预约演示
更新于:2025-05-07
SOD3
更新于:2025-05-07
基本信息
别名 EC-SOD、Extracellular superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn]、SOD3 + [2] |
简介 Protect the extracellular space from toxic effect of reactive oxygen intermediates by converting superoxide radicals into hydrogen peroxide and oxygen. |
关联
2
项与 SOD3 相关的药物靶点 |
作用机制 SOD3调节剂 |
在研机构- |
在研适应症- |
非在研适应症 |
最高研发阶段无进展 |
首次获批国家/地区- |
首次获批日期1800-01-20 |
靶点 |
作用机制 SOD3调节剂 |
在研机构- |
在研适应症- |
最高研发阶段无进展 |
首次获批国家/地区- |
首次获批日期1800-01-20 |
1
项与 SOD3 相关的临床试验NCT03096756
A Phase 1, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Single Ascending Dose Study Designed to Compare the Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Orally Administered Superoxide Dismutase Mimetic GC4702 With Intravenously Administered Superoxide Dismutase Mimetic GC4419 (Part 1), With Assessment of Food Effect (Part 2), in Healthy Volunteers
A Phase 1 study will test the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of a single dose of GC4702 when given as an oral tablet. This study will compare capsules containing a dry powder or gel suspension of GC4702 when given orally to a similar drug called GC4419 which will be given as an intravenous infusion. This study will also assess the effect of food on the GC4702 effects.
开始日期2016-07-26 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 SOD3 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 SOD3 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 SOD3 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
1,534
项与 SOD3 相关的文献(医药)2025-06-01·Food and Chemical Toxicology
Arsenolipid-induced reproductive toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans: Elucidating the mechanism through the HUS-1-CEP-1-EGL-1-CED-9-CED-4-CED-3 signaling pathway
Article
作者: Cheung, Kit-Leong ; Song, Bingbing ; Li, Caiyan ; Li, Rui ; Zhao, Qiaoli ; Chen, Jianping ; Wang, Zhuo ; Jia, Xuejing ; Zhong, Saiyi ; Liu, Xiaofei
2025-06-01·Biogerontology
Vorinostat, a potential hormetin, extends lifespan and enhances stress resistance via the SKN-1 pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans
Article
作者: Huang, Shuai ; Shi, Zhidan ; He, Ling ; Wu, Jiawei ; Shi, Hang
2025-05-01·Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety
Chlorantraniliprole-induced oxidative stress, DNA damage, and apoptosis in Caenorhabditis elegans: Mechanistic insights and ecological risk implications
Article
作者: Hu, Guokun ; Ji, Xiaoxue ; Han, Shaohua ; Qiao, Kang ; Yang, Mengzhen ; Hu, Fengyuan
3
项与 SOD3 相关的新闻(医药)2023-02-28
-mRNA encoding immunomodulatory proteins IκBα-SR and SOD3 ameliorated symptoms in bacterial pneumonia model
-Factor is investigating nebulized mRNA formulations for other therapeutic indications and next-generation vaccine applications
CAMBRIDGE, Mass., Feb. 28, 2023 /PRNewswire/ -- Factor Bioscience Inc. ("Factor"), a Cambridge-based biotechnology company focused on developing mRNA and cell-engineering technologies, announced the results of preclinical testing of aerosolized mRNA formulations currently under development for the treatment of pneumonia-associated lung inflammation. The study was led by Factor's collaborator, Dr. Daniel O'Toole, Senior Research Fellow, Senior Lecturer in Lung Regenerative Medicine and Principal Investigator in the CÚRAM and REMEDI institutes at the University of Galway.
"mRNA offers unmatched flexibility as a vector for expressing therapeutic proteins safely and reliably."
"Pneumonia is a debilitating disease in which infection causes inflammation of lung tissue, often leading to pulmonary edema, and in severe cases, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and death," said Dr. O'Toole. "There are currently no effective specific therapies for ARDS, and the mortality rate remains high. The ability to directly express anti-inflammatory proteins in lung tissue makes aerosolized mRNA an attractive candidate therapy for pneumonia. In particular, the speed with which cells express proteins when treated with mRNA is particularly important in the context of a rapid-onset disease such as ARDS."
