更新于:2024-11-01

Kangmei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
更新于:2024-11-01
概览
标签
消化系统疾病
心血管疾病
泌尿生殖系统疾病
化学药
中药
小分子化药
疾病领域得分
一眼洞穿机构专注的疾病领域
暂无数据
技术平台
公司药物应用最多的技术
暂无数据
靶点
公司最常开发的靶点
暂无数据
| 排名前五的药物类型 | 数量 |
|---|---|
| 化学药 | 10 |
| 中药 | 6 |
| 小分子化药 | 2 |
关联
18
项与 康美药业股份有限公司 相关的药物靶点 |
作用机制 ADRA1拮抗剂 |
在研机构 |
原研机构 |
非在研适应症- |
最高研发阶段批准上市 |
首次获批国家/地区 日本 |
首次获批日期1990-01-23 |
作用机制 L-type calcium channel阻滞剂 |
非在研适应症 |
最高研发阶段批准上市 |
首次获批国家/地区 日本 |
首次获批日期1989-01-17 |
靶点- |
作用机制- |
在研机构 |
原研机构 |
在研适应症 |
非在研适应症- |
最高研发阶段临床申请 |
首次获批国家/地区- |
首次获批日期- |
3
项与 康美药业股份有限公司 相关的临床试验甲硝唑片在健康受试者中的随机、开放、单剂量、双周期、自身交叉空腹及餐后生物等效性试验
以康美药业股份有限公司提供的甲硝唑片为受试制剂,按生物等效性试验的有关规定,与欧盟上市的持证商为Winthrop Pharmaceuticals UK Limitid公司的甲硝唑片(商品名:FLAGYL,参比制剂)对比在健康人体内的相对生物利用度,研究两制剂的人体生物等效性和安全性。
开始日期- |
申办/合作机构 |
阿莫西林胶囊在健康受试者中随机、开放、单剂量、双周期、自身交叉空腹及餐后状态下的生物等效性试验
主要目的:以康美药业股份有限公司生产的阿莫西林胶囊(0.25g/粒)为受试制剂,以Beecham Group plc公司生产的阿莫西林胶囊(商品名:Amoxil®,0.25g/粒)为参比制剂,按生物等效性试验的相关规定,比较两制剂在中国健康受试者体内的药代动力学行为,评价其生物等效性。次要目的:评价中国健康受试者单次空腹/餐后口服两制剂后的安全性。
开始日期2018-05-14 |
申办/合作机构 |
琥珀酸普芦卡必利片在健康受试者中随机、开放、单剂量、双周期、自身交叉空腹和餐后状态下的生物等效性试验
主要目的:以康美药业股份有限公司提供的琥珀酸普芦卡必利片(2mg/片)为受试制剂,按生物等效性试验的有关规定,与Janssen Cliag S.p.A.公司生产、西安杨森制药有限公司分包装的力洛®参比制剂(2mg/片),对比在健康人体内的相对生物利用度,考察两制剂的人体生物等效性;次要目的:观察受试制剂琥珀酸普芦卡必利片和力洛®在健康受试者中的安全性。
开始日期2018-01-27 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 康美药业股份有限公司 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 康美药业股份有限公司 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
53
项与 康美药业股份有限公司 相关的文献(医药)2021-07-29·Combinatorial Chemistry & High Throughput Screening
Metabolic Profile of Dendrobine in Rats Determined by Ultra-high-performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry
Article
作者: Li, Jian-hua ; Zhang, Jing ; Bai, Jun-qi ; Gong, Lu ; Xu, Wen ; Qiu, Xiao-hui ; Huang, Zhi-hai ; Huang, Juan ; Su, He ; Guo, Qian-xiang ; Luo, Yu-bing
2020-09-01·Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis3区 · 医学
Analysis of curcuminoids and volatile components in 160 batches of turmeric samples in China by high-performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography mass spectrometry
3区 · 医学
Article
作者: Guo, Qi-Lei ; Ye, Min ; Qiao, Xue ; Shang, Zhan-Peng ; Zhang, Xiao-Li ; Xu, Lu-Lu ; Bo, Tao ; Li, Pi ; Le, Zhi-Yong ; Lu, Ying-Ying ; Bai, Zong-Li ; Sun, Long
2020-08-31·Journal of Analytical Methods in Chemistry4区 · 化学
Quantification Analysis of 13 Organic Components and 8 Inorganic Elements in Angelica Sinensis Radix and Its Different Parts Combined with Chemical Recognition Pattern
4区 · 化学
ArticleOA
作者: Gao, Shanshan ; Dong, Yangli ; Xiang, Fangtao ; Yao, Yixin ; An, Chang ; Wang, Xiaoxiao ; Li, Xi
144
项与 康美药业股份有限公司 相关的新闻(医药)2024-10-10
·药闻康策
☝ 点击上方 一键预约 ☝
最新最热的医药健康新闻政策
2024
1010
药品高端会员区
HOT
高端会员1
【会员编号】y1172
【所在地区】北京,河北,山西
【所在公司】黑龙江久久药业有限责任公司
【工作职务】河北山西招商经理
【相关产品】
①【香砂养胃颗粒】基药,独家无蔗糖,国家专利保护剩余19年,医保甲,OTC乙。
②【刺五加颗粒】独家剂型无蔗糖,医保乙,OTC甲。
③【小儿清热止咳口服液】妇儿急抢目录,医保乙,OTC甲。
④【健儿消食口服液】基药,医保乙,OTC甲。
【自身资源】基独家,基药
【需要资源】河北,山西三终端,或临床代理
高端会员2
【会员编号】y1199
【所在地区】吉林省
【所在公司】长春海悦药业有限公司
【工作职务】省区经理
【相关产品】海悦美奥,悦思立普,伏立康唑,丙戊酸钠注射用浓溶液,他达拉非,注射用阿奇霉素(儿童),曲克芦丁,盐酸氨溴索,盐酸美金刚等
【自身资源】吉林省内分泌专家以及医院资源,商业公司合作资源(大商业以及地方商业);吉林省慢病产品市场布局及推广策略(策略层面)
【需要资源】吉林省及东北三省的准入资源,消化内科准入以及一线客户资源(多方式合作);阿奇霉素注射液市场分析报告(成人&儿童)、奥美拉唑市场分析报告
高端会员3
【会员编号】y1211
【所在地区】陕西
【所在公司】北京轩竹生物科技有限公司
【工作职务】省区经理
【相关产品】安奈拉唑钠
【自身资源】政府事务(医保局) 核心医院ICU临床
【需要资源】医院准入 药剂关系 代理商
高端会员4
【会员编号】y1198
【所在地区】川渝藏
【所在公司】江西青峰药业有限公司
【工作职务】省区经理
【相关产品】艾司奥美拉唑镁肠溶片、枸橼酸托法替布片、阿哌沙班片、富马酸丙酚替诺福韦片、恩替卡韦分散片/胶囊、盐酸乌拉地尔注射液、阿普米司特片、雷贝拉唑钠肠溶片、枳实总黄酮片。
【自身资源】政府事务,四川省消化专家以及医院资源,商业公司合作资源
