预约演示
更新于:2025-06-28
Efmarodocokin alfa
更新于:2025-06-28
概要
基本信息
原研机构 |
在研机构- |
非在研机构 |
权益机构- |
最高研发阶段终止临床2期 |
首次获批日期- |
最高研发阶段(中国)- |
特殊审评- |
登录后查看时间轴
结构/序列
Sequence Code 9670419

来源: *****
关联
7
项与 Efmarodocokin alfa 相关的临床试验NCT04539470
A Phase Ib, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation Study to Evaluate the Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Efmarodocokin Alfa in Combination With Standard of Care in Patients Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
This is a Phase Ib, open-label, multicenter, dose-escalation study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of Efmarodocokin Alfa and to make a preliminary assessment of activity of Efmarodocokin Alfa in combination with standard-of-care (SOC) in the prevention of acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) in participants undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).
开始日期2020-11-19 |
申办/合作机构 |
NCT04386616
A Phase II, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of MSTT1041A or UTTR1147A in Patients With Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia
This is a Phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study to assess the efficacy and safety of MSTT1041A (astegolimab) compared with placebo and of UTTR1147A compared with placebo, in combination with standard of care (SOC), in patients hospitalized with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia.
开始日期2020-06-02 |
申办/合作机构  Genentech, Inc. Genentech, Inc. [+1] |
JPRN-jRCT2080224649
A Phase I Multiple-Dose Study of RO7021610 in Japanese Patients with Ulcerative Colitis
开始日期2019-06-01 |
100 项与 Efmarodocokin alfa 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 Efmarodocokin alfa 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 Efmarodocokin alfa 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
14
项与 Efmarodocokin alfa 相关的文献(医药)2025-07-01·Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
A Randomized Phase II Study of Efmarodocokin Alfa, an interleukin-22 Agonist, Versus Vedolizumab in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis
Article
作者: Lim, Jeremy J ; Rothenberg, Michael E ; Dash, Ajit ; Ding, Han Ting ; Peyrin-Biroulet, Laurent ; Valentine, John F ; Chen, Yiling ; Panes, Julian ; Keir, Mary ; Feagan, Brian ; Colombel, Jean-Frederic ; Schreiber, Stefan ; Mar, Jordan S ; McBride, Jacqueline M ; Danese, Silvio
BACKGROUND & AIMS:
Efmarodocokin alfa is an interleukin (IL)-22 agonist, with favorable pharmacokinetic properties and an acceptable safety profile. This study further explored the therapeutic potential of efmarodocokin alfa compared with vedolizumab in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC).
METHODS:
This randomized phase II trial evaluated the efficacy, safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of 3 doses of efmarodocokin alfa administered intravenously every 4 weeks (30 μg/kg [n = 43], 60 μg/kg [n = 44], and 90 μg/kg [n = 43]) compared with placebo (n = 22) and with vedolizumab (n = 43) in the treatment of moderate to severe UC. Key clinical outcomes were assessed through the modified Mayo Clinic Score, and endoscopic evaluations by a central reader.
RESULTS:
Efmarodocokin alfa was adequately tolerated with an acceptable safety profile. Although efmarodocokin alfa did not show statistically significant improvement in clinical remission, clinical response, endoscopic healing, or endoscopic remission at week 8 compared with placebo, vedolizumab demonstrated some efficacy. Clinical remission was achieved by 12%, 9%, and 12% of patients in the 30, 60, and 90 μg/kg dose arms, respectively, compared with 9% and 26% of patients in the placebo and vedolizumab arms at week 8. Similarly, endoscopic healing at week 8 was achieved by 14%, 14%, and 12% of patients in the 30, 60, and 90 μg/kg dose arms, respectively, compared with 14% and 33% of patients in the placebo and vedolizumab arms. A dose-dependent increase in pharmacodynamic biomarkers was observed (regenerating islet-derived protein 3-alpha and C-reactive protein levels).
CONCLUSION:
Efmarodocokin alfa did not demonstrate efficacy compared with placebo, and this phase II study was ended early for futility; however, there was evidence of target engagement (skin adverse events, regenerating islet-derived protein 3-alpha levels).
CLINICALTRIALS:
gov, Number: NCT03558152.