These results are the latest in the long-standing collaboration between Factor and CÚRAM, the Science Foundation Ireland Centre for Research in Medical Devices, which is now in its sixth year. Factor and CÚRAM have multiple active collaborative projects, including projects focused on the development of mRNA-reprogrammed induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell-derived therapies for the treatment of pulmonary diseases as well as next-generation aerosolized mRNA vaccines.
"We are incredibly proud of our collaboration with CÚRAM, and are excited about the results of this study," said Dr. Christopher Rohde, Chief Technology Officer of Factor. "mRNA offers unmatched flexibility as a vector for expressing therapeutic proteins safely and reliably, and the results of this study support the use of aerosolized mRNA formulations for expression of therapeutic proteins in the lung. We are excited to continue this work with the team at CÚRAM and advance product candidates based on these results towards clinical development."
The results of this study were published last week in Nucleic Acid Therapeutics:
About Factor Bioscience
Founded in 2011, Factor Bioscience develops technologies for engineering cells to advance the study and treatment of disease. Factor's gene-editing technologies enable the precise deletion, insertion, and repair of DNA sequences in living cells to correct disease-causing mutations, make cells resistant to infection and degenerative disease, modulate the expression of immunoregulatory proteins to enable the generation of durable allogeneic cell therapies, and engineer immune cells to more effectively fight cancer. Factor's cell-reprogramming technologies enable the generation of clonal lines of pluripotent stem cells that can be expanded and differentiated into any desired cell type for the development of regenerative cell therapies. For more information, visit .
