预约演示
更新于:2025-07-24
Nitroxoline
硝羟喹啉
更新于:2025-07-24
概要
基本信息
非在研机构 |
最高研发阶段临床3期 |
首次获批日期- |
最高研发阶段(中国)临床3期 |
特殊审评- |
登录后查看时间轴
结构/序列
分子式C9H6N2O3 |
InChIKeyRJIWZDNTCBHXAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
CAS号4008-48-4 |
关联
16
项与 硝羟喹啉 相关的临床试验DRKS00034182
Influence of nitroxoline and other first-line therapeutics in the treatment of urinary tract infection on extracellular inflammasome particles and systemic inflammation
开始日期2025-01-01 |
申办/合作机构 |
NCT06435039
A Phase 1, Open-Label, Randomized, Crossover Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of Single Ascending Doses of APL-1501 ER Capsules Compared to APL-1202 IR Tablets in Healthy Volunteers
The primary objective of the study is to assess safety and tolerability following administration of single doses of APL-1202 (immediate release) IR tablets and APL-1501 extended release (ER) capsules in healthy participants.
开始日期2024-06-21 |
申办/合作机构  Syneos Health, Inc. Syneos Health, Inc. [+1] |
CTIS2022-501726-38-00
Treatment of KeratolytTreatment of Keratolytic Winter Erythema with systemic nitroxoline, a phase 2a randomized placebo controlled crossover study of male and female adults from three Norwegian familiesic Winter Erythema with systemic Nitroxoline, a phase 2a randomized placebo controlled cross-over study of male and female adults from three Norwegian families. - 1.0
开始日期2023-07-31 |
申办/合作机构- |
100 项与 硝羟喹啉 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 硝羟喹啉 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 硝羟喹啉 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
730
项与 硝羟喹啉 相关的文献(医药)2025-08-01·DRUG DISCOVERY TODAY
Rediscovering nitroxoline: a metal-chelating agent bridging infection and cancer
Review
作者: Papareddy, Praveen ; Wichelhaus, Thomas A ; Bachmann, Dennis ; Proschak, Ewgenij ; Graham, Marlowe ; Herwald, Heiko ; Sander, Kerstin ; Mielke, Sophie R M
Nitroxoline, a legacy antimicrobial agent, is gaining attention for its potential repurposing in infectious diseases and oncology. Its broad-spectrum activity, including biofilm disruption and metal-chelating properties, supports diverse therapeutic applications. However, its systemic use is limited by rapid urinary excretion, short plasma half-life, and limited tissue distribution. In this review, we summarize recent advances in understanding the mechanisms of action, cross-kingdom activity, and anticancer effects of nitroxoline. Despite encouraging preclinical data, clinical translation is constrained by pharmacokinetic (PK) and regulatory challenges. As interest in repurposing established drugs grows, nitroxoline presents a compelling candidate for integration into modern therapeutic strategies across infectious and neoplastic disease domains.
