预约演示
更新于:2025-05-07
HIPK
更新于:2025-05-07
基本信息
别名- |
简介- |
关联
6
项与 HIPK 相关的药物靶点 |
作用机制 HIPK2 inhibitors |
非在研适应症- |
最高研发阶段临床1期 |
首次获批国家/地区- |
首次获批日期1800-01-20 |
靶点 |
作用机制 HIPK 抑制剂 |
在研适应症- |
非在研适应症- |
最高研发阶段临床前 |
首次获批国家/地区- |
首次获批日期1800-01-20 |
1
项与 HIPK 相关的临床试验CTR20241636
随机、双盲、安慰剂平行对照、单次/多次口服、剂量递增评价RLA-23174片在健康受试者中的安全性、耐受性、药代动力学的I期临床试验
随机、双盲、安慰剂平行对照、单次/多次口服、剂量递增评价RLA-23174片在健康受试者中的安全性、耐受性、药代动力学的I期临床试验
开始日期2024-05-13 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 HIPK 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 HIPK 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 HIPK 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
794
项与 HIPK 相关的文献(医药)2025-05-01·International Immunopharmacology
KLF15 regulates macrophage polarization patterns in deep vein thrombosis
Article
作者: Ge, Weiqing ; Yang, Jing ; Xiang, YaoYu ; Li, Jizheng ; Song, En ; Yang, Xianguang ; Shentu, Haopeng
2025-04-15·Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Correction for Zhang et al., HIPK2 phosphorylates HDAC3 for NF-κB acetylation to ameliorate colitis-associated colorectal carcinoma and sepsis
Article
2025-04-01·Human Genetics and Genomics Advances
Using genetics, genomics, and transcriptomics to identify therapeutic targets in juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Article
作者: Jarvis, James N ; Tarbell, Evan
12
项与 HIPK 相关的新闻(医药)2025-04-01
SAN FRANCISCO, April 1, 2025 /PRNewswire/ -- Shanghai Yingli Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Yingli Pharma), a clinical stage biotechnology company developing oral small molecule drugs for cancer, metabolic, and immune diseases, announced today that it has received clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to initiate a global registration Phase 3 study of linperlisib versus physicians' choice of standard of care for the treatment of relapsed/refractory (R/R) peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL). FDA's approval of the pivotal Phase 3 protocol follows a successful Type B End-of-Phase 2 meeting, during which Yingli Pharma discussed the overall development program and regulatory path. The Phase 3 study is planned to commence during the second quarter of 2025. Linperlisib is a potent oral small molecule inhibitor of the delta isoform of PI3 kinase (PI3Kδ) developed by Yingli Pharma.
"This is a major milestone for linperlisib.", said Michael Hui, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Yingli Pharma, "We are very excited that linperlisib has entered the global pivotal study stage with the agreement from FDA. We will continue our mission to address patient unmet clinical needs globally and to accelerate the linperlisib clinical development program to bring more treatment options for patients with R/R PTCL."
In this Phase 3 study, linperlisib will be evaluated versus physicians' choice of standard of care in R/R PTCL patients who have received one or more prior systemic therapies. The Phase 3 study will open enrollment in the U.S. and other countries.
About linperlisib
Linperlisib is a next-generation highly selective PI3Kδ inhibitor with a well-tolerated and differentiated safety profile as indicated from clinical trials in follicular lymphoma (FL), T-cell lymphoma and other hematologic and solid tumor studies. In November 2022, linperlisib was approved in China for the treatment of adult patients with R/R FL. Also in 2022, linperlisib received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Orphan Drug Designations for FL, Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/ Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma and T-Cell Lymphoma. To date, over 6000 patients have been treated with linperlisib in clinical studies and post market approval with consistent and well-tolerated safety profile.
