更新于:2024-11-01

German Oncology Center
更新于:2024-11-01
概览
关联
10
项与 German Oncology Center 相关的临床试验Whole-pelvis Hypofractionated Radiotherapy Combined With Dose-escalation to the Prostate and Androgen Deprivation Therapy in Primary Localized, NCCN and MMAI High-risk Prostate Cancer - a Prospective, Single-arm, Phase II Study
A prospective, single-arm phase II study is the individualization of RT for patients with high-risk localized PCa based on multimodal artificial intelligence (MMAI). All patients will receive the current standard of care: (i) a dose escalation to the prostate via HDR brachytherapy, (ii) two years of ADT and (iii) whole-pelvis UHF-RT (5 fractions).
开始日期2024-09-16 |
申办/合作机构 |
Testing and Evaluating the Collection of Patient Reported Outcomes In Cancer CarE Using Innovative Approaches: The ePROM Digital Health Tool
Patient Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) are patients' reports of their symptom experience, quality of life and functionality. These measures are used as an endpoint to clinical trials but rarely integrated into routine cancer care. Moreover, they are resource intensive and prone to retrospective biases. PRICE project aims to develop and evaluate a digital health tool (ePROM), collecting PROMs at the clinic and additional Ecological Momentary Assessment (EMA) of PROMs using a mobile application. In addition it tests whether patients who are identified to have elevated pain, fatigue, and stress will benefit from an Ecological Momentary Intervention (EMI) based on Virtual Reality environments. EMA can overcome biases and barriers in PROM assessment whilst EMI can offer an easy and possibly cost-effective intervention until patients re-visit the clinic. The project can contribute to monitoring patient data and achieve viable health systems. It is also timely since digital health tools are considered the future of oncology care but often lack robustness in development and evaluation. Patients treated for cancer at the German Oncology Centre in Cyprus will be randomized into three conditions: (a) Full Intervention (patients who are prompted to use the EMI based on their EMA data; (b) Partial Intervention (patients who are prompted to use the EMI irrespective of their EMA data); (c) Control (patients who only provide their EMA without an EMI). A dissemination strategy will ensure findings and innovation are available to the public, clinicians, students and policy-makers.
开始日期2023-06-20 |
申办/合作机构 |
Pilot Double-blind Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial for the Prevention of Radiodermatitis in Breast and Head and Neck Cancer Patients in Cyprus
