预约演示
更新于:2025-01-23
Shaheed Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto Medical University
2013|
Pakistan
2013|
Pakistan
更新于:2025-01-23
概览
关联
34
项与 Shaheed Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto Medical University 相关的临床试验NCT06525844
Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes With the Use of I-PRF in Mature Permanent Teeth With Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis : A Randomized Control Trial
Root canal therapy (RCT) is a classical and effective treatment that is currently utilised in dental practice, offering high success rates for pulp and periapical diseases; however, teeth after RCT are susceptible to altered pulp defence and sensory function, even fractures, as a consequence of pulp loss. Furthermore, several studies have highlighted that the actual failure rate of standard root canal treatments performed in general practice is significantly higher than expected . Moreover, these treatments are lengthy and costly and are often subject to retreatment .Inherent in this procedure(rct) is loss of dental hard tissue and subsequent weakening of the treated tooth,making them more prone to fracture. Therefore, less invasive alternative strategies could be used to treat pulpitis, even when irreversible.
Murray et al. proposed the term "Regenerative endodontic treatment (RET)" in 2007, based on a tissue engineering concept (stem cells, biomimetic scaffolds, and bioactive growth factors). The 2016 American Association of Endodontists (AAE) guidelines formally defined RET as a collection of "biologically based procedures designed to replace damaged tooth structures, including dentine and root structures, as well as cells of the pulp-dentine complex"
Murray et al. proposed the term "Regenerative endodontic treatment (RET)" in 2007, based on a tissue engineering concept (stem cells, biomimetic scaffolds, and bioactive growth factors). The 2016 American Association of Endodontists (AAE) guidelines formally defined RET as a collection of "biologically based procedures designed to replace damaged tooth structures, including dentine and root structures, as well as cells of the pulp-dentine complex"
开始日期2024-08-01 |
NCT06176430
Comparison of Twice Weekly Versus Daily Iron Therapy in Treating Anemia in Children With Cerebral Palsy