Linperlisib has been studied in three clinical trials in R/R PTCL in China, U.S. and Europe, with greater than 165 R/R PTCL patients treated. Collectively, these studies have demonstrated a high objective response rate, high complete response rate, promising progression free survival, overall survival, and a very manageable safety profile through the ongoing evaluations. Overall, Chinese, U.S. and European R/R PTCL patients have exhibited similar levels of efficacy and tolerability, establishing a strong foundation for a global registration trial.
About Yingli Pharma
Yingli Pharma is a clinical stage biopharmaceutical company founded in 2011 and located in the National Biomedical Industry Base of Shanghai Zhangjiang InnoPark. The company is dedicated to serving unmet medical needs of patients and focuses on discovery and development of therapy for cancer, metabolic and immune diseases. Yingli Pharma is advancing a portfolio of drugs through clinical development, including panRAS, TGFβR1 oral small molecule inhibitors in oncology, and URAT1 and HIPK2 inhibitors in metabolic and immune diseases. Linperlisib, the company's first drug candidate was awarded NMPA Breakthrough Therapy status in China, making Yingli Pharma the second pharmaceutical company in China and the first in Shanghai to receive this recognition.
For more information, please see:
CONTACT: Wendy Xiong, MD , Email : [email protected], Phone : 669-842-3439
SOURCE Shanghai Yingli Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
WANT YOUR COMPANY'S NEWS FEATURED ON PRNEWSWIRE.COM?
440k+
Newsrooms &
Influencers
9k+
Digital Media
Outlets
270k+
Journalists
Opted In
GET STARTED
孤儿药上市批准临床3期突破性疗法临床申请
2025-02-06
摘要:在过去十年中,环状RNA(circRNA)的研究迅速增加,近年来,circRNA作为一种有前景的治疗平台脱颖而出。环状RNA的调控功能,包括其在蛋白质翻译模板化、调控蛋白质和RNA功能中的作用,以及其独特特性,如与mRNA相比更高的稳定性和更有利的免疫学特性,使其成为基于RNA治疗的有吸引力的候选分子。在这里,我们描述了环状RNA的特性、其治疗潜力以及其合成技术。我们还讨论了实现环状RNA作为药物的全部潜力需要克服的前景和挑战。
1.引言近年来,RNA治疗领域因COVID-19 mRNA疫苗的巨大成功而迅速发展(参考文献1)。这项突破性技术使全球健康危机得到了快速有效的应对,凸显了基于RNA的方法在革新医学方面的巨大潜力。因此,研究人员越来越多地探索RNA治疗的新途径,包括将环状RNA(circRNA)作为有前景的候选分子。环状RNA是一类在大多数真核生物中表达丰富的内源性非编码转录本。这些分子的特征是其独特的环状结构,其中5′和3′末端通过共价键连接形成闭环。这种环状构型缺乏自由的5′或3′末端,使得环状RNA比其线性RNA对应物更稳定。内源性环状RNA是通过一种称为反向剪接的替代剪接机制在体内生成的,其中下游剪接供体位点与上游剪接受体位点连接。环状RNA最早于20世纪70年代在植物类病毒中被发现,但其在真核细胞中的存在及其功能相关性直到后来才被认识到。20世纪90年代初,环状RNA在真核细胞中被观察到,被认为是由罕见的错配剪接事件产生的副产物。然而,在过去十年中,随着高通量RNA测序技术和针对环状RNA的生物信息学的进步,环状RNA的真正普遍性变得显而易见。这些进步,加上关于环状RNA功能的开创性研究,现在已导致对这一RNA亚类多样性的全面理解。内源性环状RNA在细胞内被赋予了许多不同的功能——从调控基因表达和作为微RNA(miRNA)和蛋白质的分子“海绵”,到编码独特蛋白质——对多种细胞过程产生影响。除了环状RNA独特构型固有的细胞内稳定性之外,其广泛生理功能的多样性进一步凸显了其作为一种治疗方式的潜力。对内源性环状RNA生物合成途径的深入了解以及体外转录系统的发展,促进了具有精确序列和功能的环状RNA的工程化,从而为定制化治疗策略提供了机会。如今,环状RNA治疗领域正在迅速发展,学术研究团队、行业先锋和多家生物技术初创公司对基于环状RNA的平台表现出高度的兴趣和投资。在这里,我们介绍环状RNA作为一种引人入胜的新治疗方式,部分基于与闭环结构相关的内在特性。我们通过已发表的案例讨论了基于环状RNA治疗的多功能潜力。我们还详细描述了使用体外转录(IVT)或基于载体的设置有效生产环状RNA的合成和设计方法。最后,我们讨论了环状RNA作为各种疾病生物标志物的潜在用途。
2.环状RNA的治疗相关特性环状RNA因其独特的特性而具有巨大的治疗潜力,包括高稳定性和抗降解性。这种固有的稳定性转化为环状RNA比线性RNA具有更长的半衰期,使环状RNA成为持续治疗干预的理想候选分子。此外,与线性mRNA相比,体外转录(IVT)环状RNA的免疫原性降低,这对于某些治疗方式是一个优势。