2025-08-01·JOURNAL OF INORGANIC BIOCHEMISTRY
Broadening the chemical diversity of oxidovanadium(V) complexes for targeting neglected tropical diseases
Article
作者: Pérez-Díaz, Leticia ; Blacque, Olivier ; Machado, Ignacio ; Scalese, Gonzalo ; Gambino, Dinorah ; Sanabria, Yasmina ; Pereyra, Josefina ; Pérez, Nicolás
Chagas disease and Leishmaniasis, caused by Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania spp., respectively, are highly prevalent neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) that pose significant global health challenges. In our pursuit of effective vanadium-based therapeutics against these diseases, we previously developed several series of oxidovanadium(V) complexes featuring bidentate bioactive ligands and Schiff base tridentate ligands. The current study extends our previous research by incorporating in the same molecule, a tridentate bromo-substituted isonicotinyl hydrazone Schiff base ligand, BrIS, and a 8-hydroxyquinoline derivative (L), leading to the synthesis and comprehensive characterization of five new complexes, [VVO(BrIS-2H)(L-H)]. Most of new complexes exhibited activity in the micromolar range against the infective trypomastigote form of T. cruzi (EC50, 24h: 0.73-7.95 μM) and against L. infantum promastigotes (IC50, 5 days: 1.14-1.16 μM) and some of them showed good selectivity indexes towards the parasites (SI up to 52). Notably, the vanadium uptake by the parasites was higher for the new [VVO(BrIS-2H)(L-H)] compounds compared to [VVO(IN-2H)(L-H)] analogues previously developed, where IN is the structurally related 2-hydroxy-1-naphtaldehyde isonicotinoylhydrazone ligand, with accumulation in the soluble cell fraction. High-dose incubations resulted in trypanocidal effects and suggested the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Further analysis revealed that [VVO(BrIS-2H)(L-H)] complexes induced a higher percentage of apoptosis, whereas the [VVO(IN-2H)(L-H)] series was associated with autophagic cell death. These findings highlight the potential of the [VVO(BrIS-2H)(L-H)] series as promising anti-T. cruzi agents and underscore the need for further research to optimize their therapeutic efficacy and explore their mechanisms of action.
2025-07-16·JOURNAL OF MICROBIOLOGICAL METHODS
Biphasic bactericidal activity of nitroxoline against Acinetobacter baumannii assessed by Raman-DIP.
Article
作者: Wang, Minggui ; Zhang, Jianfeng ; Xu, Xiaogang ; Chen, Xin ; Yi, Xiaofei
The increasing antimicrobial resistance (AMR) of Acinetobacter baumannii presents a challenge to clinical management and underscores its role as a critical pathogen in refractory urinary tract infections (UTIs). Nitroxoline has gained renewed interest as a potential therapeutic option. Raman deuterium stable isotope probing (Raman-DIP), which allows for the analysis of bacterial metabolic activity, has shown promise as a tool for assessing antimicrobial efficacy. The aim of this study was to evaluate the bactericidal activity of nitroxoline against A. baumannii and the potential of Raman-DIP to assess this activity. Thirty-four A. baumannii isolates were collected from patients with UTI. Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs), minimum bactericidal concentrations (MBCs), optimal bactericidal concentrations (OBCs), and time-killing curves were determined. Raman-DIP evaluated nitroxoline's effects on bacterial metabolism and survival, using the CD ratio (CD to the sum of the C - H and C - D band intensities) as a metabolic activity metric. Nitroxoline demonstrated potent antimicrobial activity against A. baumannii, with MIC50/90 and MBC50/90 values of 2/2 and 2/4 mg/L, respectively. Notably, it showed biphasic bactericidal characteristics with an OBC50/90 value of 4/8 mg/L. Raman-DIP revealed a decrease in the CD ratio with an increase in nitroxoline concentration, indicating reduced metabolic activity. An inverse correlation was observed between bacterial survival and the CD ratio at concentrations above the OBC. These findings underscore the necessity to optimize dosing regimens for enhancing the efficacy of nitroxoline. Raman-DIP may serve as an effective tool for investigating the effect of nitroxoline on bacterial metabolism, thereby informing its clinical applications.