【需要资源】一线客户资源和代理商资源
高端会员5
【会员编号】y1087
【所在地区】湖南
【所在公司】清华德仁西安幸福制药有限公司
【工作职务】大区经理
【相关产品】生血宝合剂、五灵胶囊、热炎宁合剂、童康颗粒
【自身资源】厂家产品资源
【需要资源】临床类型代理商:湖南省级代理商;湖南省地区代理商。
高端会员6
【会员编号】y0134
【所在地区】北京
【所在公司】北京杏林知松科技有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】环磷腺苷葡胺、益心胶囊、盐酸曲马多分散片
【自身资源】北京临床渠道多年、全国总代产品
【需要资源】各省总代资源、厂家资源
高端会员7
【会员编号】y1150
【所在地区】贵州
【所在公司】贵州佳德同汇健康咨询服务有限公司
【工作职务】业务负责人
【相关产品】安奈拉唑钠肠溶片、头孢呋辛钠氯化钠注射液、甘草酸单铵半胱氨酸氯化钠注射液等三十几个产品
【自身资源】贵州省代。贵州部分医院资源,产品资源。
【需要资源】有医院资源的客户,需具备开发能力。可提供品种和资金。
高端会员8
【会员编号】y0855
【所在地区】北京
【所在公司】北京伟林恒昌医药科技有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】自己持有:阿托伐他汀钙片,奥洛他定片
【自身资源】招商和对外贴牌生产
【需要资源】需要各省OTC销售团队
高端会员9
【会员编号】y1002
【所在地区】北京
【所在公司】国药控股北京有限公司
【工作职务】采购中心市场部经理
【相关产品】药品、器械等
【自身资源】北京招采信息
【需要资源】全国招采信息
高端会员10
【会员编号】y1142
【所在地区】江苏南京
【所在公司】凡森特医药
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】抗生素/化药/器械/中成药
【自身资源】渠道、产品、学术
【需要资源】客户、渠道
高端会员11
【会员编号】y1193
【所在地区】北京
【所在公司】北京康辰生物
【工作职务】法务合规经理
【相关产品】原研药品-骨松骨痛相关
【自身资源】药械合规及法律相关
【需要资源】关于医药行业的合规及法律相关的信息
高端会员12
【会员编号】y0317
【所在地区】湖南长沙
【所在公司】湖南广药恒生医药有限公司
【工作职务】采购总监
【相关产品】一类麻精产品
【自身资源】广药集团国企、有一类麻精配送资质、全省医疗机构覆盖配送、新品开发进院能力较强、招商产品可协助推广。
【需要资源】医院自营产品、零售分销业务全省配送。
高端会员13
【会员编号】y1128
【所在地区】云南省昭通市
【所在公司】云南蓝蝶医疗器械有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】医疗产品
【自身资源】昭通市及昭通周边地区的客户资源
【需要资源】优质的医疗产品,及其他地州的客户资源
高端会员14
【会员编号】y1226
【所在地区】四川成都
【所在公司】四川启源药业有限公司
【工作职务】总监
【相关产品】医保甲类基药
【自身资源】厂家临床基药医保产品
【需要资源】江西省区临床团队及省第三终端资源
高端会员15
【会员编号】y1187
【所在地区】南京
【所在公司】悦康药业
【工作职务】招商经理
【相关产品】活心丸
【自身资源】基药,甲类,安全性高
【需要资源】江苏地区招商
高端会员16
【会员编号】y1116
【所在地区】福建(主战区)江西、浙江、江苏
【所在公司】康美药业股份有限公司
【工作职务】区域经理
【相关产品】厂家直销,包含中药饮片、燕窝虫草等贵系礼品
【自身资源】1.国家膏方丸剂代煎等试点单位以及集采中标单位之一;2.可自产600多个品种上万个品规;3.可根据医院要求定制高标及小包装饮片;4.药剂科资源
【需要资源】1、福建、江西、浙江、江苏区域的代理商;2、各大医院及中医馆高层资源
高端会员17
【会员编号】y1140
【所在地区】北京
【所在公司】吉林天衡药业有限公司
【工作职务】市场运营部部长
【相关产品】铝碳酸镁咀嚼片、瑞舒伐他汀钙片、秋水仙碱片
【自身资源】可合作CRO、CMO、CDMO
【需要资源】销售代理商;寻找生产场地:片剂,适应症为痛风,特点是该原料为细胞毒药物,寻求细胞毒专线或可与细胞毒药物共线的生产场地。
高端会员18
【会员编号】y0584
【所在地区】天津
【所在公司】天津市医药集团泰宁医药
【工作职务】市场总监
【相关产品】狗皮膏、护肝胶囊、更年安胶囊、连翘败毒片、葡萄糖酸钙片等基药品种,全国多个省和直辖市已中标
【自身资源】熟悉国各省招投标政府事务,有成熟的全国销售网络
【需要资源】急需各省和直辖市的临床团队
高端会员19
【会员编号】y0907
【所在地区】北京、天津
【所在公司】海诚医药集团有限公司
【工作职务】省区经理
【相关产品】肌苷注射液(静注)、龙血竭胶囊(肠溶)、强力枇杷露(炼蜜)、磷酸川芎嗪注射液(供静脉注射用)、注射用伏立康唑、甘油灌肠剂、注射用哌拉西林钠、注射用头孢唑肟钠、注射用头孢哌酮钠舒巴坦钠、注射用氨苄西林钠舒巴坦钠、曲克芦丁注射液、核黄素磷酸钠注射液、注射用尼麦角林等产品
【自身资源】全国总代理产品资源
【需要资源】寻临床代理商、省总、地总团队合作
高端会员20
【会员编号】y1219
【所在地区】内蒙古
【所在公司】源浩医疗
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】处方药
【自身资源】整个乌兰察布市二级医院、卫生院、诊所资源
【需要资源】独家基药、集采品种、OTC控销产品厂家资源
高端会员21
【会员编号】y0947
【所在地区】江西南昌
【所在公司】江西金耐康医药科技有限公司
【工作职务】经理
【相关产品】神外、妇产、肿瘤领域产品
【自身资源】福建和江西省代和医院客户资源,江西神经外科及妇产科专家资源
【需要资源】厂家岗位或产品
高端会员22
【会员编号】y1197
【所在地区】辽宁
【所在公司】辽宁好护士集团医药有限公司
【工作职务】省区经理
【相关产品】肾炎温阳片、肾炎解热片
【自身资源】独家,挂网,空间好
【需要资源】操作肾病产品的医院资源团队
高端会员23
【会员编号】y1096
【所在地区】河南
【所在公司】浙江仙琚制药
【工作职务】招商大区
【相关产品】屈螺酮炔雌醇片(||)
【自身资源】河南、河北、江西、安徽、北京、天津等地重点医院客户资源
【需要资源】河南、河北、江西、安徽、北京、天津等地妇科团队资源
高端会员24
【会员编号】y1264
【所在地区】枣庄市
【所在公司】某医药公司
【工作职务】经理
【相关产品】肿瘤药
【自身资源】等级医院客户
【需要资源】最新化药产品资源
高端会员25
【会员编号】y0321
【所在地区】厦门、上海
【所在公司】承葛医药集团
【工作职务】项目经理
【相关产品】微生态移植及相关产业
【自身资源】微生态检测、移植、微生态口服产品、微生态研发
【需要资源】各类医药资源
高端会员26
【会员编号】y1221
【所在地区】广东
【所在公司】陕西盘龙药业集团
【工作职务】省区经理
【相关产品】1、盘龙七片(骨科)全国独家专利产品、医保甲类无后缀。2、骨松宝片(预防更年期骨质疏松症)。3、克比热提片(独家口服,皮肤科)4、复方醋酸绵酚片(妇科)
【自身资源】独家、商业公司合作资源
【需要资源】医院准入、广东临床类型代理商
高端会员27
【会员编号】y1278
【所在地区】陕西
【所在公司】西安典茂轩医药科技
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】雾化全系列,抗生素、心脑血管领域产品。
【自身资源】陕西省招商全渠道和连锁OTC自营团队及政务商业资源
【需要资源】集采药,国谈化药,进口化药
高端会员28
【会员编号】y1114
【所在地区】四川/西藏
【所在公司】浙江孚诺/浙江惠迪森
【工作职务】市场/销售主管
【相关产品】复方多黏菌素B软膏/注射用拉氧头孢钠
【自身资源】1.四川省皮肤科、烧伤科、肛肠科深耕细作10年建立上层专家资源,临床一线专人覆盖,自建团队,高效专业;2.四川、西藏都有自己的分销渠道,西藏有自己的商业配送公司,承接全国产品。
