预约演示
更新于:2025-05-07
TAS1R3
更新于:2025-05-07
基本信息
别名 Sweet taste receptor T1R3、T1R3、TAS1R3 + [4] |
简介 Putative taste receptor. TAS1R1/TAS1R3 responds to the umami taste stimulus (the taste of monosodium glutamate). TAS1R2/TAS1R3 recognizes diverse natural and synthetic sweeteners. TAS1R3 is essential for the recognition and response to the disaccharide trehalose (By similarity). Sequence differences within and between species can significantly influence the selectivity and specificity of taste responses. |
关联
1
项与 TAS1R3 相关的药物靶点 |
作用机制 TAS1R3 modulators |
在研适应症 |
非在研适应症- |
最高研发阶段临床前 |
首次获批国家/地区- |
首次获批日期1800-01-20 |
100 项与 TAS1R3 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 TAS1R3 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 TAS1R3 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
684
项与 TAS1R3 相关的文献(医药)2025-08-01·Food Chemistry
From prediction to design: Revealing the mechanisms of umami peptides using interpretable deep learning, quantum chemical simulations, and module substitution
Article
作者: Ji, Huizhuo ; Zuo, Min ; Kong, Jianlei ; Su, Lijun ; Li, Jian ; Yan, Wenjing ; Ma, Zhenren ; Zhang, Qingchuan
2025-06-01·Food Chemistry
Identification and taste presentation characteristics of umami peptides from soybean paste based on peptidomics and virtual screening
Article
作者: Jiang, Jinhui ; Liu, Qu ; Pan, Guoyang ; Tong, Xing ; An, Feiyu ; Wang, Yaqi ; Tao, Dongbing ; Deng, Li ; Wu, Junrui ; Ji, Shuaiqi ; Yang, Ning ; Wu, Rina
2025-06-01·Food Chemistry
Cross-modal correspondence between visual information and taste: Deciphering the relationship between color and umami using hydrolysates of salmon head as a case study
Article
作者: Ye, Jing ; Chen, Qianqian ; Yuan, Xuan ; Wu, Jiajia ; Shi, Cui ; Wei, Lai ; Lu, Yanbin ; Dai, Zhiyuan
1
项与 TAS1R3 相关的新闻(医药)2023-12-18
·生物谷
血糖高了怎么办?大多数人的第一反应是控制饮食、吃降糖药、打胰岛素,有条件再买个血糖仪监测血糖。糖尿病控制真的有这么容易吗?血糖仪监测空腹血糖正常就可以一劳永逸了吗?
血糖高了怎么办?大多数人的第一反应是控制饮食、吃降糖药、打胰岛素,有条件再买个血糖仪监测血糖。糖尿病控制真的有这么容易吗?血糖仪监测空腹血糖正常就可以一劳永逸了吗?
根据2021年12月6日,国际糖尿病联盟(IDF)官网发布的最新报告,全球约5.37亿20-79岁的成年人患有糖尿病,平均每10个人中就有1位糖尿病患者。预计到2030年该数字将上升至6.43亿,2045年将上升至7.83亿[1]。我国目前是中国糖尿病患病人数最多的国家。且根据全国性横断面调查结果显示,我国糖尿病患者总体血糖达标率为31.7%~39.7%,处于较低水平,糖尿病治疗及管理形势刻不容缓[1]。
据IDF统计,世界范围内死亡率的主要驱动因素即糖尿病。血糖控制不佳是导致糖尿病患者大血管和微血管受损的关键因素,可造成心、脑、肾、眼和周围神经等并发症,极大增加死亡风险,血糖控制达标有助于降低并发症风险,成为管理糖尿病的基石。
在医学上,餐后血糖(PPG)被用作糖尿病的诊断标准之一。一般来说,正常人餐后2小时的血糖应低于7.8mmol/L。用餐2小时后血糖升高在2型糖尿病患者中较常见。
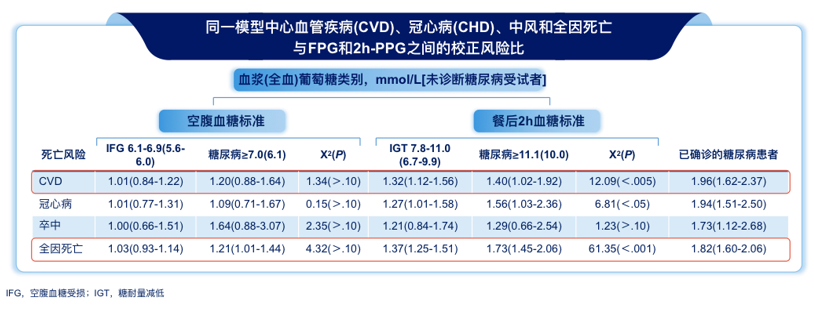
一项研究分析了欧洲10个前瞻性队列研究的结果显示:餐后2h血糖(2h-PPG)较空腹血糖(FPG)能更好的预测CVD及全因死亡风险!
