/ Not yet recruitingN/AIIT The PROmoting Pain Self-Management (PROs) Trial: Holistic Pain Care in the Military Health System
The goal of this study is to improve pain care in the MHS by identifying effective, whole-person, non-pharmacologic interventions for persons with chronic musculoskeletal pain. The investigators will evaluate two promising, evidence-based holistic health interventions and compare them to usual care.
A Non-Invasive, Non-Sedating Device to Mitigate Motion Sickness and Spatial Disorientation
The purpose of this research study is to learn how a wearable nerve stimulation device, the Spark Biomedical's Sparrow Ascent System™, impacts the development of spatial disorientation and/or motion sickness in a healthy population.
Spatial disorientation is when there is a "mismatch" between where a person is, and where the sense organs in their body tell them where they are. These sense organs include the inner ear (the vestibular system), the eyes (the visual system), the sense of where one's legs, back, and neck are (proprioceptive system), and one's higher thinking (cognitive centers). If spatial disorientation is severe or occurs in motion-naïve individuals, spatial disorientation can lead to motion sickness.
The Sparrow Ascent System™ is a wearable, battery-operated transcutaneous auricular (ear) neurostimulation (tAN) device. This means that it uses electrical pulses to stimulate branches of nerves on and/or around the ear, specifically the "vagus" and "trigeminal" nerves. These nerves are also responsible for your sensation of nausea and your heart rate (vagus nerve), as well as headaches (trigeminal nerve). The Sparrow System utilizes a flexible earpiece with embedded hydrogel electrodes that stick to the skin, the earpiece is disposable after use. This device is already Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for use in humans and is safely used for control of symptoms in a variety of other medical conditions, such as opioid withdrawal and acute stress reaction. In this study, we will determine if the Sparrow Ascent System™ impacts the development of spatial disorientation or motion sickness.
/ Active, not recruitingN/AIIT Visual Outcomes Comparison of LASIK Using Wavefront Optimized and SMILE
The study will compare the 6-month visual outcomes (i.e., visual acuity, contract sensitivity, higher order aberrations), quality of vision (i.e., double vision, glare, starburst, halos, etc.) and dry eye symptoms of patients undergoing contralateral LASIK using iDesign and SMILE surgery.
100 项与 59th Medical Wing 相关的临床结果
0 项与 59th Medical Wing 相关的专利(医药)
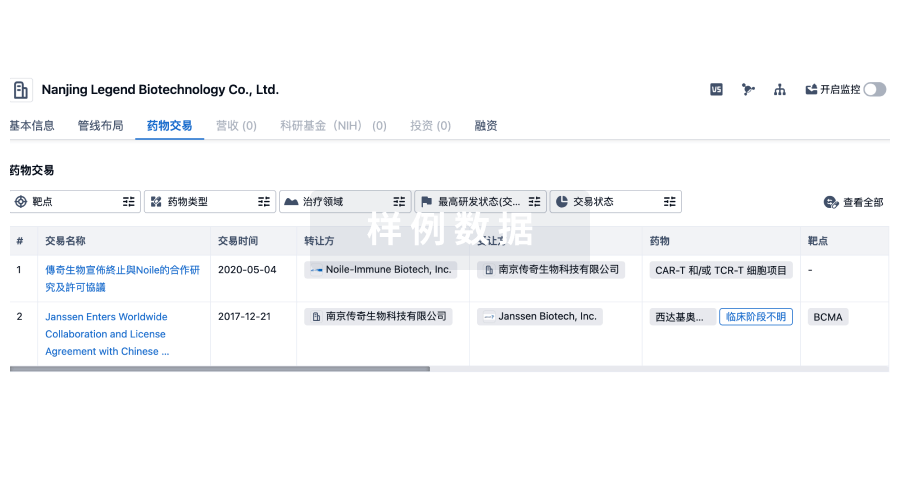
100 项与 59th Medical Wing 相关的药物交易
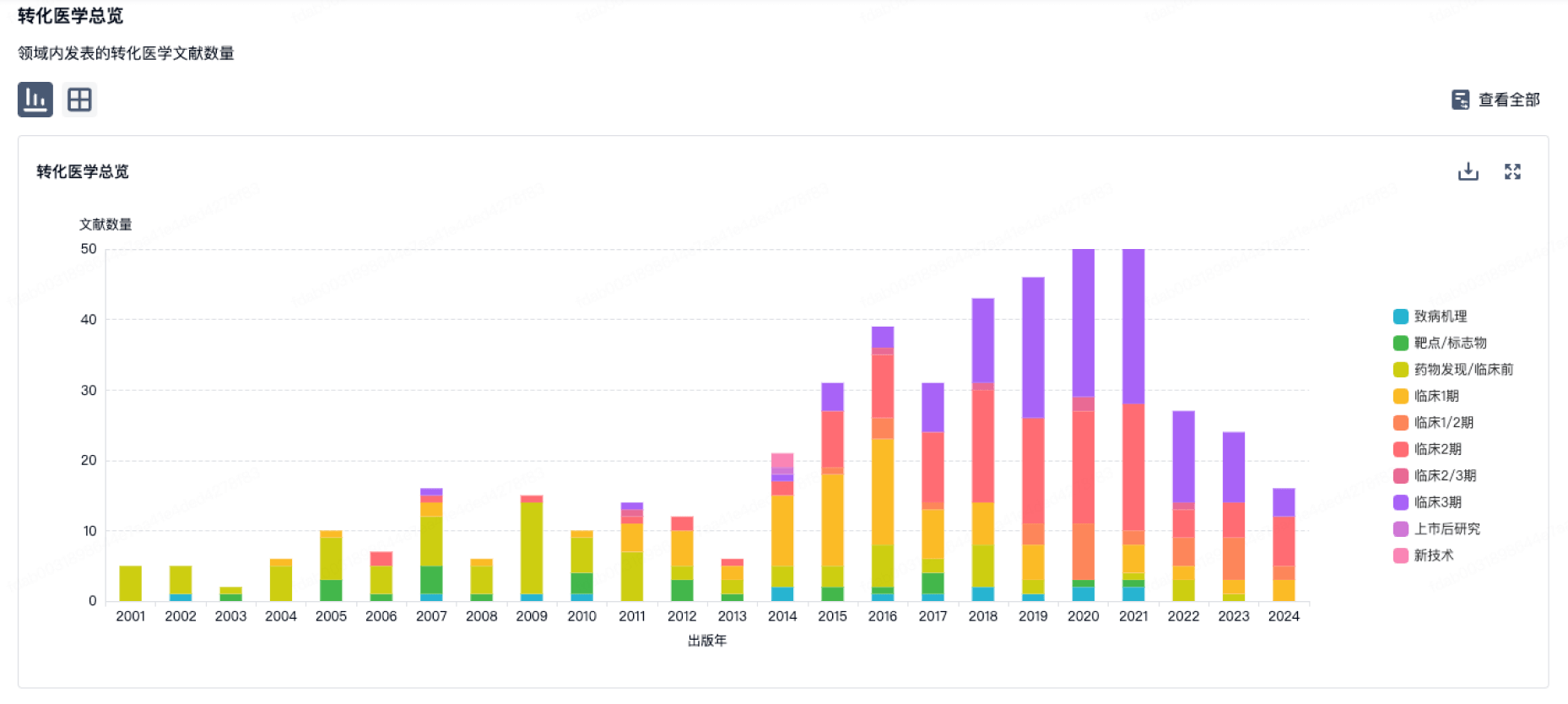
100 项与 59th Medical Wing 相关的转化医学