About CÚRAM
CÚRAM is the Science Foundation Ireland Centre for Research in Medical Devices, based at the University of Galway. CÚRAM's innovative approach incorporates biomaterials, drug delivery, cell-based technologies, glycosciences and device design to enhance, develop and validate both traditional and new combinational medical devices from molecular design stage to implant manufacturing. For more information, visit
疫苗信使RNA免疫疗法基因疗法
2022-12-26
·生物谷
从酵母到高等哺乳动物,有限数量的基因操作和治疗可以延长多种物种的寿命。
从酵母到高等哺乳动物,有限数量的基因操作和治疗可以延长多种物种的寿命。尽管这些操作的起源截然不同,但它们似乎都激活了长寿保证途径,最终通过切换到替代代谢程序或通过刺激细胞保护机制,最终导致对各种压力的抵抗力增强。增强韧性导致寿命延长的概念并不新鲜,然而,人们对衰老过程中调节应激抵抗的分子机制知之甚少。
图片来源: https://doi-org.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/10.1016/j.redox.2022.102533
近日,来自德国的研究者们在Redox Biology杂志上发表了题为“Mitochondria-originated redox signalling regulates KLF-1 to promote longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans”的文章,该研究强调了氧化还原调节信号作为线虫长寿诱导途径的关键调节因子的重要性,并将精确计时的线粒体来源的过氧化氢定位在其中。
线虫线虫由中度线粒体功能障碍引起,氧化还原代谢的改变与线虫寿命的延长有关,尽管潜在的信号级联在很大程度上尚不清楚。在此之前,研究者发现转录因子Krüppel-like factor-1(KLF-1)是线虫长寿突变体中细胞保护长寿保障途径的主要调节因子。
在本研究中,研究者证明了KLF-1转位到细胞核和信号级联的激活依赖于发育后期线粒体衍生的过氧化氢(H_2O_2),此时是有氧呼吸和体细胞线粒体生物发生的高峰期。研究者进一步证明,线粒体诱导的超氧化物歧化酶-3(SOD-3)和电压依赖的阴离子通道-1(VDAC-1)是促进生命的过氧化氢信号所必需的,而过氧化氢还蛋白-3(PRDX-3)进一步调节了这一信号通路。
细胞质中过氧化氢释放的增加激活了p38MAPK信号级联反应,从而诱导KLF-1易位到细胞核,并激活了线虫长寿促进基因的转录,包括细胞保护性细胞色素P450氧化酶。
线粒体H_2O_2的释放依赖于SOD-3、PRDX-3和VDAC-1,KLF通过p38MAPK,尤其是PMK-3向胞核转运
图片来源: https://doi-org.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/10.1016/j.redox.2022.102533
综上所述,这些结果确定了线虫线粒体突变体长寿所必需的氧化还原信号级联,它依赖于线粒体过氧化氢信号、氧化还原酶SOD-3和PRDX-3以及OMM转运蛋白VDAC-1。一旦进入细胞质,过氧化氢就激活压力诱导的p38MAPK信号级联,这是线虫KLF-1转位到细胞核和激活细胞保护性寿命保证计划所必需的。