2.1.细胞内稳定性环状RNA的闭环结构使其在细胞内比其线性RNA对应物(如mRNA)更稳定。这一点已在细胞内表达的环状RNA和外源性递送的环状RNA和得到证实。尽管如此,我们对调节环状RNA内切酶降解以维持稳态水平的主动过程的理解仍然有限。有少数例子表明,内源性环状RNA通过argonaute 2介导的沉默。此外,外泌体复合体外切酶DIS3的内切酶活性已被证明可在体外导致环状RNA的降解,在病毒感染的情况下,RNaseL作为先天免疫反应的一部分,在激活双链RNA激活蛋白激酶R(PKR)时会破坏环状RNA。单个环状RNA的稳定性差异显著,类似于mRNA,文献估计的中位半衰期约为20小时,通过4-硫尿苷标记确定,到超过50小时,通过放线菌素D关闭转录或基于诱导型环状RNA表达系统测量。然而,在所有情况下,环状RNA的稳定性明显超过其相应的mRNA。因此,使用基于载体的表达系统,假设生产速率相近,环状RNA将随着时间的推移积累到比mRNA更高的稳态水平。体外转录(IVT)环状RNA的半衰期经验估计为56到86小时;相比之下,IVT mRNA的半衰期为15到24小时,具体取决于细胞类型。对于编码蛋白质的环状RNA,其较长的半衰期导致更长的表达曲线,并且与基于mRNA的治疗方式相比,具有三到五倍的产量优势,这可能导致治疗效果的增加或通过剂量节省减少毒性。进一步研究环状RNA的周转途径可能有助于设计避免特定内切酶触发因素的序列,从而进一步稳定环状RNA。
2.2.免疫原性体外转录(IVT)环状RNA是否为免疫刺激分子的问题仍然存在争议。IVT环状RNA被证明通过激活核酸传感器视黄酸诱导基因I(RIG-I)来诱导免疫基因的表达。在内源性环状RNA中观察到的N6-甲基腺苷(m6A)修饰,与未修饰的环状RNA相比,降低了其免疫原性,这表明未修饰的环状RNA确实具有内在的免疫原性。相比之下,使用高度纯化的IVT环状RNA进行的类似研究表明,RIG-I途径的激活和免疫基因的表达仅最小化,这表明环状RNA诱导的免疫反应可能部分是由于环状RNA制造过程中的污染物,而不是环状RNA的内在特性。此外,在某些IVT制造方法中,最终环状RNA序列中保留的外源核糖酶衍生序列(称为“疤痕”)可能通过激活PKR增加环状RNA的免疫原性,而环状RNA内的短结构区域已被证明可以结合并抑制PKR的激活。深入了解环状RNA的免疫原性特征对于优化环状RNA治疗的合成路线和指导治疗适应症的选择至关重要,这将增强临床效益,同时简化未来的制造过程。
3.环状RNA的治疗相关功能内源性环状RNA被赋予了多种生理功能,包括作为蛋白质编码模板、锚定和抑制蛋白质和miRNA、核蛋白复合物以及破坏RNA二级结构(图1)。环状RNA治疗的势头日益增强,其在关键治疗领域的潜力在于其在疗效和多功能性方面可能超越mRNA方式,无论是对于IVT还是基于载体的环状RNA。环状RNA的独特特性,包括其更高的稳定性、更长的表达时间和蛋白质编码及非编码功能,使其成为需要持续治疗效果的应用的理想候选分子。因此,目前许多环状RNA的治疗途径正在被探索(表1)。
图 1 | 环状 RNA 的治疗相关功能及潜在应用。环状 RNA(circRNAs)被赋予了多种生理功能,这些功能可以通过适当设计 circRNA 而被重新定向并应用于其他目标。a,环状 RNA 的高稳定性和内部核糖体进入位点(IRES)介导的增强型蛋白质翻译使其与基于 mRNA 的蛋白质表达相比能够产生更多的蛋白质。环状 RNA 的蛋白质生产可用于传染病疫苗、癌症疫苗、嵌合抗原受体(CAR)T 细胞疗法以及遗传性疾病的蛋白质替代疗法。b,环状 RNA 可以以序列依赖的方式有效结合微小 RNA(miRNA)以使其失活(称为 miRNA“海绵”),同时对 miRNA 介导的不稳定具有抵抗力。例如,环状 RNA 可以用于抑制癌症中的促肿瘤 miRNA 的功能。环状 RNA 还可以以序列依赖的方式靶向 mRNA,从而导致翻译抑制(例如病毒 mRNA)或改变剪接(例如通过介导外显子跳跃部分恢复杜氏肌营养不良中的抗肌萎缩蛋白表达)。c,环状 RNA 可能通过竞争性退火比 mRNA 更有效地破坏 RNA 的二级结构,这归因于环状 RNA 在细胞内的高稳定性。从理论上讲,这可以用于破坏致病的异常宿主 RNA 结构或病原性病毒 RNA 结构。d,类似于 miRNA 海绵的机制,环状 RNA 可以持续结合 RNA 结合蛋白(RBPs)以使其在细胞内失活。可以靶向诸如 PKR 或 HNRNPL 等 RBP,以抑制它们与炎症或肿瘤发生相关的疾病功能。e,环状 RNA 可以作为蛋白质支架促进蛋白质之间的功能相互作用 —— 例如,促进蛋白降解靶向嵌合体(PROTAC)与待降解的目标蛋白之间的相互作用 —— 与 mRNA 相比具有更持久和持久的效果。PROTAC 介导的降解可以靶向朊病毒样疾病中的错误折叠蛋白聚集。f,类似于竞争性 RNA 退火(如 c 部分所示),环状 RNA 可以被设计为提高基因编辑效率 —— 通过作为 CRISPR–Cas 或 Prime 编辑的引导 RNA(gRNA)(上图)。环状 RNA 还可以通过形成 RNA 编辑酶(如 RNA 上的腺苷脱氨酶(ADAR))的底物来增强 RNA 编辑,该酶被环状 RNA 与目标 RNA 之间形成的相邻双链片段积极招募(下图)。A,腺苷;G,鸟苷;I,肌苷;ORF,开放阅读框;Ub,泛素。
3.1.蛋白质生产
目前,大多数基于治疗性环状 RNA 的平台都专注于开发编码蛋白质的环状 RNA,利用其高稳定性实现长期蛋白质表达(图 1a)。与 mRNA 不同,环状 RNA 没有 5′ 帽结构,因此必须使用帽独立机制来招募翻译机制并启动翻译。这通常是通过使用内部核糖体进入位点(IRES)来实现的,IRES 常见于小 RNA 病毒科(Picornaviridae)的单链 RNA 病毒家族。对来自国家生物技术信息中心核苷酸数据库的 60 多个小 RNA 病毒属的近 10,000 个完整小 RNA 病毒基因组的分析,导致了大约 8,000 个独特 IRES 的注释,这些 IRES 可能具有广泛的效力和细胞类型特异性。此外,通过系统优化这些天然 IRES 的序列和结构,提高了它们的翻译效率,这突显了根据特定治疗需求调整 IRES 介导翻译特性的潜力。最近,一种帽依赖型环状 RNA 设计被引入——由于这种结构与字母 Q 相似,被称为 Q-RNA——在这种设计中,一个带有 5′ 帽结构的寡核苷酸通过点击化学连接到开放阅读框(ORF)上游核苷酸的底部。研究表明,这种设计能够招募真核起始因子 EIF4E,从而有力地支持翻译的启动。体外转录(IVT)环状 RNA 最有前景的应用之一是开发传染病疫苗。在这方面,与假尿苷修饰的 mRNA 编码的抗原相比,SARS-CoV-2 环状 RNA 编码的抗原显示出增加和延长的表达,从而在小鼠和恒河猴中引发了更强的免疫反应。此外,含有编码狂犬病病毒糖蛋白的 IVT 环状 RNA 的淋巴结靶向脂质纳米颗粒(LNPs),在狂犬病小鼠模型中引发了强大的免疫反应。这些发现可以转化为其他正在开发 mRNA 基方法的传染病疫苗,例如流感病毒、HIV、呼吸道合胞病毒、单纯疱疹病毒和巨细胞病毒。除了传染病疫苗,针对常见新抗原的癌症疫苗是环状 RNA 技术的另一个有前景的应用方向。在一个使用表达卵清蛋白的黑色素瘤小鼠模型的概念验证研究中,包裹在促炎 LNPs 中的编码卵清蛋白的环状 RNA 被证明具有抗肿瘤效果。IVT 环状 RNA 还有潜力作为表达免疫刺激分子、溶瘤蛋白以及免疫细胞表达嵌合抗原受体(CARs)-和转基因 T 细胞受体(TCRs)的平台。其中最先进的项目之一是 CAR T 细胞治疗的开发,在这种治疗中,编码针对 CD19 的 CAR 构建体的环状 RNA 被包裹在 LNPs 中,用于在免疫细胞中原位产生 CAR。这种方法避免了与体外工程化 CAR T 细胞移植相关的淋巴细胞耗竭需求,并促进了 CAR T 细胞、CAR 自然杀伤细胞和 CAR 巨噬细胞的同时生成。最近,用编码识别巨细胞病毒 pp56 抗原的 TCRs 的 IVT 环状 RNA 转导的原代 T 细胞,实现了对表达 pp56 的肿瘤细胞的特异性和持久性杀伤。这些例子突显了环状 RNA 技术在免疫治疗中的多功能性和潜力。此外,由于环状 RNA 有可能通过实现增加和延长的蛋白质表达来超越传统的 mRNA 和蛋白质替代策略,从而减少频繁再给药的需求,因此其在基因治疗中的应用引起了广泛关注。在再给药不可行或提供次优治疗效果的情况下,单独使用 IVT mRNA 或 IVT 环状 RNA 可能无法作为治疗方式提供足够的持久性。相反,基于载体的表达平台可能为基因治疗提供增加和持续的疗效(在 “治疗性环状 RNA 的生产” 部分有更详细的描述)。目前被认为是基因替代治疗黄金标准的腺相关病毒(AAV)疗法,需要非常高的剂量水平才能实现治疗效果,导致高水平的毒性和高昂的生产成本。通过用更持久的环状 RNA 表达盒替换 AAV 载体中的传统 mRNA 表达盒,从而获得更高的稳态 RNA 水平,可能可以增加每个 AAV 载体的基因治疗输出,从而减少所需的剂量。这种方法可以提高这些疗法的疗效和安全性。