61
项与 硝羟喹啉 相关的新闻(医药)2025-07-04
·医脉通
今天的医疗圈发生了哪些与你有关的大事?更新、更全的医学动态3分钟一网打尽********今日关键词:医保诈骗案,食脑虫,慢性病来源 | 医脉通作者 | 晚报君新闻60秒➤上海警方公布多起医保诈骗案 @警民直通车上海 7月3日,上海市公安局召开新闻发布会,披露多起医保诈骗案。会议通报,2025年以来,上海警方持续推进打击欺诈骗保专项行动,截至目前共捣毁全市医保诈骗团伙7个,抓获犯罪嫌疑人130余名,涉案金额达1400余万元。此外,上海市各级医保部门通过线上稽核、现场检查等方式,累计检查定点医药机构1657家,通过审核扣减、追款、自查自纠等手段追回医保基金3.07亿元。其中,一个以定点医疗机构为主体的医保诈骗团伙,连续数年骗取国家医保基金超1200万元,被成功打击。上海虹口警方抓获主要犯罪嫌疑人34人,并抓获协助诈骗的上海市参保人员59人。 ➤男童打水仗后发烧感染食脑虫,治疗进展引关注 @人民日报健康客户端 近日,“男童打水仗后发烧感染食脑虫”引发广泛关注。7月3日,男童妈妈发文称,孩子如今意识很好,但是走路有点飘、没办法好好走路。复旦大学附属华山医院感染科副主任王新宇已来到复旦大学附属儿科医院进行会诊,专家建议使用国产的硝羟喹啉进行治疗,目前已与制药公司联系上,在走伦理用药流程。医药60秒➤正大天晴重组人凝血因子VIIa获批治疗血友病 @国家药品监督管理局 7月3日,国家药品监督管理局官网显示,正大天晴的注射用重组人凝血因子VIIa(TQG203)已获批上市,适应症为抑制物阳性先天性血友病A或B患者以及某些特定类型罕见出血性疾病患者群体出血的治疗和外科手术或有创操作出血的防治。 ➤恒瑞医药干眼病创新药国内获批上市 @国家药品监督管理局 7月3日,国家药品监督管理局官网显示,恒瑞医药引进的SHR8058滴眼液获批上市,用于治疗睑板腺功能障碍相关干眼病。临床研究显示,SHR8058滴眼液组可缓解干眼症状,包括疼痛、干眼症症状意识、干燥频率等。健康60秒➤世卫组织呼吁:大幅提高烟酒和含糖饮料价格 @新华社 世界卫生组织7月2日发起一项名为“三三五”的倡议,意为“到2035年落实三项健康税”,旨在通过征税“到2035年将烟草、酒和含糖饮料这三类不健康产品中任一类、两类或全部三类的实际价格提高至少50%”。以此,呼吁各国通过征税大幅提高烟酒和含糖饮料的价格,以增加公共收入,减少慢性病。具体措施将考虑各国不同国情。 世卫组织称,这三类产品的消费助长了非传染性疾病的流行,而心脏病、癌症和糖尿病等非传染性疾病导致的死亡人数占全球死亡人口的75%以上。仅烟草一类就每年导致700多万人死亡。最近一份报告显示,将这三类产品的价格一次性提高50%,预计可在今后50年内避免5000万例过早死亡病例。此外,这样做预计还可在今后10年内,在减少不健康产品消费的同时,在全球增加1万亿美元公共收入。 ➤热浪来袭!警惕“高温杀手”热射病 @新华社 高温、热浪,局地最高气温超过40℃……近来,我国多地医疗机构接诊的热射病病例不断增加。作为最严重的中暑类型,热射病的危害大、死亡率较高。专家介绍,炎热酷暑、高温高湿环境中,人体产热与散热调节功能失衡,“冷却系统”崩溃,核心温度迅速升高、超过40℃,大脑“宕机”,出现谵妄、惊厥、昏迷,以及多器官功能障碍。这是热射病的发病机制和症状。一旦发生疑似热射病症状,则需立即就医,在等待救护车时,可用冰袋敷于颈部、腋下等,帮助快速降温。责编|Atai封面图来源|医脉通重磅!两部门联合发文支持创新药,将给医生带来怎样的挑战?降薪潮下,医护正在迎来职业危机医脉通是专业的在线医生平台,“感知世界医学脉搏,助力中国临床决策”是平台的使命。医脉通旗下拥有「临床指南」「用药参考」「医学文献王」「医知源」「e研通」「e脉播」等系列产品,全面满足医学工作者临床决策、获取新知及提升科研效率等方面的需求。☟戳这里,更有料!