本研究数据进一步突出了更多研究的明显需要,这些研究更多地关注氧化应激以外的ROS信号的机制深入研究,这些研究将跨越不同的物种,并可能确定与年龄相关的疾病的潜在治疗靶点。(生物谷 Bioon.com)
参考文献
Johannes CW Hermeling et al. Mitochondria-originated redox signalling regulates KLF-1 to promote longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Redox Biol. 2022 Dec;58:102533. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102533.
临床研究
2022-07-29
·生物谷
在适量运动的基础上,运动在多个方面给人体带来好处。那么你知道好处有哪些吗?针对此,小编针对生物谷近期发表的新闻进行一番盘点,以飨读者。
在适量运动的基础上,运动在多个方面给人体带来好处。那么你知道好处有哪些吗?针对此,小编针对生物谷近期发表的新闻进行一番盘点,以飨读者。
1.Cancer Cell:有氧运动增强免疫系统对胰腺癌的攻击
doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2022.05.006
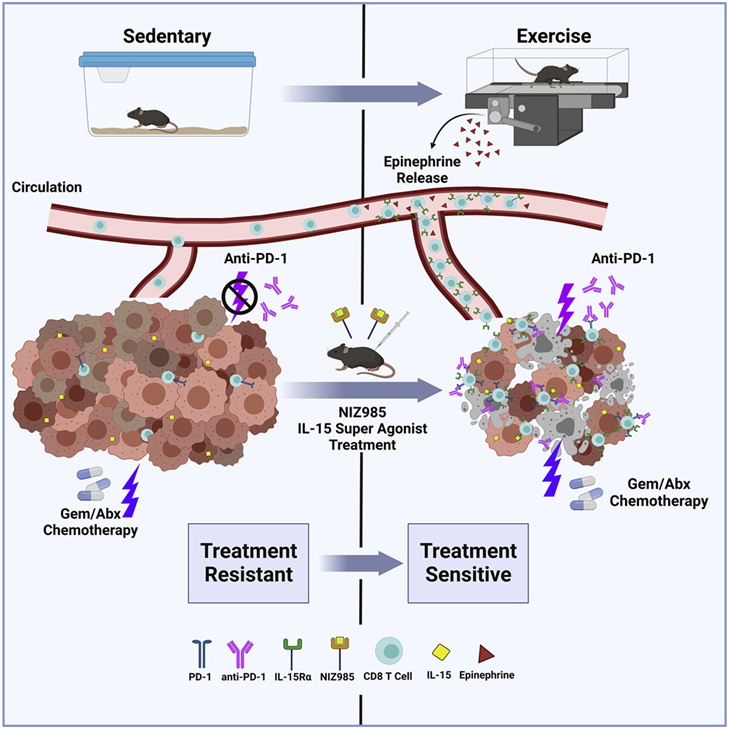
在一项新的研究中,来自纽约大学格罗斯曼医学院和德克萨斯大学MD安德森癌症中心等研究机构的研究人员发现有氧运动能对免疫系统进行重新编程,以减少胰腺肿瘤的生长并放大免疫疗法的效果。相关研究结果于2022年6月2日在线发表在Cancer Cell期刊上,论文标题为“Exercise-induced engagement of the IL-15/IL-15Rα axis promotes anti-tumor immunity in pancreatic cancer”。
图片来自Cancer Cell, 2022, doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2022.05.006。
这项新的研究为哺乳动物中旨在攻击细菌等外来入侵者的免疫系统也能将癌细胞识别为异常的提供了新的见解。这些作者表示,运动引起的肾上腺素水平的增加导致了免疫系统的变化,包括对信号蛋白白细胞介素-15(IL-15)做出反应的细胞的活动。
这项新的研究发现运动促进了对IL-15敏感的CD8 T细胞的生存,并使它们归巢到小鼠胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)肿瘤的数量翻倍。这类“效应”T细胞已被其他研究证明能够杀死癌细胞。其他测试发现,每周5次、每次30分钟的有氧运动使一种PDAC小鼠模型的癌症形成率降低了50%,而在跑步机上跑步三周使另一种小鼠模型的肿瘤重量减少了25%。
这些作者随后发现,就参加“胰腺癌新辅助治疗期间的术前康复(Preoperative Rehabilitation During Neoadjuvant Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer)”临床试验的人类患者而言,在手术切除胰腺肿瘤前进行锻炼的人有更多的CD8效应T细胞,这些T细胞表达一种叫做颗粒酶B(granzyme B)的蛋白,这种蛋白赋予肿瘤细胞杀伤力。此外,在2017年开始的这项试验中,那些进行锻炼并拥有更多这些细胞类型的患者在五年内的总生存率比拥有更少这些细胞的患者高50%。
论文第一作者、纽约大学格罗斯曼医学院的Emma Kurz博士说,“我们的研究结果首次显示了有氧运动如何影响胰腺肿瘤内的免疫微环境。这项新的研究有助于揭示胰腺癌中IL-15信号的激活可能是未来的一种重要治疗方法。”
2.Nature:揭示运动有助于减肥新证据,提高血浆中的Lac-Phe水平
doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04828-5