3.2.RNA-RNA 互作
通过隔离来调节 miRNA 是内源性环状 RNA 在基因调控中的一个众所周知的功能(图 1b)。这种 “海绵” 机制可以很容易地通过具有工程化 miRNA 结合位点的人工环状 RNA 重定向到任何 miRNA。由于环状 RNA 对 miRNA 通过外切酶过程介导的靶 RNA 不稳定化具有抵抗力,因此它们是高效的 miRNA 抑制剂。实际上,将细胞内表达的环状 RNA 与线性、结构稳定的硬诱饵 RNA 进行基准测试表明,当在相同浓度下测试时,环状 RNA 作为 miRNA 抑制剂优于硬诱饵 RNA。以 miRNA 靶向环状 RNA 的治疗潜力为例,通过 AAV 载体驱动表达针对促肥大、心脏 miRNA miR-132 和 miR-212 的环状 RNA 海绵,在心脏疾病小鼠模型中减缓了主动脉缩窄的进展。在经过环状 RNA 治疗的小鼠中,肥大性疾病症状得到缓解,心脏功能得以恢复。还通过 IVT 环状 RNA 展示了对 miRNA 的抑制。例如,一个针对 miR-122 的 IVT 环状 RNA 被证明可以阻断细胞培养中已知有助于丙型肝炎病毒(HCV)复制的 HCV 扩增。在另一项研究中,通过聚乙烯亚胺基纳米颗粒递送的含有针对致癌 miRNA miR-21-5p 的四个海绵位点的 IVT 环状 RNA,在异种移植小鼠中抑制了肺腺癌。此外,针对 miR-21 的环状 RNA 海绵在胶质母细胞瘤大鼠模型和胃癌细胞中被证明是抑制肿瘤生长的有效抑制剂,导致凋亡增加以及蛋白质合成全面减少。环状 RNA 的 miRNA 海绵能力特别有希望用于治疗以 miRNA 上调为特征的疾病,这些 miRNA 对疾病病因至关重要。除了抑制 miRNA 之外,环状 RNA 还可以被设计成靶向并与其前体 mRNA 和 mRNA 互作,分别调节它们的剪接和阻止它们的翻译。例如,反义环状 RNA 被证明可以成功地介导杜氏肌营养不良相关转录本的外显子跳跃,以恢复抗肌萎缩蛋白的表达。此外,通过 AAV 介导递送反义环状 RNA 纠正了开放阅读框,并在杜氏肌营养不良小鼠模型中恢复了抗肌萎缩蛋白的表达。
针对RNA-RNA相互作用的环状RNA(circRNAs)的广泛概念,为治疗应用提供了广阔范围。RNA在细胞内形成复杂的二级结构,这些结构对于所有生物体的正常功能至关重要,从病毒到人类皆是如此。病原体,如病毒,利用其RNA的二级结构来捕获宿主细胞蛋白以实现复制。类似地,遗传缺陷可能会产生异常的RNA二级结构,这些结构在细胞内捕获蛋白质,从而导致疾病。在此,设计环状RNA来结合并破坏这些病原性或缺陷性RNA的二级结构,可能是一种有前景的治疗概念,以缓解这些疾病状态(图1c)。环状RNA与mRNA的广泛互补性也可以抑制翻译。设计用于靶向并捕获SARS-CoV-2 mRNA的5'非翻译区的反义环状RNA的表达,成功抑制了它们的翻译,与线性反义RNA在细胞培养中实现的抑制效果相比,对病毒增殖的抑制效果更强。
总之,环状RNA的稳定性及其对通常在RNA-RNA相互作用时激活的外切核酸酶降解途径的抗性,使得闭环环状RNA设计成为一种有前景的方法,可通过直接的碱基配对相互作用有效调节RNA功能。
3.3.RNA-蛋白相互作用
除了直接调节RNA功能外,环状RNA还被认为参与调节蛋白活性或蛋白-蛋白相互作用(图1d)。作为概念验证,表达含有CA重复序列的环状RNA,这些重复序列作为剪接因子HNRNPL的结合位点,导致HNRNPL从细胞核重新分布到细胞质,从而消除了其在剪接中的功能。在癌细胞中,环状RNA介导的HNRNPL功能下调可能增强肿瘤抑制蛋白p53的功能,或许通过调节p53抑制因子MDM4的剪接来实现,进而导致癌细胞凋亡增加。此外,环状RNA介导的HNRNPL捕获可能是前列腺癌的一种治疗策略,在前列腺癌中,HNRNPL的过表达与前列腺肿瘤特异性基因(如雄激素受体)的异常剪接有关。HNRNPL的功能抑制还可能通过下调其转录因子的表达来降低免疫检查点分子PD-L1的表达,从而恢复癌细胞对T细胞介导杀伤的敏感性。在另一个例子中,靶向脾脏的双链RNA嵌入环状RNA调节PKR活性,在银屑病小鼠模型中减少了炎症。此外,从AAV载体表达的PKR调节环状RNA在阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型中减少了神经炎症和淀粉样β斑块的形成。
环状核酸适配体可能比其线性对应物具有更大的持久性和效力,这可能允许更低的剂量和减少的非靶向效应。这一特性最初在一项研究中被探索,该研究利用细菌中的环状RNA合成来产生环状链霉亲和素结合适配体。最近,研究表明稳定表达的环状适配体能够结合代谢物S-腺苷甲硫氨酸,可在人类细胞中作为荧光代谢物生物传感器。更广泛地说,这些研究表明环状RNA适配体可用于靶向细胞中的疾病相关蛋白。
通过RNA-蛋白相互作用被动调节蛋白功能存在一定的化学计量挑战。相反,治疗性环状RNA模式最好具有一个主动成分,以允许每个RNA拷贝数调节多个靶标分子。这可以通过环状PROTAC(蛋白降解靶向嵌合体)支架方法实现,通过靶向泛素化后由蛋白酶体介导的蛋白降解,主动诱导环状RNA结合的特定靶标蛋白的衰变。这为环状RNA提供了独特的机会,使其既可以作为蛋白生产的模板(如上所述),也可以作为定向和特异性蛋白衰变的支架(图1e)。PROTACs是治疗朊病毒样疾病的一种有前景的治疗策略,这种疾病以错误折叠蛋白的聚集和传播为特征,其传播方式类似于朊病毒。RNA结合蛋白的聚集,如TAU(也称为MAPT)、TDP43(也称为TARDBP)和FUS,已知与几种神经退行性疾病的发病机制有关。设计环状RNA来结合这些病理性RNA结合蛋白,并将其导向PROTAC介导的衰变,是一种有前景的新策略。
3.4.核酸编辑
使用环状RNA作为CRISPR-Cas系统的向导RNA(gRNAs)是一种新兴策略,旨在提高基因编辑工具的效率和稳定性(图1f)。环状RNA的固有稳定性使其成为线性gRNAs的有吸引力的替代品,后者通常具有较短的半衰期。事实上,CRISPR-Cas9 gRNA的环状化已被证明可以增加其在体外和细菌中的稳定性和DNA编辑效率。使用Tornado(Twister优化的RNA用于持久过表达)系统(见“基于载体的环状RNA表达”部分)生成的环状gRNAs与线性gRNAs相比也具有增加的稳定性,这提高了Cas12a和Cas13d基础的DNA和RNA编辑在体外和体内的效率。值得注意的是,该研究还表明,环状gRNAs增强了基于Cas12a的报告基因转录激活,使用失活的Cas12a与转录激活因子融合,在体内产生了更强和更持久的信号。
Prime编辑需要一个prime编辑向导RNA(pegRNA)——由靶向RNA、引物结合位点(PBS)和逆转录模板(RTT)组成——用于基因组编辑。PBS和RTT成分的环状化增加了基于Cas12a的Prime编辑的效率,与它们的线性对应物相比,这表明RTT-PBS RNA的稳定性和丰度与编辑效率呈正相关。此外,最近的一项研究表明,几个RTT-PBS RNAs可以被纳入到一个单一的环状RNA中,从而同时编辑多达四个基因,尽管效率较低。