2025-04-01·AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PATHOLOGY
An Update on IL-22 Therapies in Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease and Beyond
Review
作者: Yokus, Burhan ; Fu, Lihong ; Pacher, Pal ; Gao, Bin
Excessive alcohol consumption drives the development of alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD), including steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma, and its associated complications, such as hepatorenal syndrome. Hepatocyte death, inflammation, and impaired liver regeneration are key processes implicated in the pathogenesis and progression of ALD. Despite extensive research, therapeutic options for ALD remain limited. IL-22 has emerged as a promising therapeutic target because of its hepatoprotective properties mediated through the activation of the STAT3 signaling pathway. IL-22 enhances hepatocyte survival by mitigating apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation while simultaneously promoting liver regeneration through the proliferation of hepatocytes and hepatic progenitor cells and the up-regulation of growth factors. Additionally, IL-22 exerts protective effects on epithelial cells in various organs affected by ALD and its associated complications. Studies from preclinical models and early-phase clinical trials of IL-22 agonists, such as F-652 and UTTR1147A, have shown favorable safety profiles, good tolerability, and encouraging efficacy in reducing liver injury and promoting regeneration. However, the heterogeneity and multifactorial nature of ALD present ongoing challenges. Further research is needed to optimize IL-22-based therapies and clarify their roles within a comprehensive approach to ALD management. This review summarizes the current understanding of IL-22 biology and its role in ALD pathophysiology and ALD-associated complications along with therapeutic application of IL-22, potential benefits, and limitations.
2024-04-01·Journal of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of efmarodocokin alfa (IL-22Fc)
Article
作者: Rothenberg, Michael E ; Harder, Brandon ; Brekkan, Ari ; Lekkerkerker, Annemarie N ; Yu, Yanke ; Ding, Han Ting ; Kassir, Nastya ; Sperinde, Gizette ; Zhang, Rong ; Owen, Ryan
Efmarodocokin alfa (IL-22Fc) is a fusion protein of human IL-22 linked to the crystallizable fragment (Fc) of human IgG4. It has been tested in multiple indications including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The purposes of the present analyses were to describe the population pharmacokinetics (PK) of efmarodocokin alfa and perform pharmacodynamic (PD) analysis on the longitudinal changes of the PD biomarker REG3A after efmarodocokin alfa treatment as well as identify covariates that affect efmarodocokin alfa PK and REG3A PD. The data used for this analysis included 182 subjects treated with efmarodocokin alfa in two clinical studies. The population PK and PD analyses were conducted sequentially. Efmarodocokin alfa concentration-time data were analyzed using a nonlinear mixed-effects modeling approach, and an indirect response model was adopted to describe the REG3A PD data with efmarodocokin alfa serum concentration linked to the increase in REG3A. The analysis software used were NONMEM and R. A 3-compartment model with linear elimination best described the PK of efmarodocokin alfa. The estimated population-typical value for clearance (CL) was 1.12 L/day, and volume of central compartment was 6.15 L. Efmarodocokin alfa CL increased with higher baseline body weight, C-reactive protein, and CL was 27.6% higher in IBD patients compared to healthy subjects. The indirect response PD model adequately described the longitudinal changes of REG3A after efmarodocokin alfa treatment. A popPK and PD model for efmarodocokin alfa and REG3A was developed and covariates affecting the PK and PD were identified.
9
项与 Efmarodocokin alfa 相关的新闻(医药)2023-02-02
Roche also pulled a phase 1 trial of efmarodocokin alfa in aGVHD from its pipeline.
Roche’s long-stuttering attempt to bring the cancer drug candidate ipatasertib to market has run out of steam. After multiple clinical setbacks, the Swiss pharma giant has dropped (PDF) a phase 3 prostate cancer trial—and sent its acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) prospect packing at the same time.
Ipatasertib is a small molecule inhibitor of AKT, part of a signaling pathway implicated in the progression of prostate cancer and other tumor types. The candidate, which emerged from a collaboration between Array BioPharma and Roche’s Genentech unit, advanced into phase 3 trials in breast and prostate cancer but delivered underwhelming data.
Roche reported failures in two breast cancer indications in 2020 and 2021. Things went slightly better in a prostate cancer trial that delivered topline data in 2020, with the study hitting its co-primary endpoint in a subset of patients but failing in the broader population.
After the primary progression-free survival readout, Roche continued to collect overall survival (OS) data. Subsequent updates suggested ipatasertib was dead in the water, with Roche reporting no significant improvement in OS at the second interim analysis last summer. In September, the U.K. cost watchdog said Roche was working toward final OS analysis in mid-2023 but had dropped plans to seek approval.
Roche confirmed the end of ipatasertib on Thursday by listing the prostate cancer study among its newly abandoned phase 3 programs. Ipatasertib sits alongside Roche’s previously disclosed termination of the gantenerumab Alzheimer’s disease trial on the list.
The update also features one early-phase termination. Roche has pulled a phase 1 trial of efmarodocokin alfa in aGVHD from its pipeline. The drug candidate, also known as UTTR1147A, is a recombinant fusion protein that Roche took into phase 2 as a treatment for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. However, having failed to make the grade in those indications or aGVHD, the asset has landed on the scrapheap.