在一项新的研究中,来自贝勒医学院和斯坦福大学医学院等研究机构的研究人员报告说,他们在血液中发现了一种在运动中产生的分子,它能有效减少小鼠的食物摄入和肥胖。这些发现提高了人们对运动和饥饿之间相互作用的生理过程的理解。相关研究结果于2022年6月15日在线发表在Nature期刊上,论文标题为“An exercise-inducible metabolite that suppresses feeding and obesity”。
论文共同通讯作者、贝勒医学院分子与细胞生物学教授Yong Xu博士说,“定期运动已被证明有助于减肥、调节食欲和改善代谢状况,特别是对超重和肥胖的人而言。如果我们能够了解运动引发这些益处的机制,那么我们就更接近于帮助许多人改善他们的健康状况。”
论文共同通讯作者、斯坦福大学医学院病理学助理教授Jonathan Long博士说,“我们想了解运动是如何在分子水平上发挥作用的,以便能够了解它的一些好处。例如,不能进行足够运动的老年人或体弱者,有一天可能会从服用一种可以帮助减缓骨质疏松症、心脏病或其他疾病的药物中受益。”
细胞和小鼠中CNDP2蛋白的进一步表征和验证。图片来自Nature, 2022, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04828-5。
Xu、Long和他们的同事们对小鼠在高强度跑步机上跑步后的血浆化合物进行了全面分析。运动后最显著产生的一种分子是一种叫做Lac-Phe的改性氨基酸。它是由乳酸(一种剧烈运动的副产物,是造成肌肉燃烧感觉的原因)和苯丙氨酸(一种氨基酸,是蛋白的组成成分之一)合成的。
在饮食引起的肥胖小鼠(喂食高脂肪饮食)中,与对照组小鼠相比,高剂量的Lac-Ph在12小时内抑制了大约50%的食物摄入,而不影响它们的运动或能量消耗。当给这些肥胖小鼠服用10天后,Lac-Phe减少了累积的食物摄入量和体重(由于身体脂肪的减少),并改善了葡萄糖耐受性。
这些作者还确定了一种名为CNDP2的酶,它参与了Lac-Phe的产生,并发现缺乏这种酶的小鼠在运动计划中的体重下降幅度不如执行同样运动计划的对照组小鼠。
有趣的是,这些作者还发现,在赛马和人类的体育活动后,血浆中的Lac-Phe水平显著升高。来自人类运动队列的数据显示,短跑运动(sprint exercise)诱发了血浆Lac-Ph的最大幅度的增加,其次是阻力训练(resistance training),然后是耐力训练(endurance training)。Long说,“这表明Lac-Phe是一个古老而保守的系统,它调节进食,并与许多动物物种的体育活动有关。”
3.FASEB J: 揭示运动增加外泌体分泌促进血管生成机制,可对抗糖尿病对血管的损伤
doi:10.1096/fj.202101323R
根据美国疾病控制与预防中心的数据,约有十分之一的美国人患有糖尿病。源自2型糖尿病(T2DM)患者的外泌体是细胞-细胞交流的关键媒介,表现出有害的影响。运动在一定程度上通过将外泌体分泌到血液循环中来改善内皮功能。胞外超氧化物歧化酶(SOD3)是一种主要的分泌性铜(Cu)抗氧化酶,它的活性需要铜转运蛋白ATP7A。然而,在T2DM中,SOD3在循环血浆外泌体对血管内皮细胞的血管生成作用中所起的作用尚不清楚。
血管生成是形成新血管的能力,而糖尿病不仅损害现有的血管,它还阻碍了这种在面对疾病和损伤时生长新血管的先天能力。血管内皮细胞排列在我们的血管内壁,对新血管的生长至关重要。
在一项新的研究中,来自奥古斯塔大学乔治亚医学院的研究人员提供第一个证据表明就糖尿病而言,即使是45分钟的中等强度运动,也能使更多的外泌体---充满生物活性物质的亚显微囊泡---直接向血管内皮细胞递送更多的蛋白ATP7A,这可启动血管生成。这意味着运动可以对抗糖尿病损害血管的一种方式是,当现有的血管受到这种疾病的破坏时,可以激活一种天然的系统来生长新的血管。相关研究结果于2022年2月10日在线发表在FASEB Journal期刊上,论文标题为“Exercise improves angiogenic function of circulating exosomes in type 2 diabetes: Role of exosomal SOD3”。