2025-04-18
SHANGHAI, April 18, 2025 /PRNewswire/ -- Asieris Pharmaceuticals today released its 2024 Annual Report, highlighting a bold and determined journey forward. With a specialty pharma strategy and operational efficiency, the company exceeded its commercialization targets and advanced its innovative products — APL-1702 and APL-1706 (Hexvix®) — toward market launch. R&D efforts also gained strong momentum, with 12 products in the pipeline and 16 ongoing research projects. As of the end of the reporting period, Asieris held approximately RMB 1.89 billion in cash, cash equivalents, and trading financial assets, providing a solid foundation for continued growth.
Revenue Tops RMB 200M in 1st Year of Commercialization, with the specialized commercialization platform poised for action
2024 marked Asieris' first full year of commercialization. The company has made strides in refining market strategies and ensuring high-quality execution, while effectively managing costs and expenses. Asieris posted operating revenue of RMB 202 million, demonstrating robust growth and successfully reaching break-even targets in commercial operations.
During the reporting period, the company's two commercialized products, Ouyoubi and Dipaite, saw strong uptake, reaching over 1,000 and 500 target hospitals respectively. Sales grew rapidly, with Ouyoubi capturing 27% of the neratinib tablet market and Dipaite securing 12% of the pazopanib tablet market.
To further strengthen its presence in key focus areas, the company introduced multiple products and established sales partnerships in women's health and genitourinary (GU) tumors. In March 2025, it licensed-in the eribulin mesylate injection, a novel microtubule inhibitor for the treatment of advanced breast cancer. With this addition, the company's breast cancer portfolio now covers both early and late-stage disease.
To further enhance commercialization efficiency, the company has launched its Commercial Operation 2.0 — building on past successes to create a leaner, more agile operating model. Key initiatives include appointing a seasoned Chief Commercial Officer to lead the function end-to-end; streamlining the organizational structure and strengthening commercial capabilities; and strategically expanding the team in line with priority areas and product launch timelines. The company has also set clear five-year business targets, including accelerating growth for existing products, preparing for the commercial rollout of Hexvix® and APL-1702, introducing new products within core therapeutic areas, maximizing synergies across the pipeline, and driving sales efficiency to the next level.
Accelerating product launches to build momentum for sales
In women's health, APL-1702, a combination of drug and medical device designed for photodynamic non-surgical treatment of cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL), is making steady progress toward market approval. In May 2024, the product's marketing application was officially accepted by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). As of the report's release, the Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE), NMPA had completed the first round of technical reviews, covering toxicology, clinical data, biostatistics, clinical pharmacology, and pharmaceutical quality. During the reporting period, the Inspection Center also wrapped up its Good Clinical Practice (GCP) inspection. The company has since received written feedback and is actively coordinating its responses to help expedite the review process and bring APL-1702 one step closer to approval.
As a first-in-class treatment set to debut in China, APL-1702 is on track to become the world's first non-invasive therapy for HSIL — supported by robust clinical evidence and validated through an international Phase III trial. Experts note that, with China facing demographic pressures and a rising incidence of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) among younger women, surgical excision of the cervix poses increasing challenges — especially during the critical period of fertility preservation. APL-1702 is expected to bridge this critical treatment gap and contribute to the creation of a more fertility-friendly healthcare landscape.
To drive the commercialization of APL-1702, the company has hosted eight expert advisory meetings, focusing on Phase III clinical data, the current landscape of HSIL diagnosis and treatment, and unmet clinical needs. These sessions earned strong endorsement from leading gynecological and pharmaceutical experts, who recognized the innovation and clinical value APL-1702 brings to the table. The company has also made meaningful progress in building strategic partnerships with government agencies and leading academic associations. In collaboration with the Cancer Foundation of China, the company unveiled the first real-world showcase of its innovative cervical cancer prevention and control system at the 7th China International Import Expo (CIIE). It also signed medium- to long-term strategic cooperation agreements with both the China Women's Development Foundation and the Cancer Foundation of China during the event. The partnerships are set to roll out in 2025.