除了提高DNA编辑效率外,环状RNA还可以被设计来增强RNA碱基编辑。环状RNA的支架功能可以用来招募编辑酶到它们的靶标RNAs(图1f)。两个独立的报告表明,环状RNA可以招募作用于RNA的腺苷脱氨酶(ADAR)蛋白来编辑靶标mRNAs,其效率比线性gRNAs更高。总之,环状RNA的稳定性和多功能性使其成为一种强大的工具,用于提高DNA和RNA编辑效率,为基因编辑技术提供了有前景的进步。
4.治疗性环状RNA的生产
鉴于上述环状RNA的治疗潜力,人们对其体外和体内合成平台的开发产生了浓厚的研究兴趣。治疗性环状RNA可以分为两个具有不同治疗用途的平台:体外转录(IVT)环状RNA(图2),其需要额外的纯化协议;以及基于载体的环状RNA表达,该方法利用现有的细胞内机制进行环状RNA生产,但需要高效地将环状RNA编码载体递送至细胞内(图3)。
图 2 | 环状 RNA 的体外合成。环状 RNA(circRNAs)的体外合成通常通过酶促连接或核糖酶介导的线性体外转录(IVT)RNA 前体的环化来实现。a,对于酶促 RNA 连接,可以使用三种不同的连接酶,所有这些连接酶都通过所谓的“桥接寡核苷酸”来促进线性 RNA 末端的相互靠近(已在其他地方综述)。T4 DNA 连接酶利用 DNA 桥接寡核苷酸在完美对齐的缺口双链(ds)RNA-DNA 底物中促进 RNA 末端连接,而 T4 RNA 连接酶 2 可以使用 DNA 或 RNA 桥接寡核苷酸进行 RNA 环化。在 dsRNA 的 RNA 桥接寡核苷酸情况下,可以使用内部 RNA 序列作为自身桥接寡核苷酸来模板化反应。T4 RNA 连接酶 1 倾向于连接单链 RNA(ssRNA)底物,并且在没有桥接寡核苷酸的情况下高效环化小 RNA(小于 350 个核苷酸)。然而,对于由 T4 RNA 连接酶 1 介导的较大 circRNA 结构的形成,更倾向于使用 DNA 桥接寡核苷酸或内部 RNA 自身桥接寡核苷酸来使悬垂的 ssRNA 末端相互靠近。b,大多数核糖酶介导的环化方法基于催化性 I 型内含子,这需要添加 GTP 和 Mg²⁺ 作为辅助因子。这种方法通过 I 型内含子的标准自剪接反应实现 circRNA 的生成,涉及在特定剪接位点的两次转酯反应。在剪接过程中,鸟苷酸(G)的 3′ 羟基在 5′ 剪接位点(SS)引发转酯反应,切除 5′ 内含子。这个中间体末端释放的羟基随后参与在 3′ SS 的第二次转酯反应,导致中间区域的环化和 3′ 内含子的切除。已经开发出两种主要类型的 I 型内含子设计。在置换内含子 - 外显子(PIE)系统中,I 型内含子被分成两半,颠倒并放置在要环化的融合 5′ 和 3′ 外显子的上游和下游。在自靶向和剪接(STS)系统中,I 型内含子被放置在环化外显子的上游。在这两种情况下,该过程都涉及一个两步磷酸转移酶反应,首先是在 5′ 外显子 - 内含子连接处附着一个自由的 GTP 残基,随后将释放的 5′ 外显子附着在 3′ 外显子 - 内含子连接处。最终的 circRNA 产物包含外源外显子序列作为“疤痕”。
图 3 | 环状 RNA 的体内合成。a,依赖剪接体的环状 RNA(circRNA)体内生成。基于 RNA 聚合酶 II 的环状 RNA 表达盒的示意图,包含内部核糖体进入位点(IRES)和开放阅读框(ORF),以及特定的内含子序列。通过加入反向重复的 Alu 元件(如图所示),或非重复区域的反向互补序列,或肌肉盲蛋白(Muscleblind)或震颤蛋白(Quaking)的 RNA 结合蛋白位点(未显示),可以增强环状 RNA 的形成。这些元件有助于反向重复元件之间的碱基配对(如图所示),或 RNA 结合蛋白的二聚化(未显示),从而将下游的剪接供体(SD)位点与上游的剪接受体(SA)位点拉近。这种相互作用促进了反向剪接,这是一个由经典剪接机制介导的过程,其中 SD 位点与 SA 位点共价连接,最终导致环状 RNA 的形成。b,龙卷风核糖酶介导的体内环状 RNA 生成系统。IRES-ORF 环状 RNA 序列被茎环形成序列夹在中间,然后是 5′ 和 3′ 自我切割核糖酶。转录后,这些核糖酶切割初级环状 RNA(红色箭头),在新的 RNA 末端产生 2′,3′-环状磷酸和 5′-羟基。环状 RNA 前体的茎环形成序列随后杂交,并通过内源性 tRNA 连接酶 RTCB 的作用形成环状 RNA,RTCB 在某些 tRNA 的剪接事件中自然连接 tRNA 外显子。
4.1.体外环状RNA合成
类似于mRNA,环状RNA前体通常通过体外转录作为线性、单链RNA分子进行合成。随后RNA末端的分子内连接将这些前体转化为共价闭合环,这一过程可以通过连接酶酶或核糖酶介导(表2和图2)。
例如,通过T4 DNA连接酶、T4 RNA连接酶1或T4 RNA连接酶2(图2a)的酶促连接,催化RNA末端之间形成磷酸二酯键,这一过程以ATP依赖的方式进行。每种连接酶都有其独特的底物偏好性(表2)。相比之下,核糖酶催化的环化利用具有内在RNA介导催化活性的RNA分子;在这方面,I型内含子已成为RNA自我环化的有力工具。已报道了两种基于I型内含子的环状RNA合成设计(图2b):基于来自念珠藻前tRNA和T4噬菌体胸苷酸合成酶(td)基因的I型内含子的置换内含子-外显子(PIE)构建,以及源自四膜虫前核糖体RNA I型内含子的自我靶向和剪接(STS)构建。最近,念珠藻PIE构建被进一步优化,将最终环状RNA产物中的疤痕从多达180个核苷酸减少到27个核苷酸,从而改善了免疫原性特征。PIE环状RNA中的疤痕大小可以进一步减少到8个核苷酸,尽管其免疫原性需要进一步调查。II型内含子是另一类自我剪接RNA分子,从其也已开发出PIE构建用于有效的环状RNA合成。一般来说,自我剪接核糖酶在RNA环化方面比酶促方法具有优势,因为它们通过消除额外的连接反应和额外的纯化步骤来简化制造过程(表2)。
使用上述任何一种方法制备的生化环状RNA的报道大小范围从大约十个核苷酸到超过5,000个核苷酸。T4连接酶对于连接小于50个核苷酸的小环状RNA非常有效。尽管使用基于念珠藻的PIE系统已经制造出了超过5,000个核苷酸的环状RNA20,但制造非常大的环状RNA仍然是一个挑战。随着环状RNA序列长度的增加,T4 RNA连接酶1和基于念珠藻的PIE构建的环化效率显著下降。此外,较大环状RNA对切口的敏感性可能导致产量进一步降低。
4.2.体外环状 RNA 纯化
在合成后,体外转录的环状 RNA 需要与线性 RNA 对应物及其他杂质分离。这对于确保最终环状 RNA 产品的纯度和完整性至关重要,尤其是如果其用于重复应用。环状 RNA 和线性 RNA 在序列和理化性质上的高度相似性,给常用的纯化技术带来了持续的挑战。RNase R 是一种 3′ 到 5′ 外切酶,因其能够选择性降解线性 RNA 而保留环状 RNA,被广泛用于环状 RNA 纯化。然而,尽管其效率很高,RNase R 并不能完全去除线性 RNA;即使经过严格的 RNase R 处理,环状 RNA 的缺口和剪接外显子仍然存在。RNase R 的消化被结构化的 3′ RNA 末端(缺乏突出端)和 G-四链体 RNA 二级结构所阻断,但这种抑制可以通过聚腺苷酸化和缓冲液优化分别缓解。尽管增加 RNase R 浓度和/或延长孵育时间可以增强反应,但也可能导致环状 RNA 的非特异性降解。因此,需要对 RNase R 反应条件进行实验验证,以在大规模环状 RNA 纯化中实现纯度和产量之间的最佳平衡。除了 RNase R,外切酶 T 和 5′ 到 3′ 核糖核酸外切酶 XRN1 也用于去除线性 RNA。变性尿素聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳为环状 RNA 的分离提供了最高的分辨率,环状 RNA 的迁移速度明显慢于其线性对应物。此外,商业化的预制 EX 琼脂糖凝胶可以区分 PIE 衍生的环状 RNA 和反应副产物。尽管其分辨率与尿素聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳相比有限。毛细管凝胶电泳也可以用于环状 RNA 分析,但其分离分辨率同样有限。尽管某些凝胶电泳方法在分离环状 RNA 和副产物方面效果良好,但这些方法劳动强度大,产量低。高效液相色谱(HPLC)是一种更具可扩展性的环状 RNA 纯化方法。在尺寸排阻 HPLC 中,环状 RNA 的保留时间比线性 RNA 长。然而,分离通常不完全,环状 RNA 分数与线性 RNA 分数部分重叠。值得注意的是,离子对反相 HPLC 最近被证明在 PIE 衍生和 STS 衍生环状 RNA 的纯化中具有高分辨率。鉴于从环状 RNA 产品中去除杂质的棘手挑战,一种替代策略是使污染物失活。例如,磷酸酶处理水解残留的免疫原性三磷酸盐,从而减少对环状 RNA 的天然免疫反应。