图片来自Diabetes, 2013, doi:10.2337/db12-1228。
在一种2型糖尿病的小鼠模型和一小群50多岁的健康人中,小鼠在轮子上自愿跑了两周后和人类在一次有氧运动后增加了附着在血管内皮细胞上的外泌体中的ATP7A水平。这些作者指出,在这一点上,运动并没有明显影响小鼠的体重,但它增加了内皮功能的标志物和血管生成所需的因子,比如血管内皮生长因子。
运动还增加了强大的、天然抗氧化剂细胞外超氧化物歧化酶(SOD3)的数量,但外泌体携带的ATP7A更多,ATP7A被认为是向细胞递送必需的矿物质铜,这是充分利用SOD3的关键。
作为一种重要的天然抗氧化剂,SOD3由血管壁上的血管平滑肌细胞以及骨骼肌细胞产生,它帮助我们保持活性氧(ROS)的健康水平。ROS是我们使用氧气的一种天然副产物,是一种重要的细胞信号,使得多种功能得以实现。但在糖尿病中,高血糖水平导致高ROS水平,反而阻碍了重要的正常功能。
4.IJC:运动能抗癌实锤!运动可提高血液中抗癌蛋白的水平
doi:10.1002/ijc.33982
美国国立癌症研究院和世界癌症研究基金会发布:流行病学证据表明,定期体育活动可以预防结肠癌。目前的研究表明,进行合理水平的体育活动可以将患结肠癌的相对风险降低12%至28%。在结肠癌被诊断后,适量的体育活动会降低癌症特异性死亡率和复发的风险。
在一项新的研究中,研究者通过收集急性运动前后的人血清刺激结肠癌细胞系 (LoVo) 与非运动对照血清对癌细胞增殖的影响,观察运动引起的血清细胞因子和细胞内蛋白表达的变化。进一步探索运动抑制结肠癌细胞增殖的潜在机制途径。
急性运动增加了血清中IL-6的含量,急性有氧运动条件下的血清在体外实验中减少了结肠癌细胞增殖。与此同时,细胞内γ-H2AX水平下降,表明DNA损伤减少。研究者用重组IL-6刺激结肠癌细胞,以剂量依赖的方式减少细胞内γ-H2AX表达和细胞增殖,模仿运动的效果。因此,实验的发现表明,运动对结肠癌细胞增殖的抑制作用可能部分是由IL-6诱导的DNA损伤和修复调节驱动的。
通过研究暴露于人类血清的结肠癌细胞在急性运动前后收集的运动和细胞增殖的机制。与非运动对照血清相比,运动后获得的血清可以减少癌细胞增殖。这种效应伴随着DNA损伤标志物γ-H2AX的表达减少。DNA损伤的减少与运动诱导的血清IL-6增加有关。新发现的机制可能部分是体育活动与降低结肠癌风险之间的联系。
5.Science子刊:揭示运动预防胰岛素抵抗机制
doi:10.1126/sciadv.abl4988
在一项新的研究中,来自澳大利亚莫纳什大学的研究人员发现了一种称为NADPH氧化酶4(NADPH oxidase 4, NOX4)的酶,它是运动改善我们健康的关键。重要的是,这一发现为开发促进这种酶活性的药物以便保护人们免受衰老对代谢健康的影响提供了可能性。相关研究结果发表在2021年12月15日的Science Advances期刊上,论文标题为“Skeletal muscle NOX4 is required for adaptive responses that prevent insulin resistance”。
在这项新的研究中,这些作者发现体育活动实际上如何增强胰岛素反应性,并进而促进代谢健康。重要的是,他们所发现的对这一机制起关键作用的酶有可能通过药物加以靶向,以阻止衰老的后果,如肌肉萎缩和糖尿病。
骨骼肌中NOX4触发的过氧化氢产生是线粒体生物发生所必需的。图片来自Science Advances, 2021, doi:10.1126/sciadv.abl4988。
这些作者揭示衰老过程中骨骼肌活性氧(ROS)生成的减少在胰岛素抵抗的产生中起着重要作用。根据论文通讯作者、莫纳什大学生物医学发现研究所的Tony Tiganis教授的说法,骨骼肌不断地产生ROS,而且在运动中会增加。他说,“运动诱导的ROS驱动适应性反应,这些反应对运动的健康促进作用是不可或缺的。”
在这篇论文中,Tiganis及其团队展示了一种名为NOX-4的酶如何对运动诱导的ROS和驱动代谢健康的适应性反应至关重要。