The Women's Health Division has conducted extensive market and industry research, gaining deep insights into the needs of doctors and patients and broader commercial landscape. Based on this analysis, the team has finalized key launch strategies and mapped out a commercialization roadmap, laying the groundwork for a swift market rollout once approval is secured.
Given the relative scarcity of innovation in the gynecological field, APL-1702 stands out as a meaningful breakthrough, backed by solid clinical evidence and proven efficacy. The company will continue to prioritize APL-1702 and its photodynamic drug-device combination platform, in a bid to build a comprehensive, tiered gynecological portfolio. This strategy will center on product iteration and indication expansion, while leveraging synergies across the pipeline to drive broader growth.
In urological tumors, after the marketing application for Hexvix® was accepted in November 2023, the company's dynamic and highly skilled team sprang into action to support the review and approval process. As a result, Hexvix® received NMPA approval in November 2024, seven months ahead of the expected timeline. The product has since made history as the first diagnostic imaging agent approved in China for photodynamic blue light cystoscopy in bladder cancer detection.
The Oncology Business Unit is fine-tuning the launch strategy for Hexvix®, initially targeting patients with commercial insurance or those willing to pay out-of-pocket. The early rollout will cover the special and international medical departments of top-tier hospitals in major cities, as well as premium foreign-invested and private urology specialty hospitals. As clinical guidelines are released and endorsements from leading urology experts are established, the launch will be paired with the introduction of disposable blue light cystoscopes. Together, these efforts aim to accelerate the adoption of blue light cystoscopy in general hospitals and foster an integrated approach to the diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer.
Focusing on strategic expansion in key areas and fast-tracking high-impact R&D initiatives
Aligned with its strategic vision, Asieris has made significant strides in clinical development in 2024, with its global clinical initiatives progressing efficiently.
In the fields of women's health, breast cancer, and gynecological tumors, Asieris has made remarkable progress. Building on the strong results of the international multicenter Phase III study of APL-1702, the company received feedback from its communication meeting with the U.S. FDA in December 2024, culminating in an agreement on a new Phase III clinical design to support the U.S. launch of APL-1702. Asieris is now actively seeking international partners to advance the U.S. Phase III clinical trial application. Additionally, APL-1702 is also being investigated for its potential in HPV virus clearance. Meanwhile, the U.S. FDA and China's NMPA approved the Phase I/IIa clinical trial applications for APL-2302 (a USP1 small molecule inhibitor) in advanced solid tumors in October 2024 and January 2025, respectively, with the first patient enrolled in Phase Ia in March 2025. Progress on APL-2501 (CLDN6/9 ADC) is also on track, with its preclinical research and unique linker platform selected for a poster presentation at the 2025 American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting (AACR 2025).
In the field of urologic oncology, the Phase II clinical trial of oral APL-1202 in combination with tislelizumab as a neoadjuvant therapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) was successfully completed in September 2024, delivering encouraging efficacy signals. Among protocol-eligible patients, the pathological complete response (pCR) rates were 41% for the combination arm versus 20% for monotherapy. The combination was particularly effective in patients with low PD-L1 expression, where it achieved a pCR rate of 42% compared to just 11% with monotherapy. Meanwhile, APL-2401 — a dual FGFR2/3 small molecule inhibitor — has entered IND-enabling studies, with its findings selected for a poster presentation at AACR 2025.
In addition, the investigational new drug (IND) application for APL-1202 in the treatment of free-living amoebae (FLA) infections was approved by the NMPA in June 2024. In January 2025, the company signed an investigational drug supply agreement under the Expanded Access IND Program with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the United States for APL-1202, subject to evaluation by CDC experts, to be used for treating FLA infections.