【需要资源】1.寻找相关科室品种,签总代、有潜力的专科品种;2.寻找省内手术科室合作伙伴,推广外用抗生素品种在四川的销售。
高端会员29
【会员编号】y1294
【所在地区】浙江
【所在公司】浙江天啬生物医药有限公司 、杭州端本医院科技有限公司
【工作职务】招商经理
【相关产品】主营产品线:骨科,麻醉科,消化科;自有持证:氟比洛芬凝胶贴膏
【自身资源】1、浙江省临床品种推广网络;2、自有批文
【需要资源】1、全国省级代理合作伙伴;2、浙江省代理推广甲方产品
高端会员30
【会员编号】y1312
【所在地区】重庆
【所在公司】重庆旭达药业
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】补肾健脾口服液、食积口服液
【自身资源】产品资源、团队资源
【需要资源】产品品牌输出
高端会员31
【会员编号】y0857
【所在地区】河北
【所在公司】京津医学
【工作职务】产品经理
【相关产品】养心定悸颗粒
【自身资源】医学实验与研究,团队目前主要承接上市后医学临床再评价项目;临床推广,团队覆盖全国等级医疗及基层医疗招商,京津冀地区临床推广自营
【需要资源】全国总代产品,最好是医保或者独家
高端会员32
【会员编号】y0990
【所在地区】新疆
【所在公司】新疆迈达医药有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】OTC,临床基药产品
【自身资源】具有完善的新疆省临床基药销售渠道和OTC销售渠道
【需要资源】新特药,基药产品,集采产品,皮肤科基药产品需要在新疆推广的上游企业可接洽,以及OTC优秀品种,新疆市场可跨渠道运营
高端会员33
【会员编号】y1176
【所在地区】广西
【所在公司】洺康医疗
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】儿科、妇科、产科、乳腺、骨科、消化、内分泌、放射科 中枢神经线,心脑血管线药品为主
【自身资源】17个集采产品,8个非集采产品,拥有专业的一线自营推广队伍,全区招商队伍
【需要资源】儿科领域,神经领域,心脑血管领域等国家集采产品及国谈,基药的新药
高端会员34
【会员编号】y1395
【所在地区】长春
【所在公司】长春澜江医药科技有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】拉考沙胺口服溶液(9批集采)、托莫西汀口服溶液(9批集采)、氯雷他定糖浆(已过评)
【自身资源】MAH+CRO公司
【需要资源】产品代理销售
高端会员35
【会员编号】y1401
【所在地区】四川
【所在公司】四川九兴仁创医药科技有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】盐酸氨基葡萄糖胶囊、阿法骨化醇片、金天格胶囊、多索茶碱注射液、特立帕肽注射液等
【自身资源】在四川主要做集采业务,目前拥有一支40人的专职直营推广团队,以及一支10人招商团队,2023年产值3.5亿。
【需要资源】承接集采中选药企在四川的推广资源,希望链接更多的厂家资源
高端会员36
【会员编号】y1449
【所在地区】江西宜春
【所在公司】仁和集团江西正方医药有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】大活络胶囊、强力枇杷胶囊
【自身资源】从业30年,有一定的客户资源
【需要资源】适合临床的中成药、学习新的销售方式
器械高端会员区
高端会员1
【会员编号】X0031
【所在地区】贵州贵阳
【所在公司】贵州众鑫源科技有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】口腔辅料
【自身资源】省级公立医院客户资源
【需要资源】耗材,试剂,医美,口腔
高端会员2
【会员编号】X0028
【所在地区】北京
【所在公司】北博(北京)医疗器械有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】电热针治疗仪+耗材内热式电热针灸针
【自身资源】有源医疗器械的研发、注册、代工
【需要资源】诚招各省耗材代理商,有医保资源,本产品在《全国医疗服务项目技术规范(2023年版)》,需要增加或修订各省医保目录
高端会员3
【会员编号】X0035
【所在地区】云南省昭通市
【所在公司】云南蓝蝶医疗器械有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】医疗器械相关产品
【自身资源】云南省昭通市及昭通周边地区的客情资源
【需要资源】优质的产品
高端会员4
【会员编号】X0045
【所在地区】福建
【所在公司】福州市东瑞医疗科技有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】狂免、破免、纤原,人用狂犬疫苗等
【自身资源】福建省代,临床医学背景,部分医院、卫健及疾控部门资源
【需要资源】适合急诊外科相关药品,耗材产品资源
高端会员5
【会员编号】X0063
【所在地区】山东济南
【所在公司】山东智辰健康咨询管理有限公司
【工作职务】老板
【相关产品】静电敷贴
【自身资源】山东省及全国临床资源
【需要资源】山东各区域优质招商人员
超级高端会员区
超级会员1
【会员编号】w0201
【所在地区】湖南
【所在公司】湖南健朗药业有限责任公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】自身持有奥拉西坦胶囊、奥拉西坦注射液、泮托拉唑肠溶胶囊、羟甲烟胺片等产品。
【自身资源】招商和对外贴牌生产
【需要资源】需要购买若干化学药品注册批文,已出批文或者即将申报的均可。
超级会员2
【会员编号】w0045
【所在地区】山东东营
【所在公司】山东凤凰制药股份有限公司
【工作职务】普药事业部总监
【相关产品】盐酸二甲双胍缓释片、苯磺酸氨氯地平片、辛伐他汀片、维格列汀片、护肝片、降脂宁片、复方丹参片、胃灵颗粒、半夏露颗粒、益母草颗粒、板蓝根颗粒、微达康颗粒、感冒清热颗粒、小儿咽扁颗粒、小儿咳喘灵颗粒、灵芝胶囊、活力胶囊、穿心莲胶囊、黄柏胶囊等
【自身资源】厂家产品资源
【需要资源】市县级临床业务团队
超级会员3
【会员编号】w0150
【所在地区】山东
【所在公司】山东天元盈康医疗科技有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】人血白蛋白,破免,狂免,静丙,小儿复方氨基酸注射液,盐酸纳美芬,环磷腺苷 等产品。
【自身资源】政府事务 在山东做省代17年 有直营团队 同时通过招商团队覆盖全省医院。
【需要资源】上游厂家,国代,批文持有人,原料药
超级会员4
【会员编号】w0033
【所在地区】四川成都
【所在公司】四川省百草生物药业有限公司
【工作职务】市场总监
【相关产品】苯磺酸氨氯地平片、盐酸舍曲林胶囊、泛昔洛韦片
【自身资源】通过一致性评价产品。医保甲类。基药。大部分省份已挂网。渠道终端市场管理好。
【需要资源】临床、终端渠道代理商
超级会员5
【会员编号】w0186
【所在地区】山东
【所在公司】深圳万和制药有限公司
【工作职务】销售部经理
【相关产品】商品名:和安,和爽,和流,爱伦多等
【自身资源】消化,肝病以及普外等领域专家资源
【需要资源】政府事务相关
超级会员6
【会员编号】w0163
【所在地区】广西
【所在公司】广西炬邦乾承投资有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】集采中选:哌他,左氨氯地平,左卡尼汀,噻肟,呋塞米,他啶,曲松,丙戊酸钠,头孢地尼 呼吸:沙丁,氟替卡松,异丙,左沙,乙酰半胱氨酸,茶碱,孟鲁司特。肾内:左卡,达肝,司维拉姆,促红,百令片。围手术期:羟考酮,纳布啡。布托啡诺。抗感染:磷霉素,哌舒,唑肟,阿奇。慢病:达格列净,格列齐特,氟伐他汀,左氨氯地平,门冬氨氯地平。心脑血管:辅酶Q10,倍他司汀,曲克芦丁,吡拉西坦,己酮可可碱。