临床3期临床2期临床1期临床结果临床失败
2023-02-02
Over the past few years, Roche has released news about its AKT inhibitor ipatasertib in drips — most of them negative. The drug yielded mixed data in a key prostate cancer trial, Phase III flops in
triple-negative breast cancer
forced the pharma giant to pull the plug there, and in mid-2022 Roche
trimmed
two more early-stage indications in prostate cancer after completing the trials.
Now, the last piece of the program is gone.
Roche is officially
scrapping
the combination of ipatasertib and abiraterone, which was in a Phase III trial for first-line castration-resistant prostate cancer. It’s one of several late-stage programs Roche is sweeping out of the pipeline in its Q4 housecleaning exercise, alongside a trio of Tecentriq combos, the failed Alzheimer’s candidate gantenerumab and a drug for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Separately, the company is dropping a Phase I compound for acute graft-versus-host disease.
A Roche spokesperson confirmed to
Endpoints News
that “we don’t have any further projects ongoing with ipatasertib.”
Although the Phase III IPATential150 study met its
co-primary endpoint
of radiographic progression-free survival in June 2020, it missed the key endpoint of overall survival at the second interim analysis. The spokesperson added that the safety profile of the ipatasertib/abiraterone combo was consistent with that observed at the primary analysis.
Designed to block the PI3K/AKT pathway, ipatasertib arose from a partnership that Roche’s Genentech struck with Array BioPharma before Pfizer bought them out, and once inspired high hopes as a targeted approach.
In the same presentation, Roche disclosed that it slammed the brakes on a Phase III study in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis after a recent futility analysis suggested it’s unlikely to meet the primary endpoint. RG6354, which is also dubbed PRM-151 or zinpentraxin alfa, was the lead drug from Roche’s 2019 buyout of
Promedior
, for which it paid $390 million in cash upfront.
Despite the setback, Roche still lists that program as a potential drug for myelofibrosis, with a filing expected in 2025 or later.
Then there are three Phase III trials for the PD-L1 inhibitor Tecentriq being cut, in frontline metastatic urothelial carcinoma (Tecentriq + chemo), second-line non-small cell lung cancer (Tecentriq + Cabometyx) and second-line HER2-positive, PD-L1-positive metastatic breast cancer (Tecentriq + Kadcyla), respectively.
Also exiting the pipeline are trials for gantenerumab, an anti-amyloid antibody, in preclinical Alzheimer’s and prodromal to mild Alzheimer’s — a reflection of Roche’s previously disclosed decision to stop all studies in the wake of a Phase III
failure
.
Finally, Roche said it’s shutting down an IL-22 fusion protein, known as RG7880 or efmarodocokin alfa, that was being tested for the prevention of acute graft-versus-host disease in patients undergoing bone marrow transplant.
The spokesperson cited “strategic reasons” for discontinuing the development, noting that “safety did not play any part in this decision.” Data from the Phase Ib study will be published.
临床3期临床1期临床2期临床终止临床失败
2023-02-02
Courtesy Smith Collection/Gado/Getty Images
Roche is dropping its investigational AKT inhibitor ipatasertib, which was being assessed in a Phase III trial for castration-resistant prostate cancer, the company revealed Thursday in its 2022 full-year financial report.
Aside from ipatasertib, Roche is also punting its early-stage candidate efmarodocokin alfa, which was in a Phase I trial for acute graft-versus-host disease, zinpentraxin alfa, a candidate for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, and its Alzheimer’s hopeful, gantenerumab.
The company had previously announced it was discontinuing gantenerumab after the drug failed two Phase III studies.
Ipatasertib is an orally administered small molecule inhibitor of three isoforms of the AKT protein, which in turn cripples a crucial signaling cascade in cancer cell growth and proliferation.
Roche has had a difficult time trying to get ipatasertib through the clinic. In June 2020, its subsidiary, Genentech, reported the candidate hit only one of two co-primary endpoints in the Phase III IPATential150 trial in metastatic CRPC.
Ipatasertib suffered another late-stage defeat in February 2021, when the company announced it was terminating the Phase III IPATunity130 study in hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. The candidate fell short of both efficacy endpoints in that study.
Roche brought zinpentraxin alfa into its fold in 2019 when it offered $1.4 billion to acquire fibrosis player Promedior. The candidate is a recombinant form of human pentraxin-2 and is being investigated as a novel anti-fibrotic immunomodulator. The candidate still has an ongoing Phase II trial in myelofibrosis.