Dr. Kevin Pan, Founder, Chairman and CEO of Asieris Pharmaceuticals, commented, "2024 marks our first full year of commercialization. We delivered strong growth across our marketed products and reached a milestone by breaking even in our commercial operations. Our pipeline is entering a critical sprint toward market launch and is set to power the next wave of performance growth. While reinforcing our commercial capabilities, we're also accelerating clinical programs with a strategic focus on women's health and urological oncology. We're building a robust pipeline of first-in-class and highly-differentiated fast-follow therapies, while actively expanding into global markets to unlock the full value of our assets. With relentless innovation and execution, we are confident that Asieris will continue to make a meaningful difference for patients, deliver solid returns to shareholders, and create lasting value for society."
Note:
As of the date of this publication, APL-1702 has not been approved for the treatment of cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL). This article is intended to disclose the latest development of these products, not to serve as a promotional advertisement for the products. The relevant information is not intended for patients but is provided solely for the reference of healthcare professionals. If you like to learn more about these diseases, please consult healthcare professionals.
SOURCE Asieris
WANT YOUR COMPANY'S NEWS FEATURED ON PRNEWSWIRE.COM?
440k+
Newsrooms &
Influencers
9k+
Digital Media
Outlets
270k+
Journalists
Opted In
GET STARTED
临床2期临床3期临床1期
2025-04-18
·美通社
上海
2025年4月18日
/美通社/ -- 今日,亚虹医药发布的2024年年报显示,公司展现出了奋勇前进的态势:凭借专科化战略和高效的运营管理,超额完成商业化目标;全力推进创新产品APL-1702和APL-1706(商品名:海克威®)的上市工作;加速推进优势研发项目。截至目前,公司主要产品管线拥有12个产品、16个在研项目。报告期末现金储备约18.9亿元,为公司发展提供保障。