【自身资源】地方政府事务,专业推广能力,经销商储备,行业口碑认可。
【需要资源】甲方产品
超级会员7
【会员编号】w0160
【所在地区】内蒙古
【所在公司】商贸公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】集采药品、集采器械、化妆品、特医食品等。
【自身资源】35人销售团队
【需要资源】集采药品、集采器械、化妆品、特医食品等。
超级会员8
【会员编号】w0104
【所在地区】南京
【所在公司】翎耀生物科技(上海)有限公司
【工作职务】全国商务分销总监
【相关产品】利培酮口服溶液、氨己烯酸口服溶液用散、阿托伐他汀钙片、利伐沙班片
【自身资源】过评产品:医保、国谈,慢病系列
【需要资源】全国临床、二三终端相关领域省级经销商、终端代理商
超级会员9
【会员编号】w0127
【所在地区】山东
【所在公司】山东誉众医药
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】骨科/肿瘤/抗生素/心血管/重症/透析/呼吸产品
【自身资源】专业化的省级医药推广服务商。自营1条线+招商3条线+市场部1条线+集采产品专项。学术推广能力、政务关系、商业资源优秀。
【需要资源】优质的相关产品升级代理。
超级会员10
【会员编号】w0009
【所在地区】浙江
【所在公司】浙江明晖医药有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】全国总代:阿昔洛韦颗粒、别嘌醇片;自有持证:他达拉非片
【自身资源】1.浙江省临床品种推广网络;2、全国总代理产品;3、自有批文;4、零售电商公司;5、C端电商供应链
【需要资源】1、需要在浙江代理推广的甲方产品;2、全国省级代理合作伙伴
超级会员11
【会员编号】w0172
【所在地区】江苏南京
【所在公司】西安良医网络科技集团有限公司
【工作职务】营销中心负责人
【相关产品】1.米墨 2.超医助手
【自身资源】有一个医药互联网服务交易溯源平台“米墨”为行业发展提供新方案、新模式,为药械厂商提供深度学术推广及精准营销升级服务;以及医生资源平台“超医助手”目前大约有数百万的医疗行业从业者资源。拥有各类医疗互联网平台资源,企业资源,医药企业资源。
【需要资源】链接医药企业
超级会员12
【会员编号】w0173
【所在地区】上海市静安区
【所在公司】上海鑫意医药科技有限公司
【工作职务】董事长
【相关产品】关节镇痛巴布膏、强力天麻杜仲胶囊等
【自身资源】招标、医疗终端等
【需要资源】需要上家优质产品,需要有管理能力的业务经理
超级会员13
【会员编号】w0029
【所在地区】湖南
【所在公司】湖南思达医药有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】主营产品线:儿科,骨科,妇科,内科等
【自身资源】湖南思达医药公司主营临床新药推广,团队覆盖湖南省14个地区,团队结构:地区经理10人,专业学术经理2人,商务经理2人;现有代理推广品种包含国采,省际联盟集采,基药,医保等类型,主营产品线:儿科,骨科,妇科,内科等;具备湖南药品招标准入能力。
【需要资源】上游厂家,国代,批文持有人,原料商等,品种需要在湖南落地推广的。
超级会员14
【会员编号】w0174
【所在地区】山西太原
【所在公司】山西龙行医药
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】省代临床,OTC。呼吸科,心血管等
【自身资源】地政,临床开发,OTC操作
【需要资源】代理优秀品种,山西市场跨渠道运营
超级会员15
【会员编号】w0202
【所在地区】广西
【所在公司】广西花红药业集团有限公司
【工作职务】业务部总经理
【相关产品】花红胶囊,花红颗粒,消肿止痛酊,解毒生肌膏,葛根芩连丸
【自身资源】独家医保,基药,企业品牌优势,全国有成熟的商务体系及招商资源
【需要资源】寻求有资源的妇科,骨科,肛肠,慢创,儿科等合作优质客户
超级会员16
【会员编号】w0166
【所在地区】杭州
【所在公司】浙江和融达医疗技术有限公司
【工作职务】董事长
【相关产品】消化领域、心脑血管、骨科的药品和器械耗材
【自身资源】成立了MAH上市持有人与院内制剂转化平台,成熟的全国销售网络,目前每年立项研发的药品和器械2-3个
【需要资源】1、全国各省医疗器械和药品销售精英及MAH合伙人。2、一流研发机构和优秀生产企业战略合作。
超级会员17
【会员编号】w0048
【所在地区】杭州
【所在公司】浙江万晟药业有限公司
【工作职务】总监
【相关产品】蔓迪、芪明颗粒
【自身资源】市场准入、政策法规
【需要资源】市场准入(医保、招采)
超级会员18
【会员编号】w0216
【所在地区】江苏南京
【所在公司】武汉天安医药
【工作职务】市场总监
【相关产品】B证持有人公司,拥有泮托拉唑、奥美拉唑、倍他米松、阿托品等品种,奥美拉唑、阿托品为国采中选产品
【自身资源】定位B证公司合作平台,可一起合作开发立项
【需要资源】各省代理商资源,其中湖北、江苏拥有精细化招商团队,也可代理品种
超级会员19
【会员编号】w0221
【所在地区】浙江
【所在公司】浙江敬紫堂生物科技有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】酒制蜂胶
【自身资源】全国临床和三终端代理商资源
【需要资源】更多的终端资源
超级会员20
【会员编号】w0133
【所在地区】河北
【所在公司】河北东鼎医药科技有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】喷他佐辛注射液、盐酸曲马多注射液、氯化钾颗粒、香丹
注射液等
【自身资源】河北省内完善的等级医院客户资源,包括镇痛类、心血管、抗生素等优质的销售网络。
【需要资源】镇痛类产品,集采产品,高端学术产品。
超级会员21
【会员编号】w0231
【所在地区】河南郑州
【所在公司】河南诚济医药有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】临床基药产品销售推广业务
【自身资源】具有完善的河南省临床基药销售渠道
【需要资源】在河南有新特药、基药产品需要推广销售的上游企业可接洽
超级会员22
【会员编号】w0110
【所在地区】河南
【所在公司】医药园区
【工作职务】顾问
【相关产品】三方业务;共享仓设立GSP公司
【自身资源】政策红利(共享仓、按月返税)
【需要资源】客户资源
超级会员23
【会员编号】w0179
【所在地区】福州
【所在公司】福建润辉商务管理有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】环丙沙星缓释片(悉复欢)500mg*6片/12片
【自身资源】全国总代产品资源
【需要资源】各省份/各区域代理商
超级会员24
【会员编号】W0235
【所在地区】河北
【所在公司】海南凯瑞医药
【工作职务】营销总监
【相关产品】首儿药业全系儿科产品
【自身资源】河北、山东药械资源
【需要资源】各省医药口服产品代理商,医院、诊所、零售、院外等渠道合作伙伴
扫码加高端会员
获取更多医药资源信息
高管变更
2024-10-06
·药闻康策
☝ 点击上方 一键预约 ☝
最新最热的医药健康新闻政策
2024
1006
药品高端会员区
HOT
高端会员1
【会员编号】y1172
【所在地区】北京,河北,山西
【所在公司】黑龙江久久药业有限责任公司
【工作职务】河北山西招商经理
【相关产品】
①【香砂养胃颗粒】基药,独家无蔗糖,国家专利保护剩余19年,医保甲,OTC乙。
②【刺五加颗粒】独家剂型无蔗糖,医保乙,OTC甲。
③【小儿清热止咳口服液】妇儿急抢目录,医保乙,OTC甲。
④【健儿消食口服液】基药,医保乙,OTC甲。
【自身资源】基独家,基药
【需要资源】河北,山西三终端,或临床代理
高端会员2
【会员编号】y1199
【所在地区】吉林省
【所在公司】长春海悦药业有限公司
【工作职务】省区经理
【相关产品】海悦美奥,悦思立普,伏立康唑,丙戊酸钠注射用浓溶液,他达拉非,注射用阿奇霉素(儿童),曲克芦丁,盐酸氨溴索,盐酸美金刚等
