更新于:2024-11-01
Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias
子公司|
Mexico
子公司|
Mexico
更新于:2024-11-01
概览
关联
31
项与 Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias 相关的临床试验Assessment of Gastrointestinal Dysfunction Through GIDS Scale and Intestinal Damage Biomarkers in Critically Ill Patients Undergoing Aortic Surgery and Its Association With Clinical Outcomes.
The goal of this observational study is to determine the association of gastrointestinal dysfunction through the Gastrointestinal Dysfunction Scale (GIDS) tool and serum concentrations of citrulline and Intestinal fatty-acid binding protein (I-FABP) with primary [calories received, protein received, parenteral nutrition requirement and 28-day mortality in the intensive care unit (ICU)] and secondary (development of pneumonia, surgical and cardiovascular complications in the ICU, length of hospital and ICU stay, duration of mechanical ventilation) clinical outcomes in critically ill patients undergoing aortic surgery.
开始日期2024-07-23 |
申办/合作机构 |
Applying Artificial Intelligence to Identify Subphenotypes of Acute Kidney Injury in Mexican Patients With Severe COVID-19
The goal of this observational study was to identify subphenotypes of acute kidney injury patients with COVID-19, and the investigators analyzed their impact on mortality. The study included demographic and clinical variables of the participants. The implementation of Machine Learning algorithms and Artificial Intelligence methods are used, and some specific implementations were designed for the analysis, where each group was characterized by traditional statistical methods.
开始日期2024-06-18 |
Phase II/III Parallel, Double-blind, Non-inferiority Study With Active Control, to Evaluate the Immunogenicity and Safety of a Booster Immunization Scheme With a Single Intramuscular Dose of the Recombinant Vaccine Against SARS-CoV-2
This is a phase II/III parallel, double-blind, active-controlled, non-inferiority study to evaluate immunogenicity and safety of a booster immunization scheme of a single intramuscular dose of the recombinant vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 (AVX/COVID-12 vaccine) based on live recombinant Newcastle disease virus (rNDV) vector in healthy adults with a history of vaccination against COVID-19. The study is divided into two phases with immuno-bridging and 3000 healthy subjects showing evidence of prior immunity to SARS-CoV-2 are estimated to enrol. To verify non-inferiority in a determined number of subjects an intramuscular dose of the COVID-19 vaccine (ChAdOx-1-S[recombinant]) shall be used as active control in originally randomised subjects. The study shall be carried out in several sites of clinical research in Mexico.
开始日期2022-11-09 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
1,129
项与 Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias 相关的文献(医药)2024-10-01·Current Allergy and Asthma Reports
Impact of Enolase in Allergic Disease
Review
作者: Teran, Maria G ; Teran, Luis M ; Morales-Amparano, Martha Beatriz ; Huerta-Ocampo, José Ángel
2024-10-01·Nature Immunology
Dual blockade of IL-10 and PD-1 leads to control of SIV viral rebound following analytical treatment interruption
Article
作者: Wallace, Chelsea ; Ten-Caten, Felipe ; Paiardini, Mirko ; Howell, Bonnie J ; Chan, Chi Ngai ; Raghunathan, Gopalan ; Ribeiro, Ruy M ; Gorman, Daniel M ; Harper, Justin ; Estes, Jacob D ; Jean, Sherrie ; Pereira Ribeiro, Susan ; Pelletier, Adam-Nicolas ; Nguyen, Kevin ; Xavier de Medeiros, Giuliana ; Wu, Guoxin ; Micci, Luca ; Soudeyns, Hugo ; Sekaly, Rafick P ; Silvestri, Guido ; Rimmer, Eric ; Lifson, Jeffrey D ; Hazuda, Daria J ; Balderas, Robert ; Hoang, Timothy ; Del Rio Estrada, Perla Mariana ; Pastuskova, Cinthia ; Pacheco Sanchez, Gabriela ; Strongin, Zachary ; Ghneim, Khader
2024-09-01·Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology
17β-estradiol induces hyperresponsiveness in guinea pig airway smooth muscle by inhibiting the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase
Article
作者: Flores-Soto, Edgar ; Sommer, Bettina ; Pérez-Plascencia, Carlos ; Romero-Martínez, Bianca S ; Montaño, Luis M ; Reyes-García, Jorge ; Santiago-de-la-Cruz, José A ; Rivero-Segura, Nadia A ; Solís-Chagoyán, Héctor ; Arredondo-Zamarripa, David ; Lemini, Cristina
100 项与 Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
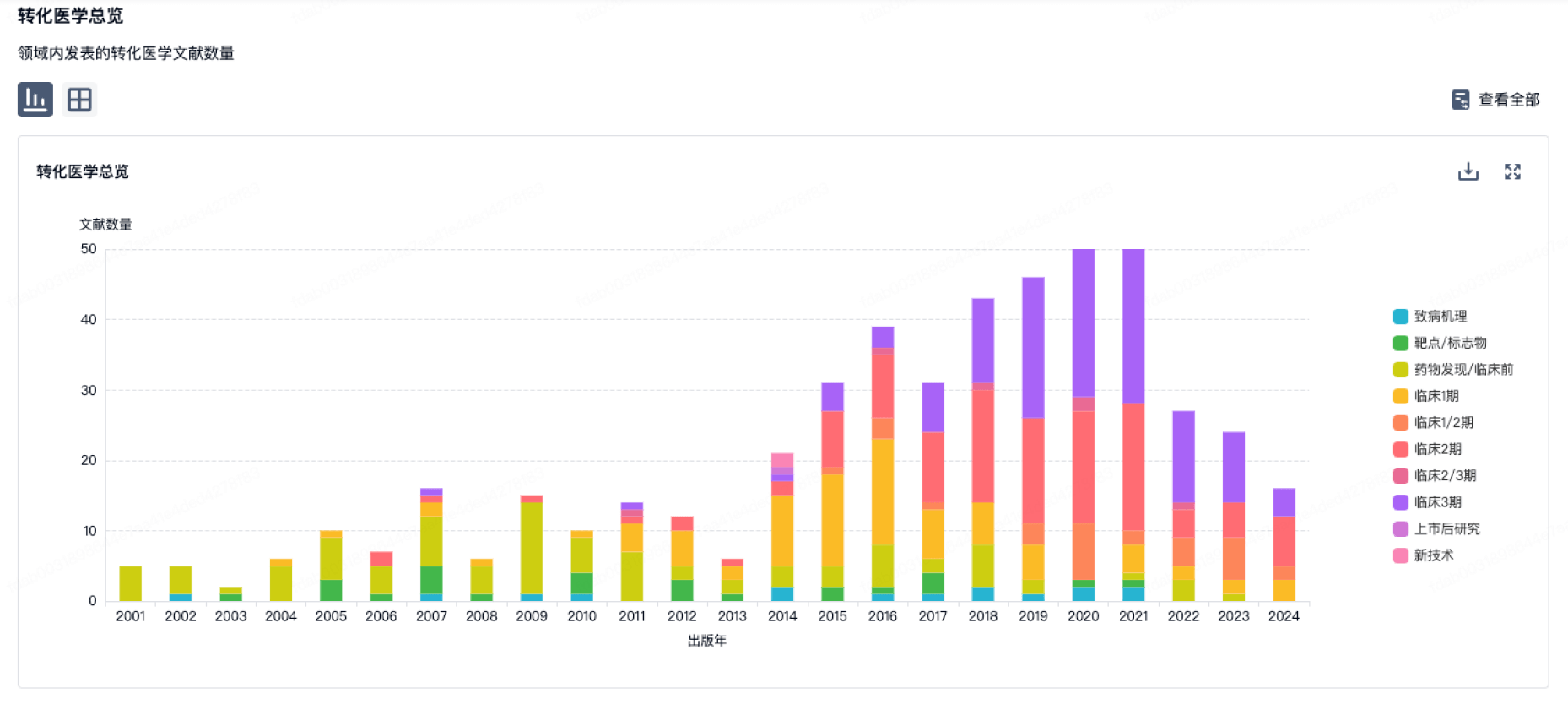
100 项与 Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
组织架构
使用我们的机构树数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