商业化元年收入超2亿元,专科营销平台蓄势待发
2024年是亚虹医药首个完整的商业化年度,通过不断优化市场策略及落地执行质量,在有效控制成本费用的前提下,公司实现营业收入2.02亿元,呈现快速增长的态势,并实现商业化运营盈亏平衡目标。
报告期内,公司两款商业化产品欧优比®和迪派特分别覆盖了1000和500多家目标医院,销售快速放量,分别占据了马来酸奈拉替尼片和培唑帕尼片27%和12%的市场份额。
同时,为持续丰富公司在专注领域的布局,公司在女性健康及泌尿生殖系统肿瘤领域积极引进多项产品或开展销售合作,并于2025年3月成功引入一款新型微管蛋白抑制剂甲磺酸艾立布林注射液,用于晚期乳腺癌的治疗。公司乳腺癌产品线扩充覆盖早晚期乳腺癌。
此外,为了不断提高商业化效率,公司在此前的积累上启动商业化2.0升级,打造高效运营体系,具体举措包括:招聘拥有丰富经验的首席商务官,全面负责商业化运营;进一步优化组织架构、强化商业化运营的组织能力;围绕专注领域、根据产品商业化进程,有计划有规划地扩充商业化团队;设立五年业务目标包括确保现有产品实现高增长,为海克威®和APL-1702做好商业化准备,围绕专注领域持续引入新产品、加强管线协同、进一步提升销售效能等。
创新产品冲刺上市,夯实后续销售
在女性健康领域,亚虹医药用于非手术治疗宫颈高级别鳞状上皮内病变(High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion,HSIL)的光动力药器组合产品APL-1702的捷报频传:该产品的上市申请于2024年5月获国家药品监督管理局(NMPA)受理;截至报告披露日,国家药品监督管理局药品审评中心已经完成首轮技术审评工作,包括药理毒理、临床、统计、临床药理、药学专业等的专业审评;核查中心于报告期内完成了该上市申请的GCP核查。当前,公司已收到书面发补通知,正倾尽全力组织相关回复工作,加快推进其上市审评审批工作,以期尽快获得上市批准。
APL-1702是全球首创、中国首发,并且具有高等级的临床证据支持,有望成为全球首个经国际Ⅲ期临床验证、疗效确切的HSIL无创疗法产品。专家认为,在我国新的人口形势下,发病趋于年轻化和以宫颈切除手术为主的治疗现状,给处于"生育力保护"重要窗口期的宫颈癌前病变管理带来新挑战,APL-1702有望填补这一临床治疗空白,助力生育友好建设。
为了更好地推进APL-1702的商业化进程,公司目前已就APL-1702的Ⅲ期临床数据、HSIL的诊疗现状及临床需求等关键课题成功召开8次专家咨询会,赢得了妇科专家和药学专家对APL-1702创新性和临床价值的认可。同时,公司在寻求政府部门和相关学协会战略合作方面也有了实质性推进,公司与中国癌症基金会合作促成首个加速消除宫颈癌创新防控体系实景展亮相第七届中国国际进口博览会上,还在进博会上与中国妇女发展基金会和中国癌症基金会签署了中长期战略合作协议,预计将在2025年落地启动。
此外,女性健康事业部通过广泛的市场及行业调研,对医患需求及行业商业化环境进行了深入分析,已完成关键上市策略制定和商业化路径规划,确保产品获批后能迅速投放市场。
鉴于妇科领域创新药相对匮乏,APL-1702作为妇科领域难得的具有临床证据且
疗效确切
的突破性创新产品,显得尤为重要。未来,公司将持续围绕APL-1702和光动力药械联用平台,拟以产品迭代、适应症扩充为中心,辅以产品协同扩充等方式,全面打造有梯度和深度的妇科产品线。
在泌尿系统肿瘤领域,海克威®的上市申请于2023年11月获得受理后,公司内部由高度专业、高效协同的团队冲刺准备相关审评审批工作,于2024年11月收到NMPA核准签发的药品注册证书,较预期提前7个月。该产品成为国内膀胱癌领域首个获批的蓝光显影剂。
肿瘤事业部正在持续完善海克威®的上市规划,包括上市初期定位在支付意愿强或者商业医疗保险覆盖的患者群体,主要渗透中心城市三甲医院的特需及国际医疗部,和高端的外资及私立泌尿专科医院等;随着指南发布、泌尿专家建立专业背书,将结合一次性蓝光膀胱镜的上市,加强蓝光膀胱镜技术向综合性医院泌尿外科市场进一步渗透,打造膀胱癌诊疗一体化诊疗理念。
专注领域深度布局,聚力加速优势研发项目