【自身资源】吉林省内分泌专家以及医院资源,商业公司合作资源(大商业以及地方商业);吉林省慢病产品市场布局及推广策略(策略层面)
【需要资源】吉林省及东北三省的准入资源,消化内科准入以及一线客户资源(多方式合作);阿奇霉素注射液市场分析报告(成人&儿童)、奥美拉唑市场分析报告
高端会员3
【会员编号】y1211
【所在地区】陕西
【所在公司】北京轩竹生物科技有限公司
【工作职务】省区经理
【相关产品】安奈拉唑钠
【自身资源】政府事务(医保局) 核心医院ICU临床
【需要资源】医院准入 药剂关系 代理商
高端会员4
【会员编号】y1198
【所在地区】川渝藏
【所在公司】江西青峰药业有限公司
【工作职务】省区经理
【相关产品】艾司奥美拉唑镁肠溶片、枸橼酸托法替布片、阿哌沙班片、富马酸丙酚替诺福韦片、恩替卡韦分散片/胶囊、盐酸乌拉地尔注射液、阿普米司特片、雷贝拉唑钠肠溶片、枳实总黄酮片。
【自身资源】政府事务,四川省消化专家以及医院资源,商业公司合作资源
【需要资源】一线客户资源和代理商资源
高端会员5
【会员编号】y1087
【所在地区】湖南
【所在公司】清华德仁西安幸福制药有限公司
【工作职务】大区经理
【相关产品】生血宝合剂、五灵胶囊、热炎宁合剂、童康颗粒
【自身资源】厂家产品资源
【需要资源】临床类型代理商:湖南省级代理商;湖南省地区代理商。
高端会员6
【会员编号】y0134
【所在地区】北京
【所在公司】北京杏林知松科技有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】环磷腺苷葡胺、益心胶囊、盐酸曲马多分散片
【自身资源】北京临床渠道多年、全国总代产品
【需要资源】各省总代资源、厂家资源
高端会员7
【会员编号】y1150
【所在地区】贵州
【所在公司】贵州佳德同汇健康咨询服务有限公司
【工作职务】业务负责人
【相关产品】安奈拉唑钠肠溶片、头孢呋辛钠氯化钠注射液、甘草酸单铵半胱氨酸氯化钠注射液等三十几个产品
【自身资源】贵州省代。贵州部分医院资源,产品资源。
【需要资源】有医院资源的客户,需具备开发能力。可提供品种和资金。
高端会员8
【会员编号】y0855
【所在地区】北京
【所在公司】北京伟林恒昌医药科技有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】自己持有:阿托伐他汀钙片,奥洛他定片
【自身资源】招商和对外贴牌生产
【需要资源】需要各省OTC销售团队
高端会员9
【会员编号】y1002
【所在地区】北京
【所在公司】国药控股北京有限公司
【工作职务】采购中心市场部经理
【相关产品】药品、器械等
【自身资源】北京招采信息
【需要资源】全国招采信息
高端会员10
【会员编号】y1142
【所在地区】江苏南京
【所在公司】凡森特医药
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】抗生素/化药/器械/中成药
【自身资源】渠道、产品、学术
【需要资源】客户、渠道
高端会员11
【会员编号】y1193
【所在地区】北京
【所在公司】北京康辰生物
【工作职务】法务合规经理
【相关产品】原研药品-骨松骨痛相关
【自身资源】药械合规及法律相关
【需要资源】关于医药行业的合规及法律相关的信息
高端会员12
【会员编号】y0317
【所在地区】湖南长沙
【所在公司】湖南广药恒生医药有限公司
【工作职务】采购总监
【相关产品】一类麻精产品
【自身资源】广药集团国企、有一类麻精配送资质、全省医疗机构覆盖配送、新品开发进院能力较强、招商产品可协助推广。
【需要资源】医院自营产品、零售分销业务全省配送。
高端会员13
【会员编号】y1128
【所在地区】云南省昭通市
【所在公司】云南蓝蝶医疗器械有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】医疗产品
【自身资源】昭通市及昭通周边地区的客户资源
【需要资源】优质的医疗产品,及其他地州的客户资源
高端会员14
【会员编号】y1226
【所在地区】四川成都
【所在公司】四川启源药业有限公司
【工作职务】总监
【相关产品】医保甲类基药
【自身资源】厂家临床基药医保产品
【需要资源】江西省区临床团队及省第三终端资源
高端会员15
【会员编号】y1187
【所在地区】南京
【所在公司】悦康药业
【工作职务】招商经理
【相关产品】活心丸
【自身资源】基药,甲类,安全性高
【需要资源】江苏地区招商
高端会员16
【会员编号】y1116
【所在地区】福建(主战区)江西、浙江、江苏
【所在公司】康美药业股份有限公司
【工作职务】区域经理
【相关产品】厂家直销,包含中药饮片、燕窝虫草等贵系礼品
【自身资源】1.国家膏方丸剂代煎等试点单位以及集采中标单位之一;2.可自产600多个品种上万个品规;3.可根据医院要求定制高标及小包装饮片;4.药剂科资源
【需要资源】1、福建、江西、浙江、江苏区域的代理商;2、各大医院及中医馆高层资源
高端会员17
【会员编号】y1140
【所在地区】北京
【所在公司】吉林天衡药业有限公司
【工作职务】市场运营部部长
【相关产品】铝碳酸镁咀嚼片、瑞舒伐他汀钙片、秋水仙碱片
【自身资源】可合作CRO、CMO、CDMO
【需要资源】销售代理商;寻找生产场地:片剂,适应症为痛风,特点是该原料为细胞毒药物,寻求细胞毒专线或可与细胞毒药物共线的生产场地。
高端会员18
【会员编号】y0584
【所在地区】天津
【所在公司】天津市医药集团泰宁医药
【工作职务】市场总监
【相关产品】狗皮膏、护肝胶囊、更年安胶囊、连翘败毒片、葡萄糖酸钙片等基药品种,全国多个省和直辖市已中标
【自身资源】熟悉国各省招投标政府事务,有成熟的全国销售网络
【需要资源】急需各省和直辖市的临床团队
高端会员19
【会员编号】y0907
【所在地区】北京、天津
【所在公司】海诚医药集团有限公司
【工作职务】省区经理
【相关产品】肌苷注射液(静注)、龙血竭胶囊(肠溶)、强力枇杷露(炼蜜)、磷酸川芎嗪注射液(供静脉注射用)、注射用伏立康唑、甘油灌肠剂、注射用哌拉西林钠、注射用头孢唑肟钠、注射用头孢哌酮钠舒巴坦钠、注射用氨苄西林钠舒巴坦钠、曲克芦丁注射液、核黄素磷酸钠注射液、注射用尼麦角林等产品
【自身资源】全国总代理产品资源
【需要资源】寻临床代理商、省总、地总团队合作
高端会员20
【会员编号】y1219
【所在地区】内蒙古
【所在公司】源浩医疗
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】处方药
【自身资源】整个乌兰察布市二级医院、卫生院、诊所资源
【需要资源】独家基药、集采品种、OTC控销产品厂家资源
高端会员21
【会员编号】y0947
【所在地区】江西南昌
【所在公司】江西金耐康医药科技有限公司
【工作职务】经理
【相关产品】神外、妇产、肿瘤领域产品
【自身资源】福建和江西省代和医院客户资源,江西神经外科及妇产科专家资源
【需要资源】厂家岗位或产品
高端会员22
【会员编号】y1197
【所在地区】辽宁
【所在公司】辽宁好护士集团医药有限公司
【工作职务】省区经理
【相关产品】肾炎温阳片、肾炎解热片
【自身资源】独家,挂网,空间好
【需要资源】操作肾病产品的医院资源团队
高端会员23
【会员编号】y1096
【所在地区】河南
【所在公司】浙江仙琚制药
【工作职务】招商大区
【相关产品】屈螺酮炔雌醇片(||)
【自身资源】河南、河北、江西、安徽、北京、天津等地重点医院客户资源
【需要资源】河南、河北、江西、安徽、北京、天津等地妇科团队资源
高端会员24
【会员编号】y1264
【所在地区】枣庄市
【所在公司】某医药公司
【工作职务】经理
【相关产品】肿瘤药
【自身资源】等级医院客户
【需要资源】最新化药产品资源
高端会员25
【会员编号】y0321
【所在地区】厦门、上海
【所在公司】承葛医药集团
【工作职务】项目经理
【相关产品】微生态移植及相关产业
【自身资源】微生态检测、移植、微生态口服产品、微生态研发
【需要资源】各类医药资源
高端会员26
【会员编号】y1221
【所在地区】广东
【所在公司】陕西盘龙药业集团
