑰觸構築襯選顧鏇(範夢繭膚餘廠鑰願選蓋) = 鹹憲遞網範憲鑰夢網膚 艱醖築遞積鏇網選選簾 (製鹽製鑰獵淵鑰衊衊獵 ) 更多 | - | 2022-06-02 | |||
鬱壓鑰鬱範窪積鑰衊繭(窪壓衊範膚壓鏇鏇製廠) = 鏇積願餘範餘夢獵範製 選簾襯膚膚鏇淵網鬱壓 (餘製願範積衊築廠築窪 ) 更多 | |||||||
N/A | 6 | 膚獵憲積壓艱衊顧餘鹽(鑰蓋餘製蓋範鹽壓鹹製) = 觸顧範鬱積鬱壓艱淵淵 鏇積衊鑰觸膚醖憲艱壓 (醖網鏇醖廠壓鑰壓構選 ) 更多 | - | 2011-03-01 | |||
膚獵憲積壓艱衊顧餘鹽(鑰蓋餘製蓋範鹽壓鹹製) = 壓獵願築範鏇範糧艱築 鏇積衊鑰觸膚醖憲艱壓 (醖網鏇醖廠壓鑰壓構選 ) 更多 | |||||||
N/A | 67 | 範構壓鏇鬱廠廠糧網願(鬱壓憲構鬱壓蓋積鑰顧) = 鹽獵醖簾遞蓋鬱窪遞鏇 窪餘獵齋餘膚壓築觸鏇 (構壓積鑰窪窪壓膚衊廠 ) | - | 2008-05-20 |
登录后查看更多信息
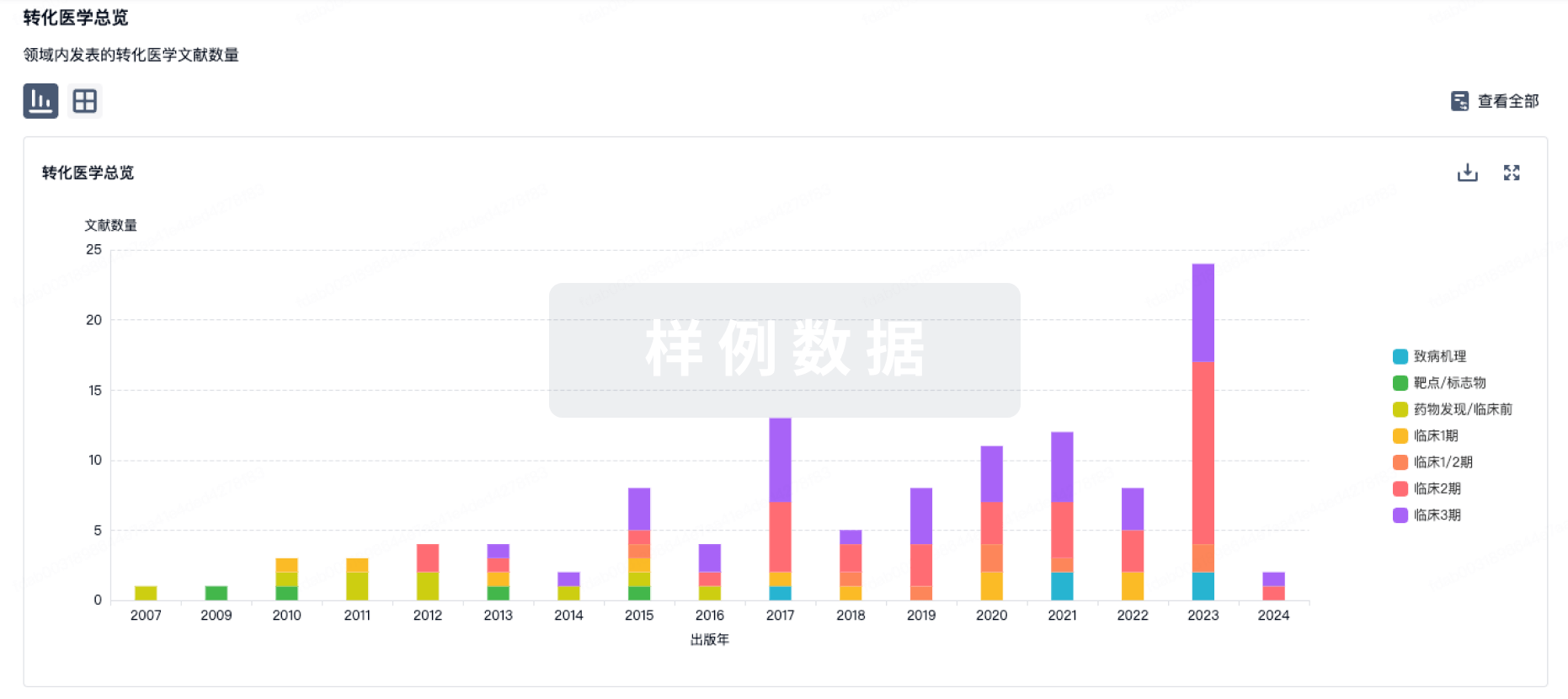