在小鼠身上,这些作者发现NOX4在运动后在骨骼肌中增加,然后导致ROS增加,引发适应性反应,保护小鼠免受胰岛素抵抗的产生,否则会随着衰老或饮食诱导的肥胖而出现胰岛素抵抗。
重要的是,这些作者发现,骨骼肌中NOX4的水平与年龄相关的胰岛素敏感性下降直接相关。Tiganis教授说,“在这项研究中,我们发现,在动物模型中,骨骼肌NOX4的丰度随着衰老而下降,这导致了胰岛素敏感性的降低。”
6.J Appl Physiol:中年时期的有氧运动或能预防多种与年龄相关的慢性疾病
doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00243.2021
中年有氧运动或能显著影响年龄相关的大脑和心血管调节的变化,中年耐力运动员要比相同年龄组的久坐成年人有着更好的血压控制和更高的动脉弹性(一种心血管疾病风险的无创测量)。近日,一篇发表在国际杂志Journal of applied Physiology上题为“Midlife aerobic exercise and dynamic cerebral autoregulation: associations with baroreflex sensitivity and central arterial stiffness”的研究报告中,来自美国和日本的科学家们通过研究发现,由于进行了有规律的有氧运动,相比年轻成年人而言,中年的耐力运动员还会显示出相当水平的上述因素。本文研究结果提供了强有力的迹象表明,血压的控制和血管弹性程度的改善或有助于更好地改善中年人群大脑血流的调节。
中年机体动脉的僵硬程度与晚年中风和痴呆症风险增加有关,同时还会增加机体患多种年龄相关慢性疾病的风险,比如高血压、慢性肾病和糖尿病等。研究人员进行这项研究目的在于调查中年时期进行有规律的有氧运动时如何通过改善与年龄相关的大脑血流调节、短期血压控制和动脉弹性的恶化来减缓上述疾病症状的。
文章中,研究人员对20名年龄在45-64岁之间接受过10年有氧训练的中年运动员,及20名45岁以下的年轻人和20名中年久坐的成年人进行了相关研究,这项研究中,研究人员将有规律的有氧锻炼定义为中度至重度跑步、骑自行车、游泳等多模式训练。这项研究的长期效益可能意味着对人类健康的明显改善,本文研究结果也具有重要的临床意义。中年时期有规律的有氧锻炼或能帮助预防这些年龄相关的慢性疾病并能延长机体健康的寿命。
7.Nat Biotechnol:利用个性化磷蛋白组学揭示人体肌肉细胞中的哪些蛋白对增加运动后的糖吸收最为关键
doi:10.1038/s41587-021-01099-9
在一项新的研究中,来自澳大利亚悉尼大学和丹麦哥本哈根大学的研究人员开发出一种新的方法来确定我们细胞中的哪些蛋白对增加运动后的糖吸收最为关键---这是运动的一个重要好处,可以帮助维持良好的血糖水平。相关研究结果于2021年12月2日在线发表在Nature Biotechnology期刊上,论文标题为“Personalized phosphoproteomics identifies functional signaling”。
质量控制和参与者特异性的人类磷蛋白质组差异,图片来自Nature Biotechnology, 2021, doi:10.1038/s41587-021-01099-9。
通过使用称为质谱法的前沿技术直接测量人体肌肉中的蛋白,这些作者发现每个人都有自己独特的蛋白活性“指纹”。
他们开发的方法可以识别不同研究参与者的蛋白变化,就像糖吸收一样。利用这种方法,他们发现了一种机制:在胰岛素刺激后,运动增加了肌肉对糖的吸收,从而为这个复杂的过程提供了新的理解。
论文共同通讯作者、悉尼大学查尔斯-帕金斯中心的David James教授说,“我们都知道,运动对我们有好处,但它也有助于预防特定的疾病。例如,它提高了我们的肌肉在饭后从血液中吸收糖分的能力。当这个过程失败时,前驱糖尿病(prediabetes)出现了---这是许多疾病的风险因素,包括心脏病、2型糖尿病和某些类型的癌症。科学家们还不知道是什么原因导致了前驱糖尿病,但如果他们知道的话,他们就可以设计出药物,在引发疾病之前治疗这种症状。”
8.Nature:重大进展!运动后的血液增强记忆和抑制大脑炎症机制!
doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04183-x
体育运动对小鼠的大脑有好处,对人类的大脑也有好处。在小鼠、人类和实验室玻璃器皿中进行的大量研究已经明确了这一点。如今,在一项新的研究中,来自美国斯坦福大学医学院的研究人员指出有可能将进行马拉松跑步的小鼠(下称马拉松小鼠)所享有的大脑益处转移给它们的久坐不动的同伴(下称久坐小鼠)身上。他们发现来自大量运动的年轻成年小鼠(即马拉松小鼠)的血液对年龄相同、久坐小鼠的大脑有益。马拉松小鼠血液中的一种蛋白似乎是这种益处的主要原因。相关研究结果于2021年12月8日在线发表在Nature期刊上,论文标题为“Exercise plasma boosts memory and dampens brain inflammation via clusterin”。
这一发现可能会开启一扇治疗之门,通过控制那些不怎么运动的人的大脑炎症,有可能降低他们患神经退行性疾病的风险或减缓其进展。
在这项新的研究中,这些作者比较了同年龄的马拉松小鼠和久坐小鼠的血液样本。他们表明,输注来自马拉松小鼠的血液可以减少久坐小鼠的神经炎症,并改善其认知能力。此外,他们还分离出了一种血源性蛋白,它似乎在运动的抗神经炎症效果中发挥了重要作用。
9.AJPM:挑战指南!每周可能需要运动5小时才可避免中年高血压
doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2020.12.018
目前,美国心脏病学会/美国心脏协会(ACC/AHA)指南推荐,成年人每周至少应该有两个半小时的中等强度运动。然而,在成年后预防高血压的最佳体育锻炼剂量仍未确定。近日,发表在American Journal of Preventive Medicine杂志的一项研究表明,年轻人必须加强锻炼,以减少患高血压几率。每周五小时中等强度的运动可以预防中年高血压,尤其是在30岁,40岁和50岁持续运动的情况下。
该研究旨在使用2017年ACC/AHA确定的高血压阈值,即130/80 mmHg,评估成人运动水平与高血压发作之间的关联。在这项研究中,研究人员对来自美国冠状动脉风险发展研究(CARDIA)的5115名年龄在18岁到30岁的参与者进行分析,详细收集了参与者的运动习惯,病史,吸烟状况,饮酒状况,监测血压和体重以及胆固醇和甘油三酸酯水平。使用线性混合模型为每个参与者开发了个性化的体育活动轨迹。
结果显示,黑人的运动水平的快速下降,导致更多的高血压。在按种族和性别分类的四个组中,黑人男性在成年初期最为活跃,其运动程度略高于白人,并且显着高于黑人女性和白人女性。但是到了60岁时,黑人的运动量从高峰时的560个运动单位下降到了约300个单位,相当于每周建议的至少两个半小时的中等强度运动的最低水平。这比白人男性(大约430单位)少得多,仅略多于白人女性(大约320单位)运动量。在这四个组中,黑人女性在整个研究期间的运动最少,并且随着时间的流逝下降到大约200个单位。另外,在20至30岁时,白人男性的运动量下降,并一直稳定在40岁左右。白人女性的运动量徘徊在380个运动单位,在30岁左右时开始下降,并一直保持到60岁。
10.EJSS:运动能够降低儿童轻度炎症反应
doi:10.1080/17461391.2021.1892830
根据芬兰最近的一项研究,儿童进行轻快且有力的体育锻炼可以有限抑制因肥胖导致的轻度炎症。该研究还报告说,饮食质量与轻度炎症质检没有独立的联系。该研究结果基于东芬兰大学进行的儿童体育锻炼与营养研究(PANIC),相关结果发表在《European Journal of Sport Science》杂志上。
长期的轻度炎症会增加II型糖尿病和心血管疾病的风险。超重和肥胖会导致轻度发炎,但长期以来,我们对儿童生活方式的改变如何影响轻度炎症反应仍知之甚少。
文章作者之一,韦斯屈莱大学运动与健康科学学院的Eero Haapala博士解释说:“我们的研究表明,身体活动能力强的孩子比身体活动能力弱的孩子炎症反应更轻。此外,我们的结果表明,高水平的剧烈运动以及较低的久坐时间对控制炎症的积极影响,部分程度是由于其对身体成分的影响而导致的。”
研究人员发现炎症反应较强的儿童往往具有以下几个特征:体育活动水平低,饮食质量差,体脂百分比高。Haapala说:“我们的研究结果表明,增加体育锻炼和减少久坐时间是预防儿童期低度炎症的关键。它们对于超重的儿童而言尤其重要。”
该研究调查了390名6至8岁儿童的体育锻炼,久坐时间,饮食质量,体脂含量和低度炎症之间的关系。通过结合使用DXA设备的心率和运动传感器以及身体成分来测量体育活动和久坐时间。使用从血液样本中测得的生物标志物评估了炎症反应的强度。(生物谷 Bioon.com)
AHA会议免疫疗法
分析
对领域进行一次全面的分析。
登录
或

Eureka LS:
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用