【工作职务】省区经理
【相关产品】1、盘龙七片(骨科)全国独家专利产品、医保甲类无后缀。2、骨松宝片(预防更年期骨质疏松症)。3、克比热提片(独家口服,皮肤科)4、复方醋酸绵酚片(妇科)
【自身资源】独家、商业公司合作资源
【需要资源】医院准入、广东临床类型代理商
高端会员27
【会员编号】y1278
【所在地区】陕西
【所在公司】西安典茂轩医药科技
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】雾化全系列,抗生素、心脑血管领域产品。
【自身资源】陕西省招商全渠道和连锁OTC自营团队及政务商业资源
【需要资源】集采药,国谈化药,进口化药
高端会员28
【会员编号】y1114
【所在地区】四川/西藏
【所在公司】浙江孚诺/浙江惠迪森
【工作职务】市场/销售主管
【相关产品】复方多黏菌素B软膏/注射用拉氧头孢钠
【自身资源】1.四川省皮肤科、烧伤科、肛肠科深耕细作10年建立上层专家资源,临床一线专人覆盖,自建团队,高效专业;2.四川、西藏都有自己的分销渠道,西藏有自己的商业配送公司,承接全国产品。
【需要资源】1.寻找相关科室品种,签总代、有潜力的专科品种;2.寻找省内手术科室合作伙伴,推广外用抗生素品种在四川的销售。
高端会员29
【会员编号】y1294
【所在地区】浙江
【所在公司】浙江天啬生物医药有限公司 、杭州端本医院科技有限公司
【工作职务】招商经理
【相关产品】主营产品线:骨科,麻醉科,消化科;自有持证:氟比洛芬凝胶贴膏
【自身资源】1、浙江省临床品种推广网络;2、自有批文
【需要资源】1、全国省级代理合作伙伴;2、浙江省代理推广甲方产品
高端会员30
【会员编号】y1312
【所在地区】重庆
【所在公司】重庆旭达药业
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】补肾健脾口服液、食积口服液
【自身资源】产品资源、团队资源
【需要资源】产品品牌输出
高端会员31
【会员编号】y0857
【所在地区】河北
【所在公司】京津医学
【工作职务】产品经理
【相关产品】养心定悸颗粒
【自身资源】医学实验与研究,团队目前主要承接上市后医学临床再评价项目;临床推广,团队覆盖全国等级医疗及基层医疗招商,京津冀地区临床推广自营
【需要资源】全国总代产品,最好是医保或者独家
高端会员32
【会员编号】y0990
【所在地区】新疆
【所在公司】新疆迈达医药有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】OTC,临床基药产品
【自身资源】具有完善的新疆省临床基药销售渠道和OTC销售渠道
【需要资源】新特药,基药产品,集采产品,皮肤科基药产品需要在新疆推广的上游企业可接洽,以及OTC优秀品种,新疆市场可跨渠道运营
高端会员33
【会员编号】y1176
【所在地区】广西
【所在公司】洺康医疗
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】儿科、妇科、产科、乳腺、骨科、消化、内分泌、放射科 中枢神经线,心脑血管线药品为主
【自身资源】17个集采产品,8个非集采产品,拥有专业的一线自营推广队伍,全区招商队伍
【需要资源】儿科领域,神经领域,心脑血管领域等国家集采产品及国谈,基药的新药
高端会员34
【会员编号】y1395
【所在地区】长春
【所在公司】长春澜江医药科技有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】拉考沙胺口服溶液(9批集采)、托莫西汀口服溶液(9批集采)、氯雷他定糖浆(已过评)
【自身资源】MAH+CRO公司
【需要资源】产品代理销售
高端会员35
【会员编号】y1401
【所在地区】四川
【所在公司】四川九兴仁创医药科技有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】盐酸氨基葡萄糖胶囊、阿法骨化醇片、金天格胶囊、多索茶碱注射液、特立帕肽注射液等
【自身资源】在四川主要做集采业务,目前拥有一支40人的专职直营推广团队,以及一支10人招商团队,2023年产值3.5亿。
【需要资源】承接集采中选药企在四川的推广资源,希望链接更多的厂家资源
器械高端会员区
高端会员1
【会员编号】X0031
【所在地区】贵州贵阳
【所在公司】贵州众鑫源科技有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】口腔辅料
【自身资源】省级公立医院客户资源
【需要资源】耗材,试剂,医美,口腔
高端会员2
【会员编号】X0028
【所在地区】北京
【所在公司】北博(北京)医疗器械有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】电热针治疗仪+耗材内热式电热针灸针
【自身资源】有源医疗器械的研发、注册、代工
【需要资源】诚招各省耗材代理商,有医保资源,本产品在《全国医疗服务项目技术规范(2023年版)》,需要增加或修订各省医保目录
高端会员3
【会员编号】X0035
【所在地区】云南省昭通市
【所在公司】云南蓝蝶医疗器械有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】医疗器械相关产品
【自身资源】云南省昭通市及昭通周边地区的客情资源
【需要资源】优质的产品
高端会员4
【会员编号】X0045
【所在地区】福建
【所在公司】福州市东瑞医疗科技有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】狂免、破免、纤原,人用狂犬疫苗等
【自身资源】福建省代,临床医学背景,部分医院、卫健及疾控部门资源
【需要资源】适合急诊外科相关药品,耗材产品资源
超级高端会员区
超级会员1
【会员编号】w0201
【所在地区】湖南
【所在公司】湖南健朗药业有限责任公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】自身持有奥拉西坦胶囊、奥拉西坦注射液、泮托拉唑肠溶胶囊、羟甲烟胺片等产品。
【自身资源】招商和对外贴牌生产
【需要资源】需要购买若干化学药品注册批文,已出批文或者即将申报的均可。
超级会员2
【会员编号】w0045
【所在地区】山东东营
【所在公司】山东凤凰制药股份有限公司
【工作职务】普药事业部总监
【相关产品】盐酸二甲双胍缓释片、苯磺酸氨氯地平片、辛伐他汀片、维格列汀片、护肝片、降脂宁片、复方丹参片、胃灵颗粒、半夏露颗粒、益母草颗粒、板蓝根颗粒、微达康颗粒、感冒清热颗粒、小儿咽扁颗粒、小儿咳喘灵颗粒、灵芝胶囊、活力胶囊、穿心莲胶囊、黄柏胶囊等
【自身资源】厂家产品资源
【需要资源】市县级临床业务团队
超级会员3
【会员编号】w0150
【所在地区】山东
【所在公司】山东天元盈康医疗科技有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】人血白蛋白,破免,狂免,静丙,小儿复方氨基酸注射液,盐酸纳美芬,环磷腺苷 等产品。
【自身资源】政府事务 在山东做省代17年 有直营团队 同时通过招商团队覆盖全省医院。
【需要资源】上游厂家,国代,批文持有人,原料药
超级会员4
【会员编号】w0033
【所在地区】四川成都
【所在公司】四川省百草生物药业有限公司
【工作职务】市场总监
【相关产品】苯磺酸氨氯地平片、盐酸舍曲林胶囊、泛昔洛韦片
【自身资源】通过一致性评价产品。医保甲类。基药。大部分省份已挂网。渠道终端市场管理好。
【需要资源】临床、终端渠道代理商
超级会员5
【会员编号】w0186
【所在地区】山东
【所在公司】深圳万和制药有限公司
【工作职务】销售部经理
【相关产品】商品名:和安,和爽,和流,爱伦多等
【自身资源】消化,肝病以及普外等领域专家资源
【需要资源】政府事务相关
超级会员6
【会员编号】w0163
【所在地区】广西