The treatment of cancer as a multidimensional disease has improved in recent years with the development of new chemotherapies, targeted biological therapies or radiation therapy protocols and have led to an overall improvement in the survival of oncology patients. These treatments often cause adverse effects on the skin, which can be accompanied by physical and mental suffering and have a significant impact on patients' quality of life. Improving the quality of life of patients is today a therapeutic challenge. The objective of this clinical study is to assess the tolerability of an innovative skin cosmetic product that will be developed specifically for use during curative anticancer treatments, as well as to study the impact on quality of life of skin side effects caused by the treatments.
开始日期2022-12-01 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 German Oncology Center 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 German Oncology Center 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
140
项与 German Oncology Center 相关的文献(医药)2024-10-28·Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM)
Thyroglobulin measurement is the most powerful outcome predictor in differentiated thyroid cancer: a decision tree analysis in a European multicenter series
Article
作者: Weber, Manuel ; Kreissl, Michael ; Vrachimis, Alexis ; Ceriani, Luca ; Milan, Lisa ; Görges, Rainer ; Campenni, Alfredo ; Schenke, Simone ; Petranović Ovčariček, Petra ; Pabst, Kim ; Giovanella, Luca ; Murat, Tuncel ; Roll, Wolfgang
2024-09-01·Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases
Role of enzalutamide in primary and recurrent non-metastatic hormone sensitive prostate cancer: a systematic review of prospective clinical trials
Review
作者: Aebersold, Daniel M ; Achard, Vérane ; Shelan, Mohamed ; Zamboglou, Constantinos ; Appiagyei, Felix ; Mohamad, Osama ; Cathomas, Richard ; Mose, Lucas ; Fankhauser, Christian D ; Zilli, Thomas
2024-06-01·Journal of Clinical Oncology
SNF-CLIMEDIN: A prospective randomized trial of digital intervention in patients with advanced NSCLC—A HeCOG study.
作者: Gkoumas, Georgios ; Panopoulos, Chris G. ; Fountzilas, Elena ; Christopoulou, Athina ; Tsoukalas, Nikolaos ; Vagionas, Anastasios ; Mountzios, Giannis Socrates ; Bafaloukos, Dimitris ; Fountzilas, George ; Vozikis, Athanassios ; Kosmidis, Thanos ; Papadopoulou, Kyriaki ; Lampaki, Sofia ; Samantas, Epaminondas ; Psyrri, Amanda ; Linardou, Helena ; Athanasiadis, Ilias ; Kosmidis, Paris A. ; Korfiatis, Nikolaos ; Koufaki, Margarita Ioanna
100 项与 German Oncology Center 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
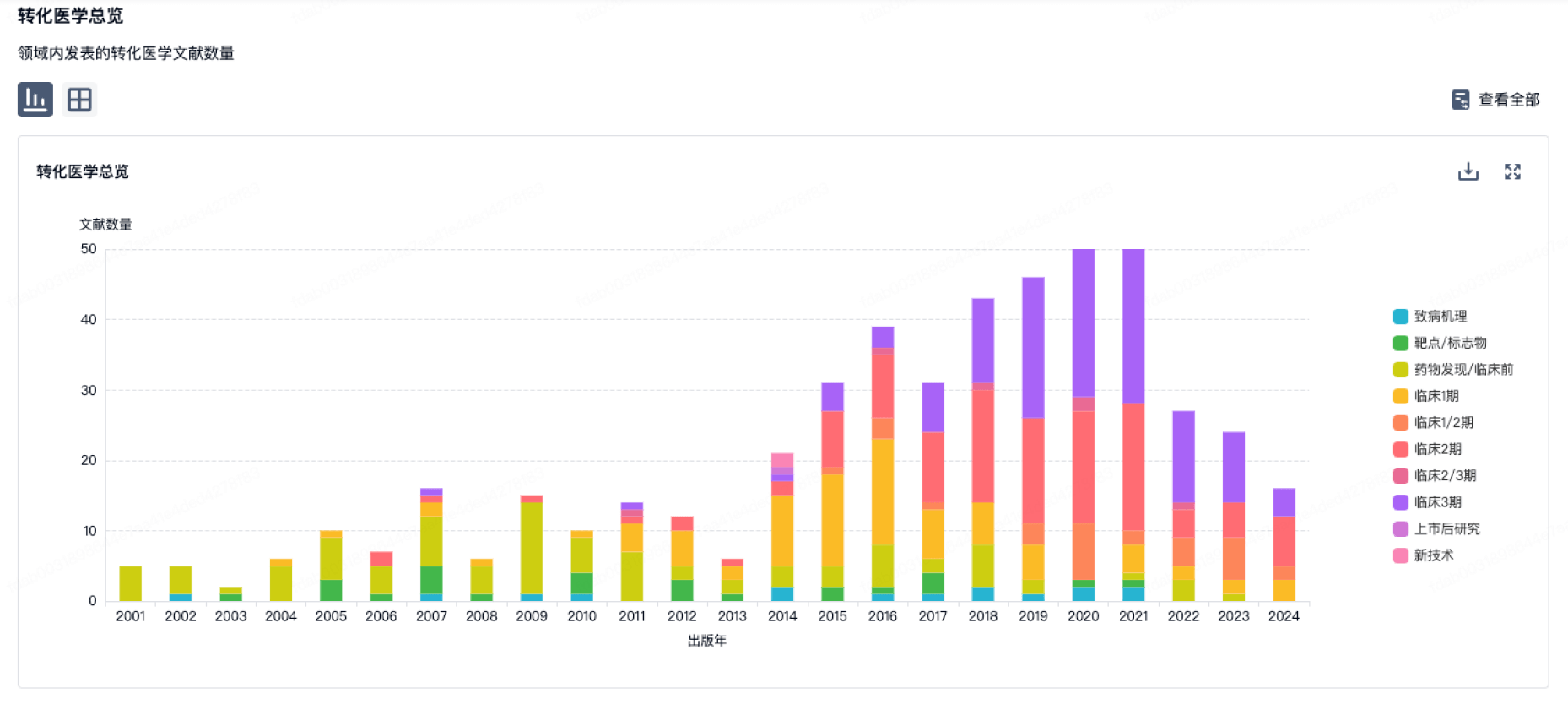
100 项与 German Oncology Center 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
组织架构
使用我们的机构树数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

管线布局
2024年11月17日管线快照
无数据报导
登录后保持更新
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
营收
使用 Synapse 探索超过 36 万个组织的财务状况。
登录
或
科研基金(NIH)
访问超过 200 万项资助和基金信息,以提升您的研究之旅。
登录
或

投资
深入了解从初创企业到成熟企业的最新公司投资动态。
登录
或

融资
发掘融资趋势以验证和推进您的投资机会。
登录
或

标准版
¥16800
元/账号/年
新药情报库 | 省钱又好用!
立即使用
来和芽仔聊天吧
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用