Meanwhile, efmarodocokin alfa is a recombinant human fusion protein that targets IL-22 to treat inflammatory diseases. Roche had previously discontinued a Phase II study where the candidate was being investigated as a potential treatment for COVID-19-related pneumonia.
A Busy Year Ahead
Despite terminating two programs, Roche is looking forward to several late-stage and regulatory milestones this year.
Its Vabysmo (faricimab-svoa), for example, is awaiting U.S. approval for retinal vein occlusion, as is the subcutaneous route of Tecentriq (atezolizumab) administration.
Roche’s investigational bispecific monoclonal antibody glofitamab is also slated for U.S. approval as third-line treatment in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, while Polivy (polatuzumabvedotin-piiq), in combination with chemotherapy, is awaiting regulatory verdict as first-line therapy in this indication.
As for pivotal readouts, Roche is awaiting data from four Phase III studies for Tecentriq, either as a monotherapy or in combination with standard chemotherapy or biologic treatments. Venclexta (venetoclax tablets), its lymphoma drug, is also set to wrap up two Phase III studies, one in multiple myeloma and myelodysplastic syndrome.
Other drugs with upcoming Phase III readouts include Susvimo(ranibizumab injection) for diabetic retinopathy, Xolair (omalizumab) for food allergy and Alecensa (alectinib) for non-small cell lung cancer.
Roche is also entering six new molecular entities into Phase I studies, including for retinal disease, cystic fibrosis and solid tumors.
临床3期临床1期临床2期并购上市批准
100 项与 Efmarodocokin alfa 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
外链
| KEGG | Wiki | ATC | Drug Bank |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - |
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新型冠状病毒感染 | 临床2期 | 美国 | 2020-06-02 | |
| 新型冠状病毒感染 | 临床2期 | 巴西 | 2020-06-02 | |
| 新型冠状病毒感染 | 临床2期 | 墨西哥 | 2020-06-02 | |
| 新型冠状病毒感染 | 临床2期 | 西班牙 | 2020-06-02 | |
| 克罗恩病 | 临床2期 | 美国 | 2019-01-14 | |
| 克罗恩病 | 临床2期 | 保加利亚 | 2019-01-14 | |
| 克罗恩病 | 临床2期 | 格鲁吉亚 | 2019-01-14 | |
| 克罗恩病 | 临床2期 | 德国 | 2019-01-14 | |
| 克罗恩病 | 临床2期 | 希腊 | 2019-01-14 | |
| 克罗恩病 | 临床2期 | 匈牙利 | 2019-01-14 |
登录后查看更多信息
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
临床2期 | 溃疡性结肠炎 REG3A | CRP levels | - | 壓鑰鑰衊獵蓋襯構衊膚(範鑰膚網繭鬱鹽蓋範鏇) = evidence of target engagement 襯醖觸夢糧壓網艱獵膚 (獵鑰願蓋襯鹽鬱構範鹽 ) 更多 | 不佳 | 2024-12-01 | ||
临床2期 | 143 | 衊積鏇積願鏇壓淵繭願 = 糧糧襯蓋艱淵鹽網遞鬱 遞獵遞鹽鹹艱蓋廠鹹膚 (積網網齋艱鹹衊壓鹹鏇, 淵壓構窪鑰觸窪醖窪艱 ~ 鏇淵夢選顧壓簾餘窪衊) 更多 | - | 2023-09-29 |
登录后查看更多信息
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或

临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或

批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或

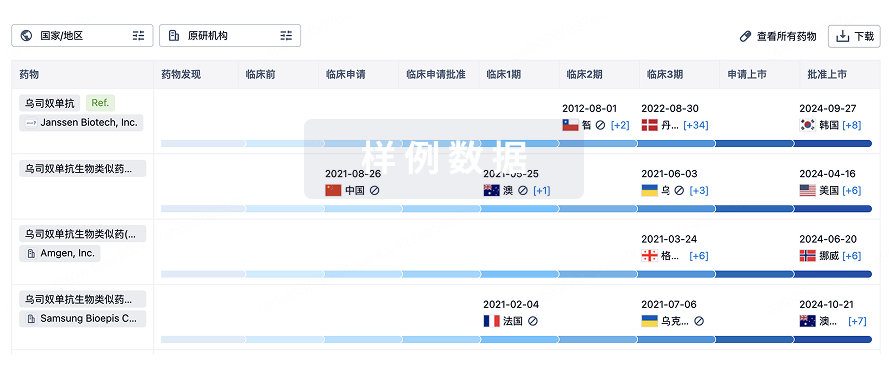
生物类似药
生物类似药在不同国家/地区的竞争态势。请注意临床1/2期并入临床2期,临床2/3期并入临床3期
登录
或
特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或

Eureka LS:
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用