【所在公司】广西炬邦乾承投资有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】集采中选:哌他,左氨氯地平,左卡尼汀,噻肟,呋塞米,他啶,曲松,丙戊酸钠,头孢地尼 呼吸:沙丁,氟替卡松,异丙,左沙,乙酰半胱氨酸,茶碱,孟鲁司特。肾内:左卡,达肝,司维拉姆,促红,百令片。围手术期:羟考酮,纳布啡。布托啡诺。抗感染:磷霉素,哌舒,唑肟,阿奇。慢病:达格列净,格列齐特,氟伐他汀,左氨氯地平,门冬氨氯地平。心脑血管:辅酶Q10,倍他司汀,曲克芦丁,吡拉西坦,己酮可可碱。
【自身资源】地方政府事务,专业推广能力,经销商储备,行业口碑认可。
【需要资源】甲方产品
超级会员7
【会员编号】w0160
【所在地区】内蒙古
【所在公司】商贸公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】集采药品、集采器械、化妆品、特医食品等。
【自身资源】35人销售团队
【需要资源】集采药品、集采器械、化妆品、特医食品等。
超级会员8
【会员编号】w0104
【所在地区】南京
【所在公司】翎耀生物科技(上海)有限公司
【工作职务】全国商务分销总监
【相关产品】利培酮口服溶液、氨己烯酸口服溶液用散、阿托伐他汀钙片、利伐沙班片
【自身资源】过评产品:医保、国谈,慢病系列
【需要资源】全国临床、二三终端相关领域省级经销商、终端代理商
超级会员9
【会员编号】w0127
【所在地区】山东
【所在公司】山东誉众医药
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】骨科/肿瘤/抗生素/心血管/重症/透析/呼吸产品
【自身资源】专业化的省级医药推广服务商。自营1条线+招商3条线+市场部1条线+集采产品专项。学术推广能力、政务关系、商业资源优秀。
【需要资源】优质的相关产品升级代理。
超级会员10
【会员编号】w0009
【所在地区】浙江
【所在公司】浙江明晖医药有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】全国总代:阿昔洛韦颗粒、别嘌醇片;自有持证:他达拉非片
【自身资源】1.浙江省临床品种推广网络;2、全国总代理产品;3、自有批文;4、零售电商公司;5、C端电商供应链
【需要资源】1、需要在浙江代理推广的甲方产品;2、全国省级代理合作伙伴
超级会员11
【会员编号】w0172
【所在地区】江苏南京
【所在公司】西安良医网络科技集团有限公司
【工作职务】营销中心负责人
【相关产品】1.米墨 2.超医助手
【自身资源】有一个医药互联网服务交易溯源平台“米墨”为行业发展提供新方案、新模式,为药械厂商提供深度学术推广及精准营销升级服务;以及医生资源平台“超医助手”目前大约有数百万的医疗行业从业者资源。拥有各类医疗互联网平台资源,企业资源,医药企业资源。
【需要资源】链接医药企业
超级会员12
【会员编号】w0173
【所在地区】上海市静安区
【所在公司】上海鑫意医药科技有限公司
【工作职务】董事长
【相关产品】关节镇痛巴布膏、强力天麻杜仲胶囊等
【自身资源】招标、医疗终端等
【需要资源】需要上家优质产品,需要有管理能力的业务经理
超级会员13
【会员编号】w0029
【所在地区】湖南
【所在公司】湖南思达医药有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】主营产品线:儿科,骨科,妇科,内科等
【自身资源】湖南思达医药公司主营临床新药推广,团队覆盖湖南省14个地区,团队结构:地区经理10人,专业学术经理2人,商务经理2人;现有代理推广品种包含国采,省际联盟集采,基药,医保等类型,主营产品线:儿科,骨科,妇科,内科等;具备湖南药品招标准入能力。
【需要资源】上游厂家,国代,批文持有人,原料商等,品种需要在湖南落地推广的。
超级会员14
【会员编号】w0174
【所在地区】山西太原
【所在公司】山西龙行医药
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】省代临床,OTC。呼吸科,心血管等
【自身资源】地政,临床开发,OTC操作
【需要资源】代理优秀品种,山西市场跨渠道运营
超级会员15
【会员编号】w0202
【所在地区】广西
【所在公司】广西花红药业集团有限公司
【工作职务】业务部总经理
【相关产品】花红胶囊,花红颗粒,消肿止痛酊,解毒生肌膏,葛根芩连丸
【自身资源】独家医保,基药,企业品牌优势,全国有成熟的商务体系及招商资源
【需要资源】寻求有资源的妇科,骨科,肛肠,慢创,儿科等合作优质客户
超级会员16
【会员编号】w0166
【所在地区】杭州
【所在公司】浙江和融达医疗技术有限公司
【工作职务】董事长
【相关产品】消化领域、心脑血管、骨科的药品和器械耗材
【自身资源】成立了MAH上市持有人与院内制剂转化平台,成熟的全国销售网络,目前每年立项研发的药品和器械2-3个
【需要资源】1、全国各省医疗器械和药品销售精英及MAH合伙人。2、一流研发机构和优秀生产企业战略合作。
超级会员17
【会员编号】w0048
【所在地区】杭州
【所在公司】浙江万晟药业有限公司
【工作职务】总监
【相关产品】蔓迪、芪明颗粒
【自身资源】市场准入、政策法规
【需要资源】市场准入(医保、招采)
超级会员18
【会员编号】w0216
【所在地区】江苏南京
【所在公司】武汉天安医药
【工作职务】市场总监
【相关产品】B证持有人公司,拥有泮托拉唑、奥美拉唑、倍他米松、阿托品等品种,奥美拉唑、阿托品为国采中选产品
【自身资源】定位B证公司合作平台,可一起合作开发立项
【需要资源】各省代理商资源,其中湖北、江苏拥有精细化招商团队,也可代理品种
超级会员19
【会员编号】w0221
【所在地区】浙江
【所在公司】浙江敬紫堂生物科技有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】酒制蜂胶
【自身资源】全国临床和三终端代理商资源
【需要资源】更多的终端资源
超级会员20
【会员编号】w0133
【所在地区】河北
【所在公司】河北东鼎医药科技有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】喷他佐辛注射液、盐酸曲马多注射液、氯化钾颗粒、香丹
注射液等
【自身资源】河北省内完善的等级医院客户资源,包括镇痛类、心血管、抗生素等优质的销售网络。
【需要资源】镇痛类产品,集采产品,高端学术产品。
超级会员21
【会员编号】w0231
【所在地区】河南郑州
【所在公司】河南诚济医药有限公司
【工作职务】销售总监
【相关产品】临床基药产品销售推广业务
【自身资源】具有完善的河南省临床基药销售渠道
【需要资源】在河南有新特药、基药产品需要推广销售的上游企业可接洽
超级会员22
【会员编号】w0110
【所在地区】河南
【所在公司】医药园区
【工作职务】顾问
【相关产品】三方业务;共享仓设立GSP公司
【自身资源】政策红利(共享仓、按月返税)
【需要资源】客户资源
超级会员23
【会员编号】w0179
【所在地区】福州
【所在公司】福建润辉商务管理有限公司
【工作职务】总经理
【相关产品】环丙沙星缓释片(悉复欢)500mg*6片/12片
【自身资源】全国总代产品资源
【需要资源】各省份/各区域代理商
超级会员24
【会员编号】W0235
【所在地区】河北
【所在公司】海南凯瑞医药
【工作职务】营销总监
【相关产品】首儿药业全系儿科产品
【自身资源】河北、山东药械资源
【需要资源】各省医药口服产品代理商,医院、诊所、零售、院外等渠道合作伙伴
扫码加高端会员
获取更多医药资源信息
高管变更
2024-09-11
·赛柏蓝
药价治理+反垄断
8月9日,市场监管总局发布《关于药品领域的反垄断指南(征求意见稿)》。
反垄断的核心是价格,该指南如果按现行内容落地实施,90%以上的医药企业都将受到影响,以往的价格政策、渠道管理、经销协议、代理协议、绩效方案等可能会作废,需要重新规划、设计。药企无法掌握渠道、零售价格会彻底失控。如何做好以价格为核心的业务流程推倒重置?
迄今半年多过去了,药品价格治理雷声大、雨点大、动作快,波及院内院外、线上线下,引发医保品种企业的高度关注。
目前,“四同药品”价格治理已近完成,“三同药品”价格治理风暴将至,其中注射剂“三同药品”价格治理已经打响了第一枪。