a randomized clinical trial to compare the effect of twice weekly versus daily iron therapy in treating anemia in children with cerebral palsy, to be conducted at Department of pediatric medicine children's hospital PIMS islamabad.
开始日期2024-02-01 |
NCT06234020
Frequency of Vertebro-spinal Anomalies in Patients Presenting With Ano-rectal Malformations
To determine the frequency of different vertebrospinal anomalies in patients with ARM
开始日期2024-01-16 |
100 项与 Shaheed Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto Medical University 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 Shaheed Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto Medical University 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
247
项与 Shaheed Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto Medical University 相关的文献(医药)2024-05-23·Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics
Design and validation of a novel multi-epitopes vaccine against hantavirus
Article
作者: Irfan, Muhammad ; Ahmad, Sajjad ; Waheed, Yasir ; Khan, Saifullah ; Sajjad, Muhammad ; Almanaa, Taghreed N ; Ullah, Asad ; Hassan, Muhammad ; Mubarak, Ayman
2024-02-08·Cureus
Evolving Spectrum of Dengue: A Two-Year Experience From a Tertiary Care Hospital in Pakistan
Article
作者: Arif, Saba Ali ; Syed, Fibhaa ; Mansoor, Valeed B ; Arif, Mohammad Ali ; Usman, Muhammad
2023-12-09·Cureus
Paget’s Disease of Bone: A Rare Incidence in Early Adult Life in Pakistan, Southeast Asia
作者: Rizvi, Ali H ; Mobeen, Hafsa ; Farhan, Ahmed ; Saghir, Hina ; Ahmad, Afaq
100 项与 Shaheed Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto Medical University 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 Shaheed Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto Medical University 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
组织架构
使用我们的机构树数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

管线布局
2025年04月26日管线快照
无数据报导
登录后保持更新
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
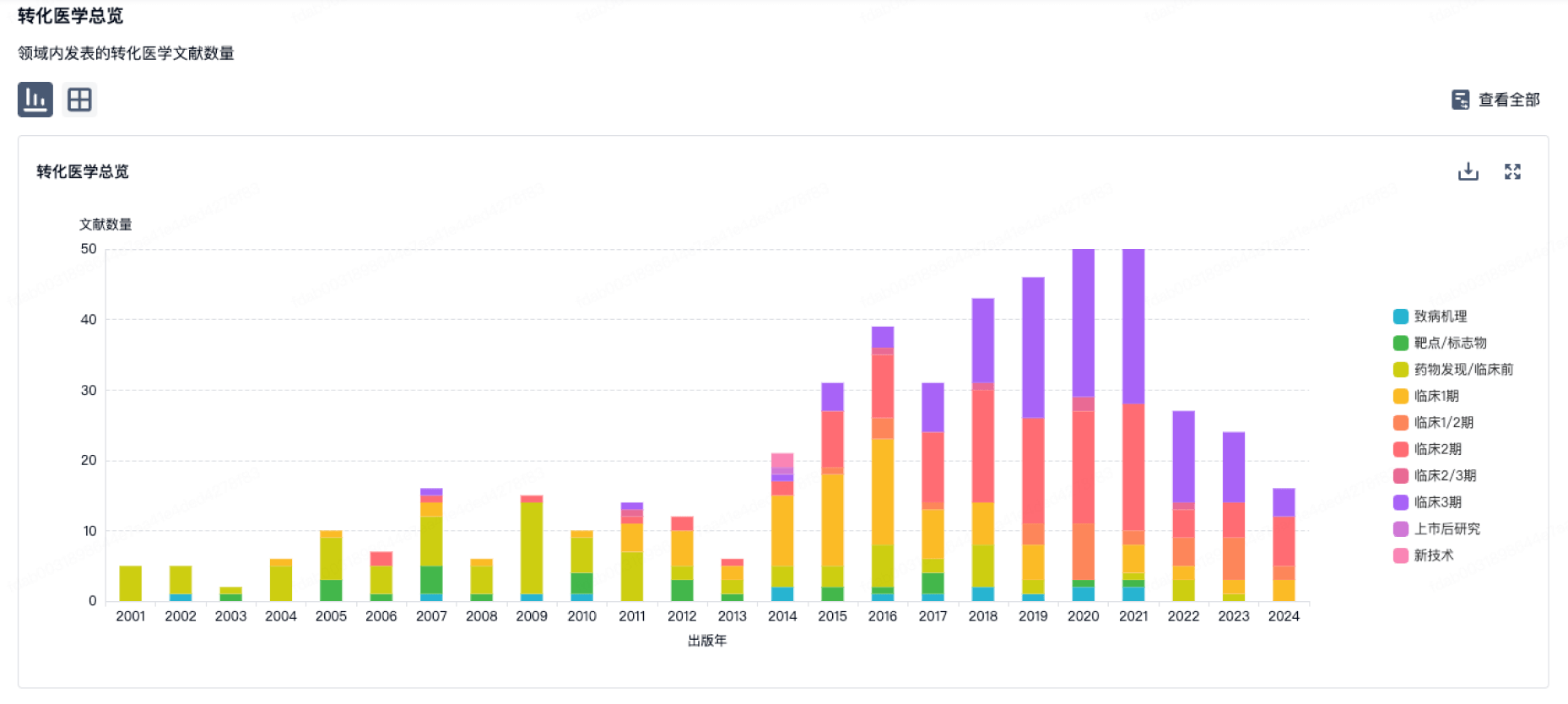
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
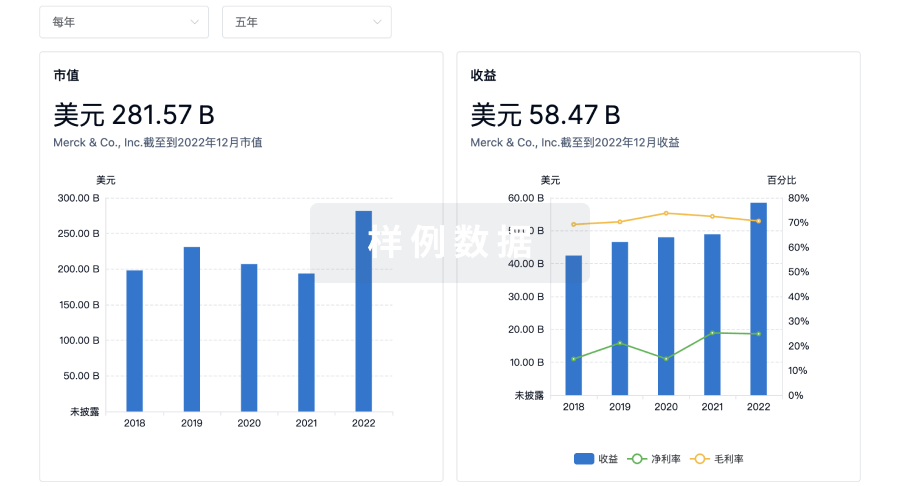
营收
使用 Synapse 探索超过 36 万个组织的财务状况。
登录
或
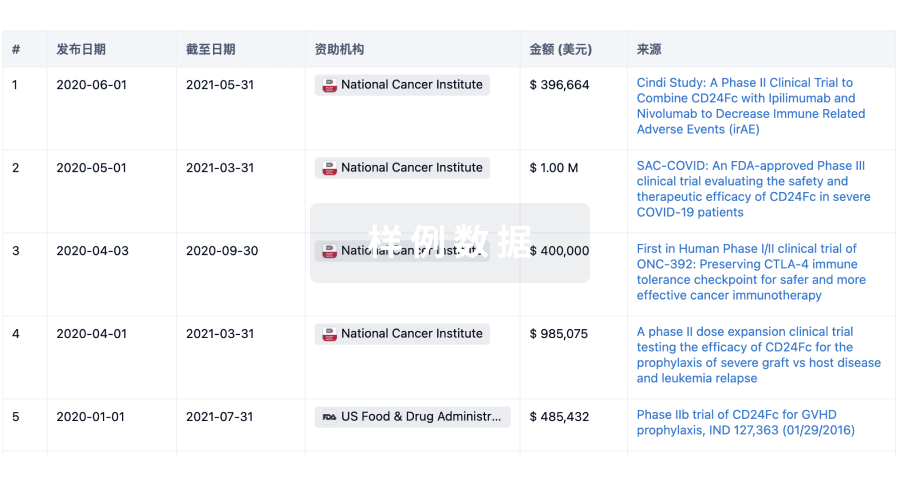
科研基金(NIH)
访问超过 200 万项资助和基金信息,以提升您的研究之旅。
登录
或
投资
深入了解从初创企业到成熟企业的最新公司投资动态。
登录
或
融资
发掘融资趋势以验证和推进您的投资机会。
登录
或
来和Eureka LS聊天吧
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用