预约演示
更新于:2025-05-07
Recurrent Grade 3b Follicular Lymphoma
复发性 3b 级滤泡性淋巴瘤
更新于:2025-05-07
基本信息
别名 Recurrent Follicular Large B-Cell Lymphoma、Recurrent Grade 3b Follicular Lymphoma |
简介 The reemergence of grade 3b follicular lymphoma after a period of remission. |
关联
18
项与 复发性 3b 级滤泡性淋巴瘤 相关的药物作用机制 CD20抑制剂 [+1] |
在研机构 |
原研机构 |
非在研适应症- |
最高研发阶段批准上市 |
首次获批国家/地区 美国 |
首次获批日期2023-05-19 |
31
项与 复发性 3b 级滤泡性淋巴瘤 相关的临床试验NCT06784726
Odronextamab for Relapsed/Refractory Large B-cell Lymphomas Before Definitive Lymphoma-Directed Therapies
This phase II trial tests the effectiveness of odronextamab given before chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell therapy (bridging therapy) in patients with large B-cell lymphomas that have come back after a period of improvement (relapsed) or that have not responded to previous treatment (refractory). Odronextamab is a bispecific antibody that can bind to two different antigens at the same time. Odronextamab binds to CD3, a T-cell surface antigen, and CD20 (a tumor-associated antigen that is expressed on B-cells during most stages of B-cell development and is often overexpressed in B-cell cancers) and may interfere with the ability of cancer cells to grow and spread. Bridging therapy has been used to maintain disease control and to increase the chance of successful receipt of CAR-T cell therapy. However, bridging therapy is typically given after leukapheresis, which does not help prevent disease progression between the decision for CAR-T cell therapy and leukapheresis. Giving odronextamab as bridging therapy before leukapheresis may delay disease progression to allow leukapheresis and increase the likelihood of successful CAR-T cell therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas.
开始日期2025-05-01 |
申办/合作机构 |
NCT06536049
Phase Ib/II Trial of Epcoritamab Plus Ibrutinib in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Aggressive B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
This phase Ib/II trial evaluates the safety, optimal dose, and efficacy of the combination of epcoritamab and ibrutinib in treating patients with aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma that has come back (relapsed) or responded to previous treatment (refractory). Epcoritamab, a bispecific antibody, binds to two different types of receptors (proteins present on the cell surface) at the same time. The two receptors that epcoritamab binds to are called CD3 and CD20. CD3 is found on T cells, which are important cells of the immune system that help fight cancer and infections. CD20 is found on the surface of most types of aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma cells. By binding to both CD3 and CD20, epcoritamab brings the two cells close together so the T cells can fight and kill the lymphoma B cells. Ibrutinib, a Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, binds to a protein on B cells, a type of white blood cell from which the lymphoma developed. By doing this it decreases the ability of the lymphoma B cells to survive and grow. Ibrutinib may also improve the health (or fitness) of T cells thus making epcoritamab safer and/or more effective.
开始日期2025-04-02 |
NCT06834373
Phase 2 Study of Golcadomide With Rituximab as a Bridging Therapy Prior to CAR-T for Patients With Relapsed or Primary Refractory Aggressive B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL)
This phase II trial tests the effectiveness of golcadomide and rituximab as bridging treatment before chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in patients with aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma that has come back after a period of improvement (relapsed) or that has not responded to previous treatment (refractory). Patients that are able to receive CAR T-cell therapy have a potential for cure, however, many will not be qualified to receive therapy due to relapse. Bridging therapy is therapy intended to transition a patient from one therapy or medication to another or maintain their health or status until they are a candidate for a therapy or have decided on a therapy. Golcadomide may help block the formation, growth or spread of cancer cells. Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody. It binds to a protein called CD20, which is found on B cells (a type of white blood cell) and some types of cancer cells. This may help the immune system kill cancer cells. Giving golcadomide and rituximab as bridging therapy before CAR T-cell therapy may kill more tumor cells and may improve the chance of proceeding to CAR T-cell therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
开始日期2025-04-02 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 复发性 3b 级滤泡性淋巴瘤 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 复发性 3b 级滤泡性淋巴瘤 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 复发性 3b 级滤泡性淋巴瘤 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
35
项与 复发性 3b 级滤泡性淋巴瘤 相关的文献(医药)2025-01-01·Blood Reviews
Bispecific antibodies for the treatment of hematologic malignancies: The magic is T-cell redirection
Review
作者: Shouse, Geoffrey
2024-12-01·British Journal of Haematology
The value of semiquantitative PET features and end‐of‐therapy PET in grade 3B follicular lymphoma
Article
作者: Barraclough, Allison ; Wilson, Don ; Hapgood, Greg ; Lee, Sze Ting ; Chong, Geoffrey ; Villa, Diego ; Hawkes, Eliza A.