4.3.基于载体的环状 RNA 表达
在哺乳动物中,首次对一个丰富表达的内源性环状 RNA 进行表征,是在小鼠的 Sry 位点,该位点被证明主要产生环状转录本。后来发现,该位点的环状 RNA 产生依赖于 Sry 外显子两侧的长反向重复序列。反向重复序列在依赖剪接体的环状 RNA 形成中的重要性进一步在核提取物中得到证实。此外,还报道了其他内源性环状 RNA 表达的例子;然而,两个主要发展推动了环状 RNA 研究兴趣的增加,即 CDR1as/ciRS-7的鉴定和功能表征,以及利用下一代测序检测环状 RNA 表达的高通量方法的发展。通过一个包含内源性外显子和剪接位点序列的载体,结合大约 800 个核苷酸的侧翼反向重复序列,实现了 CDR1as/ciRS-7 的异位过表达。这种依赖剪接体的载体设计导致了与内源性产物无法区分的环状 RNA 的表达。利用下一代测序对环状 RNA 景观进行广泛表征表明,反向重复序列(通常以 Alu 元件的形式)在反向剪接事件附近高度富集。这些研究表明,反向剪接的作用机制基于侧翼区域的碱基配对和螺旋形成,可能以共转录的方式进行,这被认为将上游受体和下游供体剪接位点定位在一起,以便进行反向剪接。这一模型与观察结果一致,即 ADAR1 介导的螺旋结构编辑和 DHX9 解旋酶活性抑制了 Alu 依赖的环状 RNA 表达。基于这种反向剪接的已建立机制,几种基于不同内源性位点的异位环状 RNA 表达载体系统已经开发出来,例如 POLR2A、ZKSCAN1、HIPK3 和 EPHB4(图 3a)。在所有情况下,用于环状 RNA 表达的内源性位点都由近端反向 Alu 元件侧翼。基于载体的环状 RNA 生物合成进一步优化,主要通过操纵侧翼序列元件和到剪接位点的距离。总体而言,这些研究表明,环状 RNA 生物合成依赖于 Alu 元件,并且表明,即使只有 40 个碱基对的修剪过的 Alu 序列侧翼要环化的外显子,也可以发生有效的环状 RNA 生物合成。与 Alu 依赖载体的发展并行,一个大约 230 个核苷酸的人工反向重复序列被用来构建第一个基于载体的蛋白质编码环状 RNA 表达系统。该构建包含增强型绿色荧光蛋白(eGFP)的开放阅读框和脑心肌炎病毒的 IRES,导致高水平的 eGFP 产生和积累。由于依赖剪接体的环状 RNA 生物合成的无痕性质,eGFP 开放阅读框被设计为反向剪接接头位于开放阅读框内;一致地,只有在形成反向剪接接头时才观察到功能性蛋白产生,并且通过剪接位点突变被消除。值得注意的是,基于质粒的环状 RNA 表达可能受到非特异性产生外显子串联产物的污染,这些产物可能是线性或环状的,几乎无法通过逆转录 PCR 和基于下一代测序的检测方法与真正的环状 RNA 区分开来。因此,使用 RNase R 介导的耗竭和 Northern 印迹分析来表征载体衍生的产量是谨慎的,并确定侧翼元件的要求,以确保高系统完整性,避免混淆的假象。依赖剪接体和反向重复序列的环状 RNA 生物合成是基于载体的内源性环状 RNA 表达最常用的方法(图 3a);然而,也描述了使用 Tetrahymena thermophila I 类内含子介导的生物合成、T4 噬菌体 td 基因的自剪接 I 类内含子或龙卷风系统(图 3b)的替代方法,该系统包括核糖酶导向的 RNA 切割,随后由内源性 tRNA 连接酶 RTCB 介导的环化。这些替代系统的优点是它们与 RNA 聚合酶 III 表达兼容,因为它们不依赖剪接体。然而,龙卷风系统最适合于较小环状 RNA(最好少于 500 个核苷酸)的生物合成,并且容易在未修饰的 IRES 和开放阅读框序列中存在的短 U 富集区域提前终止。这一限制限制了龙卷风平台的治疗潜力,尽管最近它被纳入 RNA 聚合酶 II 驱动的表达载体,并被证明可以成功表达较大的蛋白质编码环状 RNA(高达 4,719 个核苷酸)。
4.4.环状 RNA 载体的递送
基于载体的治疗药物在递送、宿主细胞对 dsDNA 的感应和核运输方面面临诸多挑战。将 DNA 制备成纳米颗粒,包括脂质纳米颗粒、聚合物和其他非病毒递送复合物,可能允许进入靶细胞,但细胞质中 dsDNA 感应途径的激活(在别处有综述)可能会限制异位 DNA 的转基因表达。此外,载体的核运输对于 RNA 转录的发生至关重要。这些挑战可以通过 CpG 减少和/或使用屏蔽纳米颗粒来防止天然免疫激活,以及通过减小尺寸和/或在载体主链中加入 DNA 运输序列来增加核定位来解决。研究表明,像 SV40 增强子和 NF-κB 结合位点这样的运输序列可以刺激 DNA 的主动核输入,从而增强转基因表达。最近,使用融合蛋白脂质载体递送 RNA 和 DNA 货物以绕过内质网摄取的需要被证明对多种组织是安全的,并且可以广泛应用于多种组织和细胞类型,可能使多种组织和细胞类型的重复给药成为可能。或者,可以使用病毒载体在细胞质中保护 DNA 货物,并有效地将其递送到细胞核中。用于 DNA 递送的最常用的病毒载体是 AAV,它已被批准用于罕见遗传病的基因递送临床应用。然而,AAV 基因组的容量有限(小于 4.7 kb),从而阻止了其用于表达许多与治疗相关的蛋白质。此外,尽管与其他病毒载体相比,AAV 通常具有较低的免疫原性,但仍然禁止重复给药。在 C57BL/6 小鼠的眼中,通过玻璃体腔注射 circRNA 编码的 AAV9 载体,观察到来自 HIPK3 衍生和 ZKSCAN1 衍生环状 RNA 盒的 eGFP 成功表达。此外,除了促进蛋白质编码环状 RNA 的表达外,AAV 还被用于表达具有非编码功能的环状 RNA,如 miRNA 捕获和 RNA 结合蛋白的细胞质捕获。慢病毒是另一类整合到基因组中的治疗性病毒载体,主要用于体外转导体细胞,以确保治疗转基因的稳定表达。然而,与 mRNA 表达相比,慢病毒载体的环状 RNA 表达较低。这种差异可能归因于病毒生产细胞中的 RNA 剪接以及在慢病毒复制的逆转录步骤中潜在的二级结构干扰。因此,转座子或 CRISPR 敲入系统可能为稳定的环状 RNA 过表达提供更可靠的选择。最后,基于载体的环状 RNA 表达已被用于开发含有环状 RNA 的非整合病毒样颗粒(VLP),在这种情况下,优化的载体盒被部署在 VLP 生产系统中,以促进环状 RNA 在 VLP 内的包装。与 mRNA 包装的 VLP 相比,VLP 包装的环状 RNA 具有更好的持久性。
5.环状 RNA 作为生物标志物
如上所述,外源性环状 RNA 有望成为治疗多种疾病的有效选择。此外,环状 RNA 的内源性表达景观已被描述为具有组织特异性,并在许多生理和病理过程中发挥重要作用(在别处有综述)。这引发了使用环状 RNA 作为各种多因素疾病生物标志物的巨大兴趣,包括癌症;自身免疫性疾病,如系统性红斑狼疮、多发性硬化症、类风湿关节炎和 1 型糖尿病;神经退行性疾病,如帕金森病、阿尔茨海默病和肌萎缩侧索硬化;以及心血管和代谢性疾病(在别处有综述)。
大多数关于环状 RNA(circRNA)作为生物标志物的研究都集中在癌症上,因为检测生物液体中的 circRNA 具有很高的兴趣,这归功于它们的高稳定性和在循环细胞外囊泡中的富集。例如,来自 MYBL1 前体 mRNA 的环状 RNA 在腺样囊性癌患者的血浆细胞外囊泡中相对于健康对照组有所增加,且该环状 RNA 的水平与肺转移和预后不良相关。