印度尼西亚艾尔朗加大学的一项描述性分析研究和横截面设计,对2014年1月至10月期间来到Dr.Soetomo医院的2型糖尿病(T2DM)患者进行随访。一种采用连续抽样的方式,将符合纳入标准的每位患者纳入研究样本,每组的最小样本量为79例,空腹血糖组和餐后2小时血糖组各采集102个样本。
数据分析显示:
FPG水平、2h-PPG水平与心血管疾病的发病率之间存在显著相关性(p=0.000)。
T2DM患者中高、低FPG水平与CVD表现的患病率为13.1,即高FPG水平患者出现CVD表现的风险是低FPG水平患者的13.1倍。FPG水平中等的患者出现CVD表现的风险是FPG水平低的患者的2.6倍[1]。
T2DM患者2h-PPG高、低水平与CVD表现的患病率为7.2,即2h-PPG高水平患者出现CVD表现的风险是2hPPG水平低的患者的7.2倍。中等2h-PPG水平的患者出现CVD表现的风险比低2h-PPG水平的患者高1.4倍[1]。
糖尿病肾病(DKD)是糖尿病最常见的微血管疾病并发症,占糖尿病并发症的35%。目前,我国三分之一以上的糖尿病患者死于肾病肾衰竭和尿毒症等。餐后血糖、空腹胰岛素(FINS)、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)与T2DM患者糖尿病肾病的发生相关,控制PPG、FINS、HbA1c水平可以有效预防糖尿病肾病的发生。
一个2型糖尿病大鼠的组织病理学分析显示,PPG和FINS与糖尿病肾病进展相关,血清PPG水平阳性与急性肾损伤相关(P< 0.05),进一步研究发现,PPG可通过抑制细胞凋亡导致肾损伤[2]。
综上所述,PPG、FINS、HbA1c是影响糖尿病患者DN发生的因素。
糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)是葡萄糖与蛋白质发生非酶促反应中形成的产物,合成速率与血糖水平呈正相关,为糖尿病患者长期血糖控制的权威指标。研究发现,HbA1c达标需要同时关注空腹和餐后血糖,两者缺一不可!
一项关于空腹及餐后血糖与糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)在血糖控制评价中的相关性、系统评价及Meta分析结果,通过MEDLINE/PubMed、Google学术、Cochrane中央图书馆和纳入研究的参考文献列表中检索了126篇文章。所有纳入的文章都对空腹和餐后血糖与HbA1c水平进行了比较,结果显示PPG与HbA1c密切相关,对总体血糖控制有显著贡献。这与当代证据一致,表明PPG与糖尿病并发症的发生之间存在密切关系。在缺乏HbA1c的情况下,监测PPG比单独监测FPG更有助于实现最佳血糖控制和预防长期糖尿病并发症[3]。
糖尿病的综合治疗包括五个方面:饮食、运动、教育、监测和药物,其中饮食治疗是重点。
饮食及营养因素对餐后血糖具有显著影响。与欧美人群相比,中国T2DM人群更易出现餐后高血糖,中国T2DM患者主食中精制米面制品的占比高达 82.15%。精制米面制品属于高碳水化合物,其对血糖的影响反应速度最快,升糖时间最短,升糖幅度最高。
在工业发达的现况下,人工甜味剂因其甜度高、热量低的特点被广泛用作食品添加剂,各个国家和地区的食品、医药行业都可见到其身影,一些商家甚至鼓吹其可作为糖尿病患者的糖类代替品。长期食用人工甜味剂可能会增加体重上升和PPG升高的风险,继而导致糖耐量下降和糖尿病患病率升高。对于糖尿病患者来说人工甜味剂也不能作为嘴馋时的选择!
Qing Shi等人选择人工甜味剂三氯蔗糖作为实验材料,将小鼠暴露于不同浓度的三氯蔗糖下12周,发现小鼠的PPG显著升高,肠道甜味受体的表达也相应增加,且暴露于浓度等于或高于0.33 g/L的三氯蔗糖的小鼠PPG显著增加[4]。
大量服用三氯蔗糖导致甜味受体和葡萄糖转运蛋白过度表达,这一作用的机制可能是人工甜味剂与肠道内分泌细胞中的甜味受体Tas1r2/Tas1r3结合并上调Slc5a1和Slc2a2的结果[4]。
目前临床上用于治疗糖尿病的药物包括胰岛素、磺脲类、双胍类、α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂、胰岛素类似物、格列奈类、噻唑烷二酮类、DPP‐4i、SGLT2i和GLP-1受体激动剂等,可有效对FPG和/或PPG进行控制。
比如德谷门冬双胰岛素同时含有基础与餐时胰岛素组分(70%德谷胰岛素+30%门冬胰岛素),可以同时兼顾FPG与PPG。
总而言之,对糖尿病患者尤其是2型糖尿病(T2DM)患者,应更多关注餐后血糖控制,在血糖管理上应采取可兼顾餐后血糖的降糖方案!
参考文献
[1]Wironegoro P M Z L .HIGH BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL INCREASE CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE RISKIN TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS[J].Folia Medica Indonesiana,2017,52(2):127-130.
[2]Li Z F X .Relationship Between Postprandial Blood Glucose, Fasting Insulin, and Glycated Hemoglobin Levels and Early Diabetic Nephropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus[J].Proceedings of Anticancer Research,2023,7(2):33-38.
[3]Tilahun K B E K .Correlation of fasting and postprandial plasma glucose with HbA1c in assessing glycemic control; systematic review and meta-analysis.[J].Archives of public health = Archives belges de sante publique,2015,73(1):43.
[4]Xiangyang S L L Q S .Sucralose regulates postprandial blood glucose in mice through intestinal sweet taste receptors Tas1r2/Tas1r3.[J].Journal of the science of food and agriculture,2023.
刘俊伟
广州市中西医结合医院内分泌科主治医师
毕业于广州医科大学临床医学系,于2007年在中国人民解放军南部战区总医院内分泌科工作11年,师承邓爱民教授及金文胜教授,致力于甲状腺放射碘治疗、甲状腺粘液性水肿治疗及糖尿病足诊治工作。
2018年至今就职于广州市中西医结合医院内分泌科,擅长内分泌科常见病如糖尿病及其并发症的诊治,甲状腺疾病、痛风、性腺、肾上腺等相关疾病的诊断与治疗。
临床结果临床研究
分析
对领域进行一次全面的分析。
登录
或

生物医药百科问答
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用