2024-12-01·British Journal of Haematology
Article
作者: Albano, Domenico
分析
对领域进行一次全面的分析。
登录
或
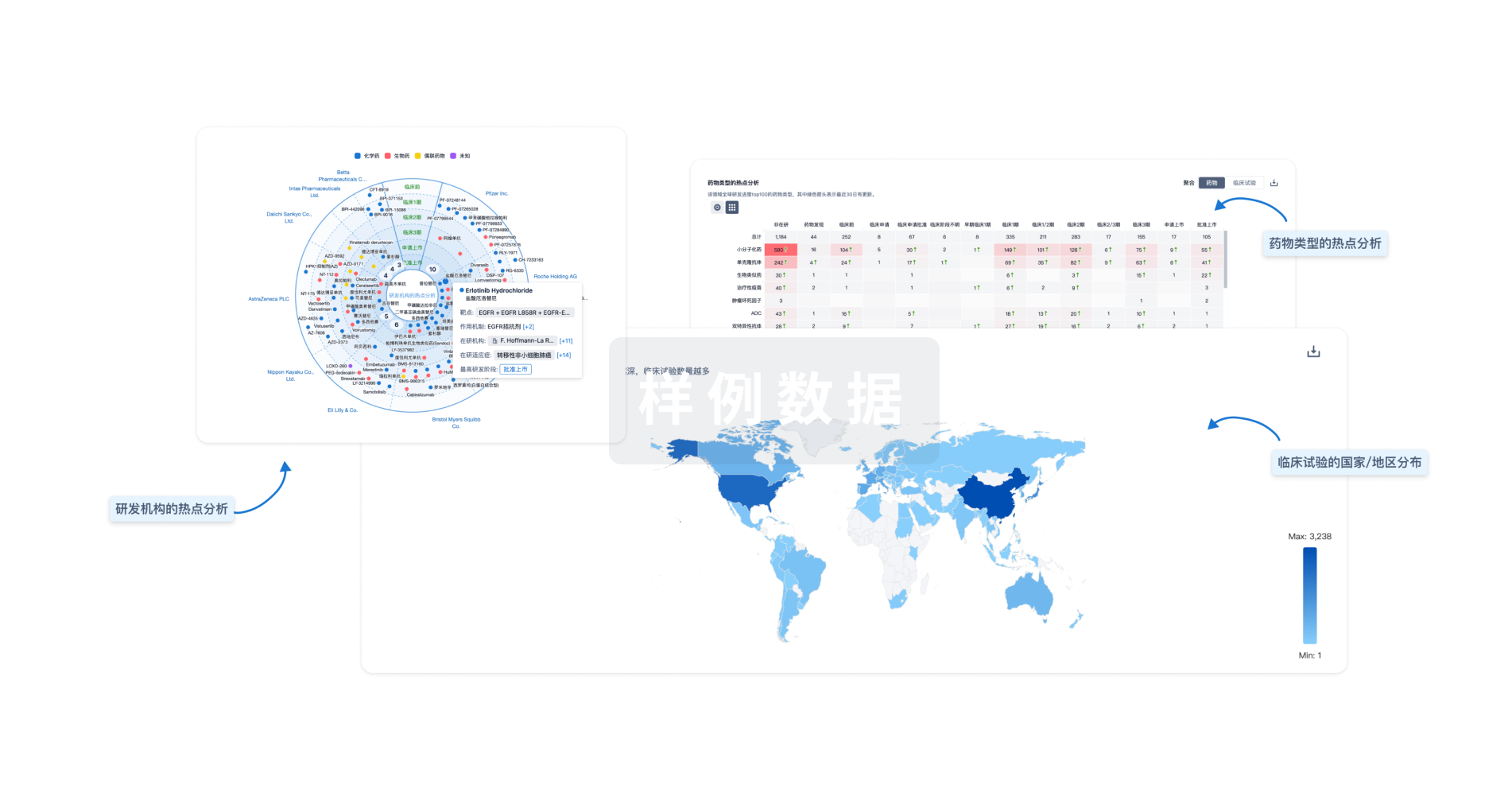
Eureka LS:
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用