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
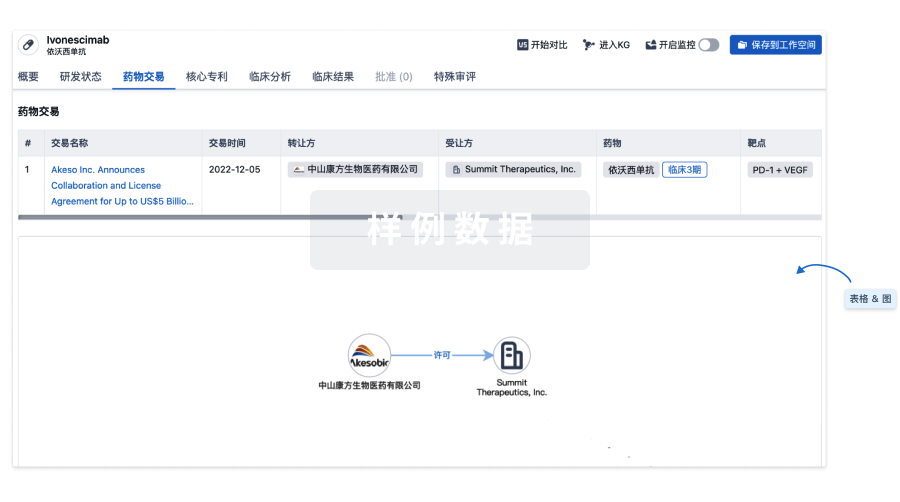
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
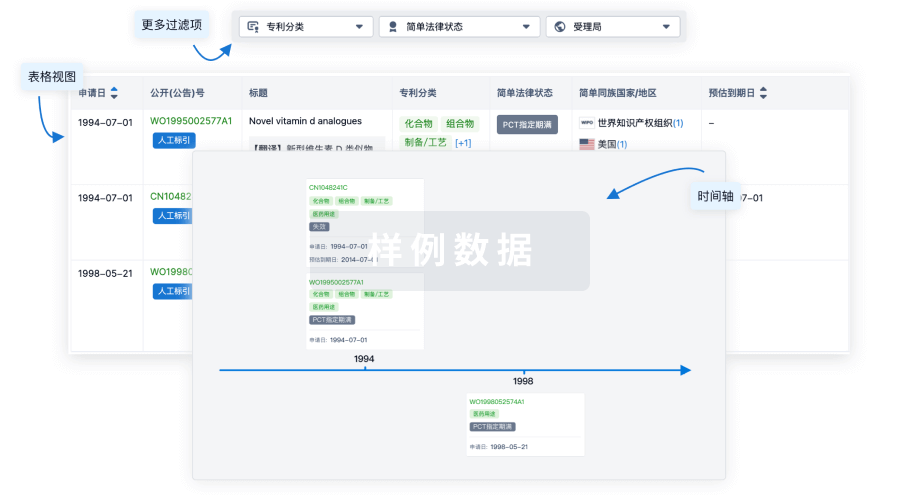
核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或
临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或
批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或
特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或
来和芽仔聊天吧
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用


