更新于:2024-11-01
水解酶 x NAD+
更新于:2024-11-01
关联
1
项与 水解酶 x NAD+ 相关的药物作用机制 水解酶抑制剂 [+1] |
在研机构 |
原研机构  南京艾美斐生物医药科技有限公司初创企业 南京艾美斐生物医药科技有限公司初创企业 |
非在研适应症- |
最高研发阶段临床申请 |
首次获批国家/地区- |
首次获批日期1800-01-20 |
100 项与 水解酶 x NAD+ 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 水解酶 x NAD+ 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 水解酶 x NAD+ 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
107
项与 水解酶 x NAD+ 相关的文献(医药)2024-07-01·International Journal of Biological Macromolecules
Comprehensive review on glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase: A critical immunometabolic and redox switch in insects
Review
作者: Chen, Junfan ; Feng, Tianxiang ; Ghani, Muhammad Usman ; Wu, Qishu ; Khosravi, Zahra ; Cui, Hongjuan ; Yang, Zihan
2024-07-01·Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and transketolase: Key factors in breast cancer progression and therapy
Review
作者: Zhen, Xin ; Sun, Jing ; Hao, Shiming ; Zhang, Mingyu
2024-06-25·Zhen ci yan jiu = Acupuncture research
热补针法对类风湿关节炎寒证家兔膝关节滑膜组织缺氧诱导因子1α和糖酵解活性的影响.
Article
作者: Chen, Ping ; Zhang, Feng-Fan ; Li, Fu-Xin ; Liu, Li-Mei ; Zhang, Xing-Hua ; Jing, Wei-Yao ; DU, Xiao-Zheng ; Li, Xiang-Jun ; Liu, Cui
分析
对领域进行一次全面的分析。
登录
或
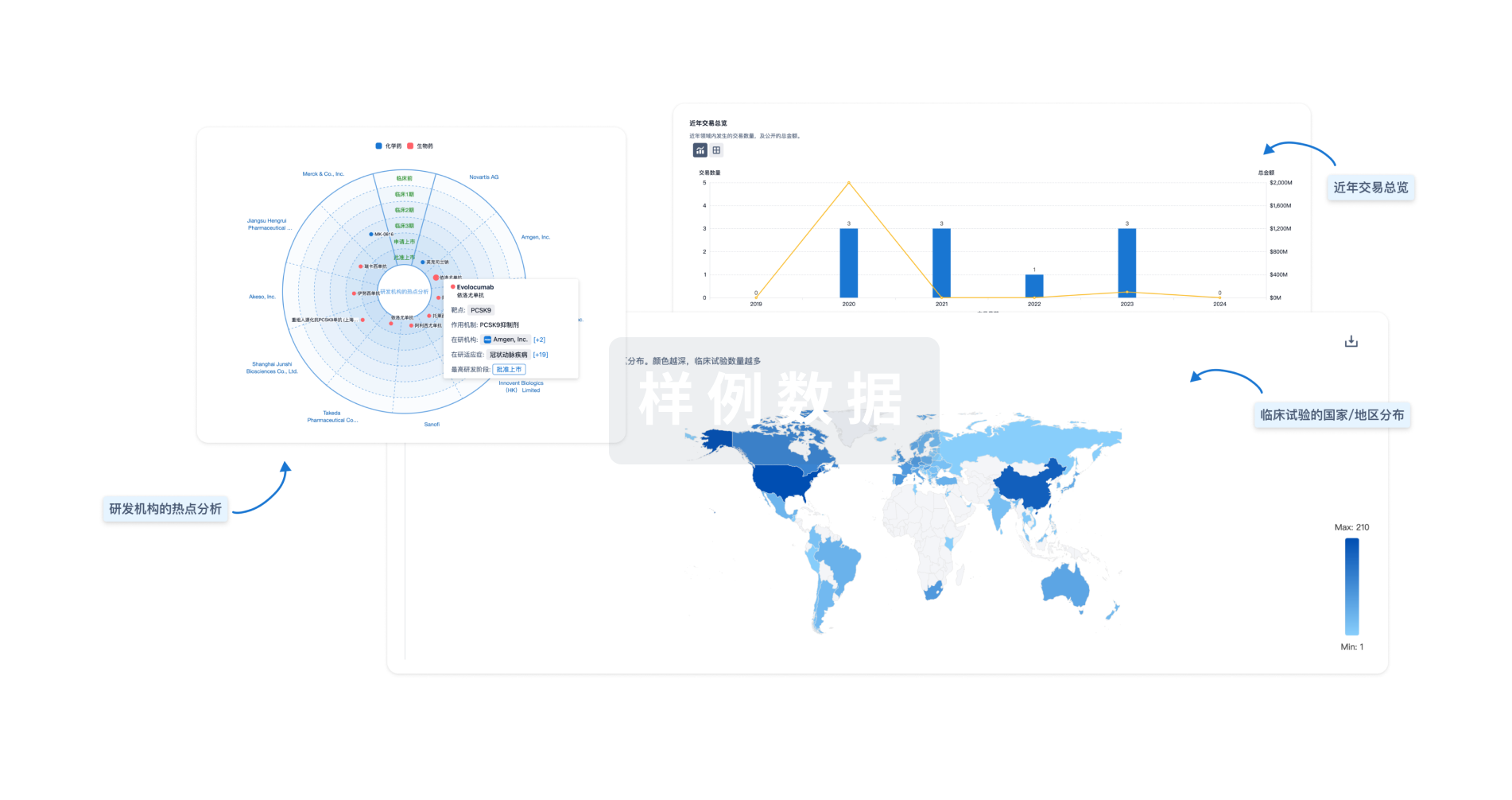
标准版
¥16800
元/账号/年
新药情报库 | 省钱又好用!
立即使用
来和芽仔聊天吧
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用