生物液体中的环状 RNA 对于非侵入性地识别早期疾病可能特别有前景,例如通过检测前列腺癌患者的尿液或血浆中的环状 RNA,以及通过分析血清和胆汁液体活检中的特定环状 RNA 签名来监测胆管癌复发,从而监测疾病进展。此外,在增殖率是预后强指标的情况下,环状 RNA 似乎可以作为预后生物标志物,例如在套细胞淋巴瘤和多发性骨髓瘤中。由于它们的生物合成速度较慢,大多数环状 RNA 在快速增殖的细胞中从未达到稳态水平,而是倾向于在静止和缓慢分裂的细胞中积累,因为它们的性质稳定。因此,环状 RNA 的表达水平与细胞增殖率密切相关。环状 RNA 用于预测治疗反应也很有前景。例如,与肿瘤免疫细胞浸润相关的环状 RNA 表达签名被证明可以预测恶性黑色素瘤患者对免疫疗法的反应,无论患者是单独接受抗 PD1 治疗还是与抗 CTLA4 联合使用。
环状 RNA 的总体水平也可能是自身免疫疾病的一个重要因素。这是因为环状 RNA 倾向于形成 16 - 26 个碱基对的不完美 RNA 双链,因此,它们可能通过结合并抑制 PKR 来抑制先天免疫反应。与之相符的是,在系统性红斑狼疮患者的外周血单核细胞中观察到 PKR 的磷酸化(激活)增加和环状 RNA 水平降低。此外,在患有慢性炎症性皮肤病(如银屑病和特应性皮炎)的人的病变皮肤中,内源性环状 RNA 水平降低。因此,确定环状 RNA 水平是否可以作为诊断生物标志物或用于管理炎症性疾病的重要生物标志物将是很有趣的。
在病理过程中具有不同作用的环状 RNA 也可能转化为具有临床应用价值的生物标志物。在心血管疾病中,INK4 位点的反义非编码环状 RNA 被证明可以调节血管细胞的关键功能,从而预防动脉粥样硬化。随后,许多其他环状 RNA 被证明可以调节心血管疾病的病理生理学。例如,来自 ATM 基因的环状 RNA(cATM)调节其宿主基因 ATM 的表达,导致激活生存途径和促进培养的平滑肌细胞的应激耐受表型。在腹主动脉瘤的人类标本和动脉瘤患者的血清样本中观察到 cATM 表达增加,表明其作为诊断生物标志物的潜力。
最近的研究表明,通过对 190 个人类大脑进行激光捕获显微切割,然后进行超深度全 RNA 测序,发现大脑中环状 RNA 的产生主要来自与帕金森病、阿尔茨海默病和其他神经精神疾病相关的位点。这些数据不仅将有助于理解环状 RNA 在神经病理学中的功能作用,而且如果它们可以在脑脊液或外周血中被检测到,它们也可能推动环状 RNA 作为有前景的诊断生物标志物。事实上,环状 RNA 在许多不同疾病的个体的血浆中差异表达,包括患有妊娠糖尿病的患者。值得注意的是,在妊娠早期测量时,两种环状 RNA 的表达水平的组合显示出对妊娠糖尿病的有前景的鉴别能力。
然而,尽管对环状 RNA 作为生物标志物的潜在使用充满热情,但还没有一个进入临床使用。需要解决几个挑战以推动这一重要的研究领域向前发展。
6.结论与未来方向
体外转录(IVT)和基于载体的环状 RNA 平台作为新一代疗法已崭露头角,适用于多种疾病指征,过去 5 年间,多家专注于治疗性环状 RNA 开发的公司纷纷成立。
体外转录环状 RNA 有望在治疗癌症或病毒感染等动态疾病方面发挥重要作用,这类疾病需要短暂但持续的治疗。相比之下,基于载体的环状 RNA 平台可为慢性疾病提供增强且持久的疗效,例如罕见遗传病、高血压或自身免疫性疾病。此外,使用组织特异性启动子可实现基于载体技术的特定情境表达。鉴于体外转录和基于载体的环状 RNA 的互补特性,在可预见的未来,为多种难以治疗的疾病指征(从急性传染病到慢性致残性疾病)开发多功能治疗方案似乎是可行的。而且,考虑到环状 RNA 基础疗法的现状以及巨大的未开发发展空间,环状 RNA 很可能会超越 mRNA,成为临床开发的首选 RNA 格式。与线性 mRNA 相比,环状 RNA 的稳定性更高,可确保更长或更高的表达水平,这在大多数情况下可带来更高的疗效、更好的安全性以及更低的成本。
最接近临床应用的环状 RNA 基础技术似乎是用于疫苗接种的瞬时蛋白生产,环状 RNA 中疫苗抗原的延长表达可转化为对病原体或癌细胞更强大且持久的免疫反应。然而,要实现这一目标,建立更具可扩展性的环状 RNA 合成和纯化流程至关重要。这一成就还将支持为治疗肝脏相关代谢疾病开发安全的环状 RNA 载体,从而因环状 RNA 的稳态水平增加以及治疗蛋白表达的相应增加,实现更低或更少的给药频率。血友病和尿素循环障碍是肝脏靶向基因治疗的主要目标疾病,因为这些疾病是由酶缺陷引起的,可通过引入功能性基因来纠正,例如血友病 A 的凝血因子Ⅷ基因或血友病 B 的凝血因子Ⅸ基因。
环状 RNA 一个有前景但相对未被充分探索的应用是其作为增强细胞过程的支架的潜力。可以想象环状 RNA 用于通过在纳米尺度上精确排列酶和底物来组装多步骤途径反应。这可能使细胞内按需产生复杂的治疗化合物成为可能。此外,环状 RNA 具有通过受控的碱基配对相互作用的能力,可提供在细胞内创建分子凝聚体的机会,从而作为自然发生过程的生物“工厂”。在相反的应用中,环状 RNA 可能在解决许多疾病特征的蛋白质聚集方面发挥作用。通过 RNA 介导的稳定化,可能抑制未折叠蛋白结构域形成有毒聚集物,为这类疾病提供一种新的治疗选择。
总体而言,环状 RNA 技术对于开发新疗法极具前景。然而,像任何新兴技术一样,环状 RNA 模式也有若干需要解决的局限性,才能实现更广泛的应用。以可扩展且可重复的方式生成体外转录环状 RNA 在技术上可能具有挑战性。此外,开发用于消除污染物的稳健工具对于确保体内低免疫原性和良好的安全性至关重要。对于基于载体的表达系统,由于内源性因素对转录和环化的双重影响,控制细胞中环状 RNA 的表达量可能具有挑战性。因此,优化环状 RNA 生物合成的特性对于提高产量和减少剪接副产物至关重要。
将环状 RNA 有效地递送至靶细胞和组织仍然是体外转录和基于载体的环状 RNA 的一个重要障碍。针对体外转录环状 RNA 递送的新型非免疫原性递送平台(如脂质纳米颗粒和外泌体)的研究正在进行中。这些平台也在为 DNA 载体开发,但非病毒 DNA 载体在递送至细胞后可能需要核转位,以促进治疗性环状 RNA 的转录和剪接。尽管基于载体的系统可使用病毒载体来靶向递送治疗性环状 RNA,但病毒载体的不利免疫原性特征使其无法进行重复给药。
解决这些局限性需要跨学科的努力以及在环状 RNA 研究和开发中的持续创新。克服这些挑战对于解锁环状 RNA 在临床应用中的全部潜力至关重要。因此,我们预计在未来几年将设计并启动许多环状 RNA 基础的临床试验,同时令人兴奋的新研究将推动环状 RNA 模式可实现的边界。
此外,环状 RNA 作为生物标志物具有潜力,部分原因是其高稳定性以及在人类疾病病理生理学中的独特作用。这可能会推动个性化医疗的进步,并有助于指导患者选择,改善包括肿瘤学、神经学和心血管疾病等不同领域的临床结果。
识别微信二维码,添加生物制品圈小编,符合条件者即可加入
生物制品微信群!
请注明:姓名+研究方向!
版
权
声
明
本公众号所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源和作者,不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系(cbplib@163.com),我们将立即进行删除处理。所有文章仅代表作者观,不代表本站立。
信使RNA核酸药物疫苗
2024-11-29
·今日头条
【导读】
环状RNA能够调节巨噬细胞的细胞质溶质性死亡(即细胞焦亡),这有可能促进炎症和基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)活性在腹主动脉瘤(AAA)中的协同作用。但环状RNA在调节AAA中巨噬细胞细胞质溶质性死亡方面的作用尚不明确。