医保事关诸多药企的发展命运,价格管理是可持续发展的关键。只有看懂药品价格治理的政策逻辑,才能制定科学的价格战略;只有用好价格政策,才能避免“掉坑踩雷”、避免涉嫌垄断被处罚!
为更好梳理、了解近期药品价格治理政策,帮助药企科学、规范调整价格,适应新时期的监管要求、反垄断要求,构建院内院外、线上线下全链条、全领域的价格策略,主动掌握药品价格管理“生命线”,减少潜在的重大价格风险,定于9月21-22日在杭州举行药价治理+反垄断下,医药企业价格体系调整管控策略研讨会。
第一部分:从“四同”到“三同”的政策梳理及影响分析
1.药品价格管理40年:4种加成管制、5次变革史
2.现阶段药品价格多样化:3种形成机制、两种管控模式、一套比价原则
3.现阶段我国药品价格管理的4大基本思路
4.医保药品价格管理6个方式方法、药品价格常态化监管的5个机制
5.现阶段药品价格监测的8个主要方向
6.四同药品价格治理政策要点:5项措施、5种结果,各省实施情况
7.“三同药品”价格治理六统一具体要求
8.医保“上网店、查药价、比数据”文件解读与四项思考
9.“四同”“三同”药品价格治理的必然趋势
10.关注河北、四川省挂网采购新政策中的新说法
11.医药“统一市场”全国价格“一盘棋”的5个新局面
12.我国药品价格治理的8个发展趋势
13.医药企业对价格治理的现阶段6大应对建议
第二部分:药品领域反垄断指南最新政策文件解读及对企业影响
1.我国医药领域反垄断执法发展历程和现状
2.医药领域8大反垄断案例解析
3.药品领域反垄断指南的8个亮点突破、六大核心内容
4.药品领域反垄断指南的中认定7种垄断行为
5.垄断协议具体十种行为表述及豁免原则、宽大制度
6.医药横向垄断与纵向垄断的区别及处罚结果
7.市场支配地位的认定指标及依据:5个维度、10种情形
8.公平竞争审查重点及滥用行政权力排除、限制竞争特点
9.药品领域垄断行为的法律责任适用、鼓励创新的规定
10.药品领域开启全链条全领域反垄断监管新时代
11.药品领域垄断案件常见的14种违法行为、处罚结果及合规建议
12.药品反垄断执行现状与《指南》要求差距分析、其他反垄断相关指南的综合学习
13.《指南》对医药企业现阶段“市场管理”的最直接挑战
14.从反垄断执法“宽容”角度看“三个指定”的要求
15.医药企业应对现阶段行业反垄断治理的10个有效动作
第三部分:“三同”“二同”药价治理深度解析及企业建议
1.国家药品价格治理6大政策依据
2.药品价格全面治理的底层逻辑
3.国家医保局“四同”药品价格治理及成果
4.“三同”药品价格治理信号及预期分析
①国家对同一药品不同规格、包装差比价的试点
②同一药品不同规格、包装差比价的现况与分歧
③“三同”药品价格治理预期分析
5.新“三同”价格治理( 挂网/线下零售、网价)应对策略
①“网络比价”专项行动要点梳理
②医保药店药价风险品种管控
③新“三同”价格治理药企应对策略
6.部分省份“二同(同通用名、同剂型)”药品价格管理初探
①四川省平台挂网药品价格监测管理分析
②江苏、新疆、上海等其他省份价格监测要点
③“二同药品”比价预警企业应对建议
7.部分省份“二同(同通用名、同剂型)”限价挂网规则
①河北、山西“二同药品”比价限价挂网规则分析
②湖南、广西、黑龙江等“二同药品”限价挂网规则
③“二同药品”比价限价挂网规则企业应对建议
第四部分:药品价格成本调查企业应对建议
1.部分药品、耗材价格构成情况核查的意图
2.药品、耗材成本核查的数据要点
3.核查药品成本价格问题整改操作指引要点梳理
4.药品价格、成本构成的要素分析
5.药企对药品成本、价格管理的系统设计建议
6.药品异常价格治理“举一反三”工作机制的企业应对
7.国家药品价格成本调查企业分类处置措施简介
第五部分:全面价格治理下药品挂网新策略
1.全面价格治理下各省挂网政策多变的应对策略
2.普通非过评药品首挂价格困难应对
3.新形势下挂网准入团队能力提升
①产品挂网价格设定及挂网省份规划
②首挂价格路径设计原则
③首挂价格产生后全国挂网落地路线图
第六部分:网络药品价格维护
1.电商维价的渠道分析
2.产品上架前的品规、渠道、平台管理
3.平台挂网+价格维护+点对点维护
4.商批、B2B、第三终端出货前的货+批号管理
5.总部监管+省区执行+个人执行+销售考核实施
6.线上线下同步的关键和事后补救
7.三同价格治理下药企“四做四不做”
8.工业挂网品种应对“淘天+某多自动跟价的六大策略”
9.如何规避Tb平台低价挂网
10.Tb平台被恶意挂网后如何处理高价收货
11.顽固性C店低价买,差,退的8步实操法
12.药品窜货管理实用教程
耿老师, 清华大学老科协医疗健康研究中心执行副主任。
程老师,知名药企集团电商中心负责人,药品网上维价专家。医药电商、新零售行业逾15年工作经验,曾任职于康美药业、葫芦娃药业、万泽医药(万泽连锁)的电商板块,操盘中药滋补板块,打造三七粉、菊皇茶、新鲜人参等核心单品,是《中国药店》《21世纪药店报》、南方所特约撰稿人,中国医药物资协会研究院医药电商研究所专家组成员、广东、湖北省医药电商协会会员。
Mr. D,国内大型制药企业集团市场准入负责人(现任)。10多年知名药企、上市耗材企业负责市场准入工作。多个产品国谈准入医保目录成功经验,善于分析集中采购、物价、医保、卫生等市场准入相关政策文件,对各类市场准入机会具有敏锐的洞察力,全局观强,能为各类市场准入机会提供战略及战术方案。
主办:赛柏蓝
时间:9月21-22日
地点:杭州
本会议适合医药企业董事长、总经理等战略管理人员;市场准入总监、政府事务总监、招标总监、营销总监等中高管;省级政府事务、市场准入负责人等企业管理层参加。
报名通道
出席大会的代表学习费、资料费、午餐费、税费4980元/人,交通、住宿自理。主办方指定以下账号为收款账户:
名称:北京蓝容科技有限公司
开户行:招商银行股份有限公司北京西二旗支行
账号:110948886810901
(汇款请注:药价+参会单位)
王显龙
杨晓亮
赵万鹏
于 宁
戴艳雯
王雅蕾
带量采购医药出海核酸药物
100 项与 康美药业股份有限公司 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
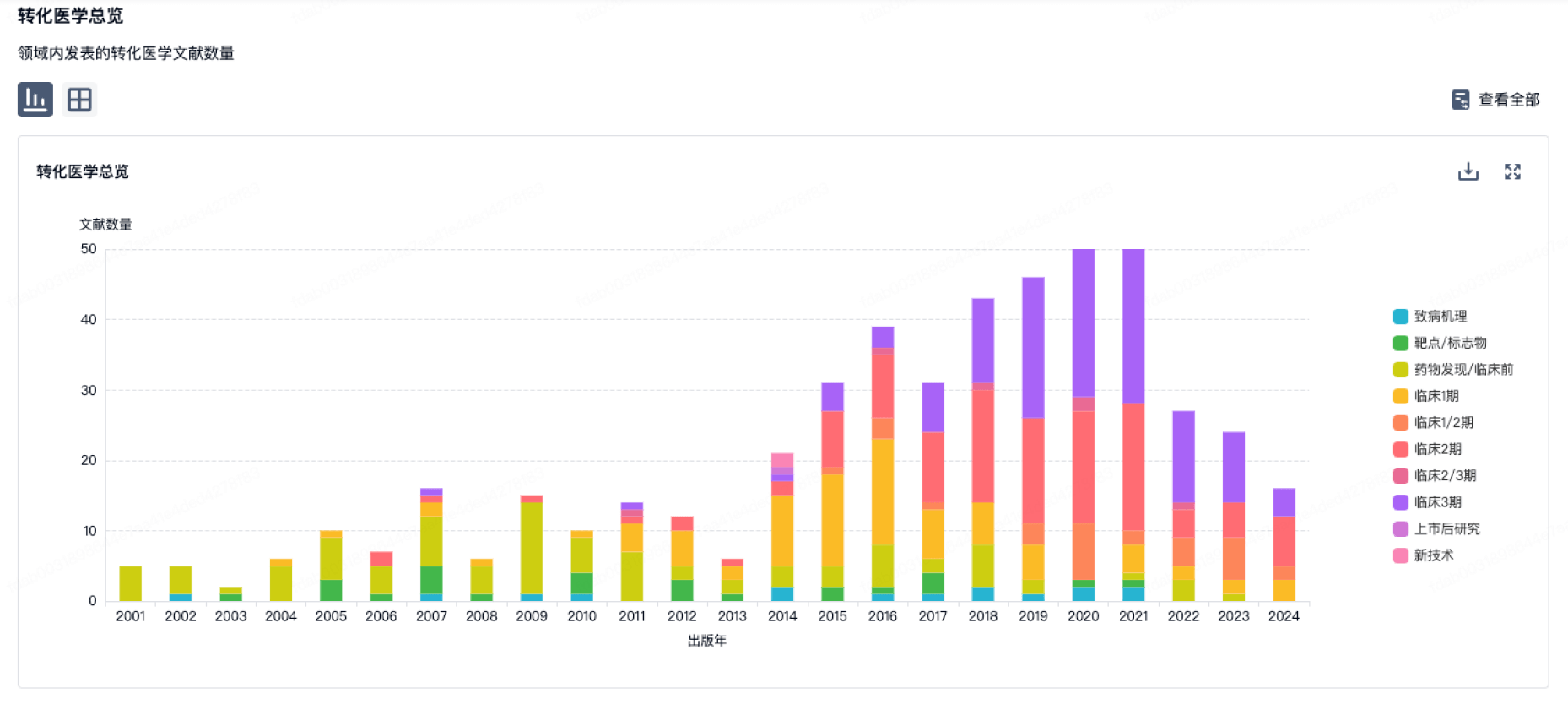
100 项与 康美药业股份有限公司 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
组织架构
使用我们的机构树数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

管线布局
2024年11月18日管线快照
管线布局中药物为当前组织机构及其子机构作为药物机构进行统计,早期临床1期并入临床1期,临床1/2期并入临床2期,临床2/3期并入临床3期
临床前
9
7
临床申请
批准上市
1
1
其他
登录后查看更多信息
当前项目
| 药物(靶点) | 适应症 | 全球最高研发状态 |
|---|---|---|
甲磺酸多沙唑嗪 ( ADRA1 ) | 高血压 更多 | 批准上市 |
尼伐地平 ( L-type calcium channel ) | 心血管疾病 更多 | 临床阶段不明 |
KM2013001 | 泌尿生殖系统疾病 更多 | 临床申请 |
KM20140707 | 消化系统疾病 更多 | 临床申请 |
KM20140706 | 消化系统疾病 更多 | 临床申请 |
登录后查看更多信息
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
营收
使用 Synapse 探索超过 36 万个组织的财务状况。
登录
或
科研基金(NIH)
访问超过 200 万项资助和基金信息,以提升您的研究之旅。
登录
或

投资
深入了解从初创企业到成熟企业的最新公司投资动态。
登录
或

融资
发掘融资趋势以验证和推进您的投资机会。
登录
或

标准版
¥16800
元/账号/年
新药情报库 | 省钱又好用!
立即使用
来和芽仔聊天吧
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用