在公司战略引导下,亚虹医药2024年在临床开发方面亦取得了多项进展,包括全球临床布局也正在高效推进中。
在女性健康、乳腺癌及妇科肿瘤领域,基于APL-1702国际多中心Ⅲ期研究的优异结果,公司已于2024年12月获得美国FDA沟通交流会议的反馈意见,与FDA就关于支持APL-1702美国上市的另一项三期临床设计达成一致,目前公司正在积极寻找海外合作伙伴,准备该项美国三期临床试验申请;同时APL-1702启动HPV病毒清除适应症的探索;APL-2302(USP1小分子抑制剂)用于治疗晚期实体瘤的I/IIa期临床试验申请分别于2024年10月和2025年1月获得美国FDA和中国NMPA批准,2025年3月完成Ⅰa期首例受试者入组;APL-2501(CLDN6/9ADC)也在稳步推进中,其临床前研究及特有的linker平台研究分别入选2025年美国癌症研究协会年会(AACR2025)壁报展示。
在泌尿系统肿瘤领域,APL-1202口服联合替雷利珠单抗作为肌层浸润性膀胱癌新辅助治疗的I/II期临床试验于2024年9月完成II期临床并取得积极疗效信号,在"符合研究方案"分析集中,联合组和单药组pCR分别为41%和20%;尤其在PD-L1低表达的亚组中,联合组较单药组显示出更强的积极疗效信号(42% vs.11%);APL-2401(FGFR2/3双靶点小分子抑制剂)已经正式进入IND Enabling阶段,其研究结果入选2025年美国癌症研究协会年会(AACR2025)壁报展示。
此外,APL-1202用于治疗自由生活阿米巴(Free-living Amoebae,FLA)感染的临床试验申请于2024年6月获得国家药品监督管理局批准;于2025年1月与美国CDC共同签署了药物拓展性研究项目下的研究用药供应协议,经CDC专家评估适用的前提下,用于治疗自由生活阿米巴(FLA)感染。
亚虹医药创始人、董事长、首席执行官潘柯博士表示:
2024年是公司首个完整的商业化年度,我们实现了上市产品的强势增长,并实现商业化运营盈亏平衡目标。创新产品已进入冲刺上市阶段,有望为下一阶段的业绩增长添加新引擎。在加强商业化的同时,公司将继续通过聚焦女性健康及泌尿系统肿瘤领域,加速推进临床项目,打造一系列结合全球首创和高度差异化的快速跟随的创新药物管线,并积极开拓产品的海外市场,最大化释放资产价值。我们坚信,通过持续的努力和创新,亚虹医药将为患者、股东和社会创造更大的价值。
说明:
截至发稿日期,APL-1702尚未获批用于治疗宫颈高级别鳞状上皮内病变。本文用于披露公司最新进展,并非产品推广广告。相关信息并非针对患者,仅供医疗卫生专业人士参考之用。如您想了解更多疾病信息,请咨询医疗卫生专业人士。
申请上市临床3期医药出海
100 项与 硝羟喹啉 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 膀胱癌 | 临床3期 | 中国 | 2020-11-04 | |
| 非肌层浸润性膀胱肿瘤 | 临床3期 | 中国 | 2017-03-30 | |
| 阿米巴病 | 临床2期 | 中国 | 2025-07-23 | |
| 肌层浸润性膀胱癌 | 临床2期 | 美国 | 2021-12-02 | |
| 前列腺癌 | 临床1期 | 中国 | - |
登录后查看更多信息
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
No Data | |||||||
登录后查看更多信息
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或
临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或

批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或
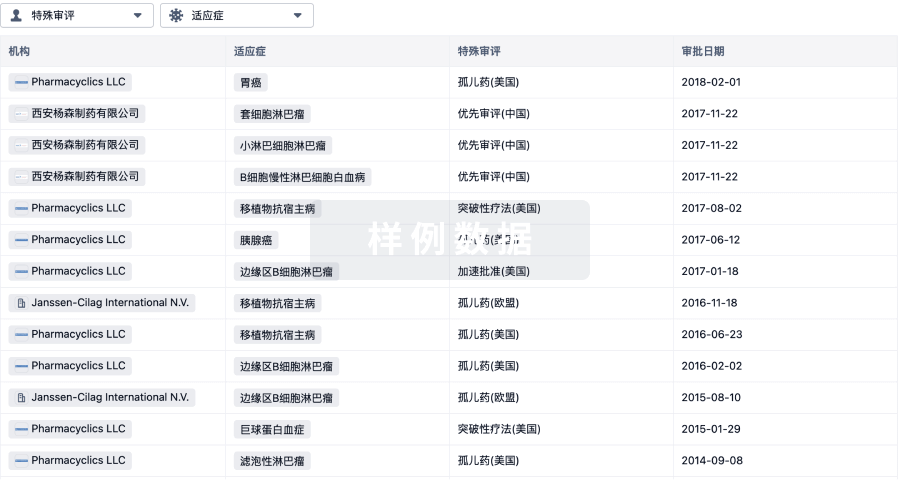
特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或
Eureka LS:
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用