管线布局
2024年11月20日管线快照
无数据报导
登录后保持更新
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
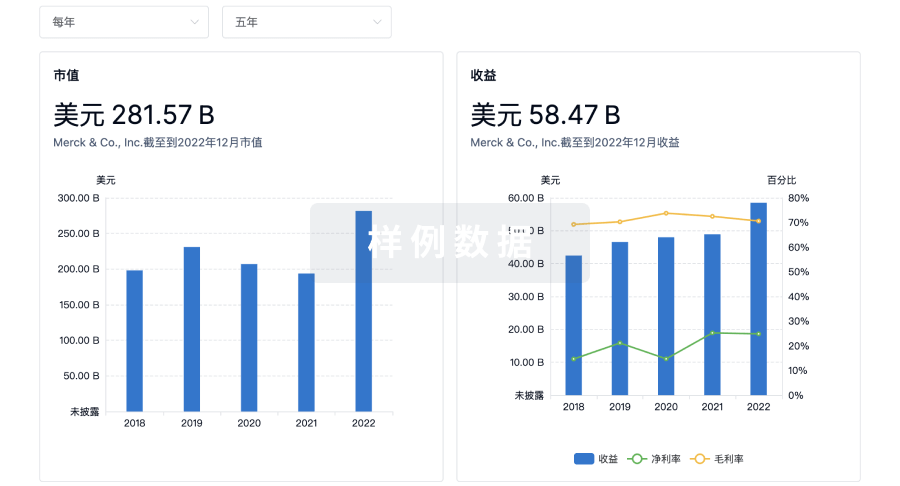
营收
使用 Synapse 探索超过 36 万个组织的财务状况。
登录
或
科研基金(NIH)
访问超过 200 万项资助和基金信息,以提升您的研究之旅。
登录
或

投资
深入了解从初创企业到成熟企业的最新公司投资动态。
登录
或

融资
发掘融资趋势以验证和推进您的投资机会。
登录
或

标准版
¥16800
元/账号/年
新药情报库 | 省钱又好用!
立即使用
来和芽仔聊天吧
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用