11月27日,南方医科大学何翔教授研究团队在期刊《Clinical And Translational Medicine》上发表了研究论文,题为“CircHipk3 serves a dual role in macrophage pyroptosis by promoting NLRP3 transcription and inhibition of autophagy to induce abdominal aortic aneurysm formation”,本研究中,研究人员发现与正常动脉相比,CircHipk3在主动脉瘤中显著上调。在circHipk3处理的小鼠中,巨噬细胞焦亡促进炎症和MMP合成的协同作用,并显著加速Ang II和PPE诱导的AAA形成。机制上,RNA纯化分离染色质(ChIRP)表明circHipk3通过与Stat3相互作用促进巨噬细胞焦亡,增加主动脉中NLRP3水平,并通过与Snd1结合促进Ptbp1 mRNA降解来抑制自噬。
因此,本研究揭示了circHipk3在巨噬细胞焦亡中的重要作用,从而显著改善AAA的预后。
https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/doi/full/10.1002/ctm2.70102
背景知识
01
腹主动脉瘤(AAA)是一种慢性炎症性疾病,可引起腹主动脉局灶性扩张超过正常直径的50%,可能导致血管破裂,并具有较高的发病率和死亡率。炎症过程对动脉瘤的发生和发展至关重要,其发生早、持续贯穿于AAA的整个病程,并增强基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)的活性和平滑肌细胞的凋亡。细胞焦亡是一种促炎症的程序性细胞死亡过程,既可以是炎症的原因,也可以是炎症的结果,形成正反馈加重炎症。细胞焦亡引起细胞肿胀和膜破裂,导致炎性细胞因子IL-1β、IL-18、高迁移率族蛋白b1 (HMGB1)和多种S100蛋白大量渗漏,进而募集炎性细胞,增加炎性细胞浸润。促炎细胞因子如肿瘤坏死因子-α (TNF-α)也激活依赖caspase8的消皮素-D加工,诱导细胞焦亡。更重要的是,既往研究发现,细胞焦亡标志物NLRP3、CASP1在AAA中表达升高,且细胞焦亡可促进AAA的多种重要病理过程,从而诱导AAA的形成,提示细胞焦亡在介导AAA形成中起关键作用。研究人员认为细胞焦亡是炎症反应的触发因素,从而导致AAA的形成。因此,抑制细胞焦亡可能有助于减轻炎症反应,最终抑制AAA的形成。
巨噬细胞被认为是白细胞介素(IL)-1β和IL-18的主要来源,而IL -1β和IL-18是与细胞焦亡相关的重要细胞因子。此外,巨噬细胞的NLRP3-CASP1级联是细胞焦亡的激活因子,它通过切割MMP的N末端抑制结构域来激活MMP,从而启动AAA的形成。因此,巨噬细胞焦亡可加重炎症反应和MMP活性,从而诱导AAA形成。抑制巨噬细胞焦亡可能是预防AAA形成的有效途径。此外,前期研究证明,下调编码基因LMP7等基因干预可通过减弱巨噬细胞焦亡来预防AAA形成。CircRNAs具有高度组织特异性调控和结构稳定性的特点,这使它们有可能在最小的全身不良影响下延缓AAA的形成。然而,CircRNAs是否通过调控巨噬细胞焦亡抑制炎症反应和MMP活性来调控AAA形成尚未得到证实。
CircHipk3通过与Stat3的相互作用促进巨噬细胞焦亡
02
研究人员进一步阐明circHipk3在巨噬细胞中发挥作用的潜在机制。研究人员进行ChIRP检测,并切除circhipk3特异性条带进行质谱分析。随后,研究人员进一步分析了GSE51227转录组数据集中10个重叠的焦亡相关蛋白的差异表达。证据表明,Stat3和Tlr2在GSE51227数据集中表现出显著不同的表达水平。qPCR证实Stat3和Tlr2在AAA中表达上调。研究人员选择Stat3作为潜在的靶蛋白,因为它在激活NLRP3炎症小体中发挥上游作用,并确定其参与AAA的进展。此外,研究人员通过RIP实验验证了circHipk3和Stat3之间的相互作用。结果表明,与非特异性IgG抗体相比,circHipk3被抗Stat3抗体富集。蛋白质免疫印迹实验验证了Stat3与circHipk3的特异性结合。研究人员下一步研究了circHipk3和Stat3之间的相互作用是否影响Stat3的水平。接下来,研究人员进一步探究过表达Stat3是否影响NLRP3和IL-1β、IL-18的蛋白表达水平。相关性分析表明,在细胞焦亡关键基因中,NLRP3与Stat3的相关性最高。既往研究表明,Stat3能够与NLRP3启动子结合并增强H3K9乙酰化和NLRP3转录,以及NLRP3/ casp1介导的细胞焦亡。过表达Stat3可上调NLRP3、IL-1β和IL-18的蛋白表达水平。本研究结果表明,过表达Stat3显著上调巨噬细胞中的RNA水平和上层清液中IL-1β和IL-18的ELISA检测水平。过表达circHipk3可增强NLRP3、IL-1β和IL-18的表达;然而,这种作用被Stat3的敲低所消除。综上所述,上述结果表明circHipk3通过Stat3-NLRP3-IL-1β/IL-18通路调控巨噬细胞焦亡。
CircHipk3通过与Stat3的相互作用促进巨噬细胞焦亡
CircHipk3通过促进Ptbp1 mRNA降解抑制自噬促进巨噬细胞焦亡
03
既往研究表明,细胞内自噬在清除过量NLRP3炎症小体中发挥重要作用。此外,研究表明circHipk3可抑制自噬的形成。过表达circHipk3可抑制自噬相关蛋白Atg5和Beclin1的表达。相反,通过免疫荧光分析和自噬通量的增加,研究人员证明了circHipk3的敲低促进了自噬的形成。此外,研究人员通过透射电镜观察到,敲低circHipk3后,巨噬细胞的自噬体显著增加,提示circHipk3对自噬的抑制作用。另外,研究人员确定了Ptbp1和Snd1是circHipk3调控自噬的下游靶点。综上所述,本研究结果表明,Snd1可能通过调节circHipk3和Ptbp1 RNA分子之间的相互作用来调节Ptbp1 mRNA水平。
结语
04
总之,本研究结果表明,环状Hipk3在促进细胞因子分泌和MMP合成的协同作用方面发挥着关键作用,从而加剧巨噬细胞的焦亡,并促进AAA的形成。机制上,环状Hipk3通过与Stat3的相互作用,增加主动脉中NLRP3的水平,并通过与Snd1结合促进Ptbp1 mRNA的降解来抑制自噬,从而促进巨噬细胞的焦亡。鉴于在AAA发生机制中的核心作用,环状Hipk3成为一种有潜力的治疗靶点,可用于缓解AAA的形成和破裂。通过调节环状Hipk3的水平或活性来预防和管理这种严重的血管疾病具有潜在的前景。
【参考资料】
https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/doi/full/10.1002/ctm2.70102
【关于投稿】
转化医学网(360zhyx.com)是转化医学核心门户,旨在推动基础研究、临床诊疗和产业的发展,核心内容涵盖组学、检验、免疫、肿瘤、心血管、糖尿病等。如您有最新的研究内容发表,欢迎联系我们进行免费报道(公众号菜单栏-在线客服联系),我们的理念:内容创造价值,转化铸就未来!
转化医学网(360zhyx.com)发布的文章旨在介绍前沿医学研究进展,不能作为治疗方案使用;如需获得健康指导,请至正规医院就诊。
热门推荐活动 点击免费报名
🕓 线上|2024年12月3日
▶ 匠“芯”独出·见微知著——时空组学技术前沿应用线上研讨会
🕓 北京|2024年12月5日
▶ 2024前沿科技与转化医学研讨会
🕓 线上|2024年12月6日-2025年1月16日
▶ 《我的2024》
🕓 全国|2024年12月-2025年03月
▶ 中国转化医学产业大会
🕓 上海|2025年02月28日-03月01日
▶ 第四届长三角单细胞组学技术应用论坛暨空间组学前沿论坛
点击对应文字 查看详情
信使RNA临床结果
分析
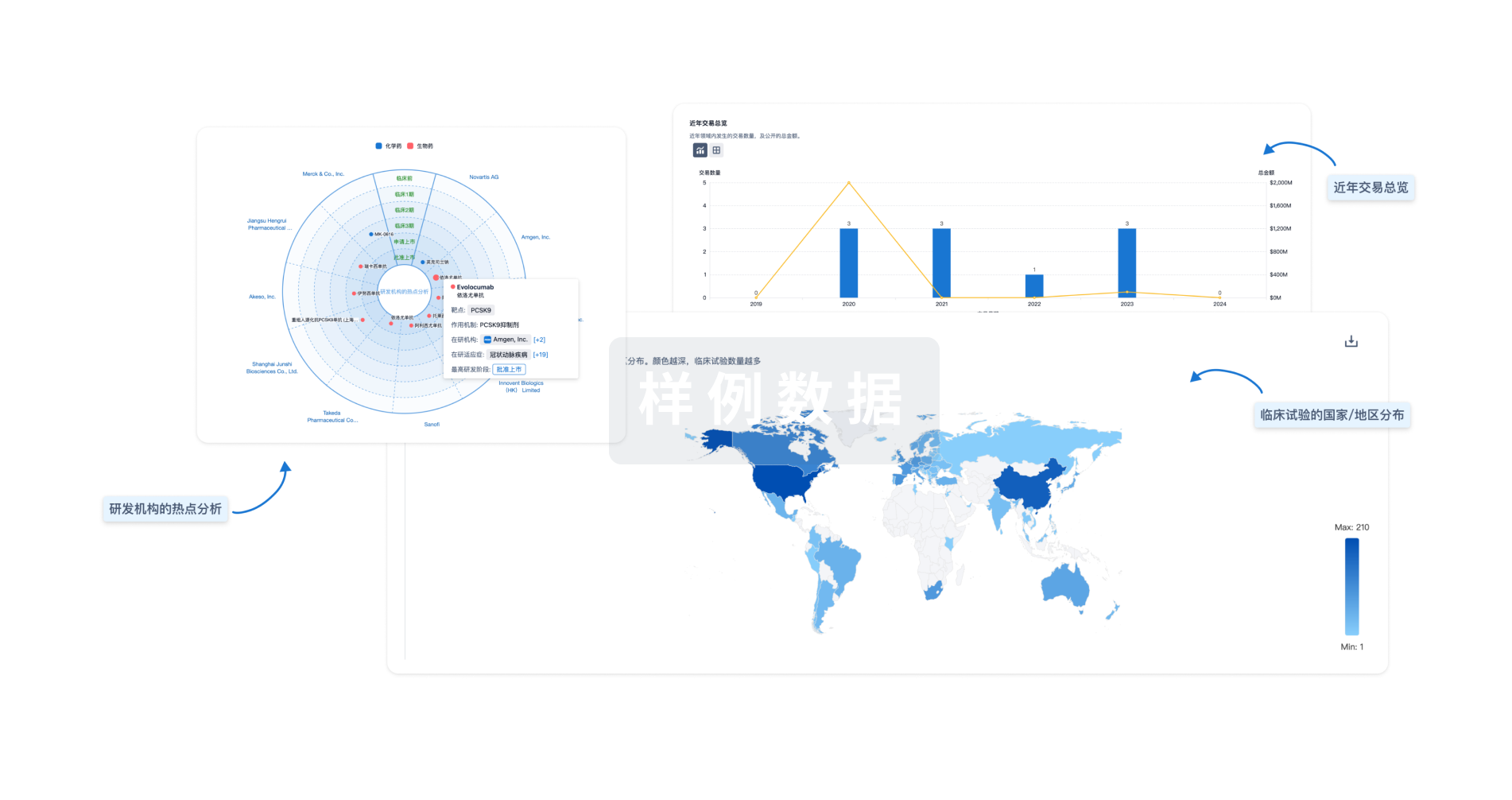
对领域进行一次全面的分析。
登录
或
Eureka LS:
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用