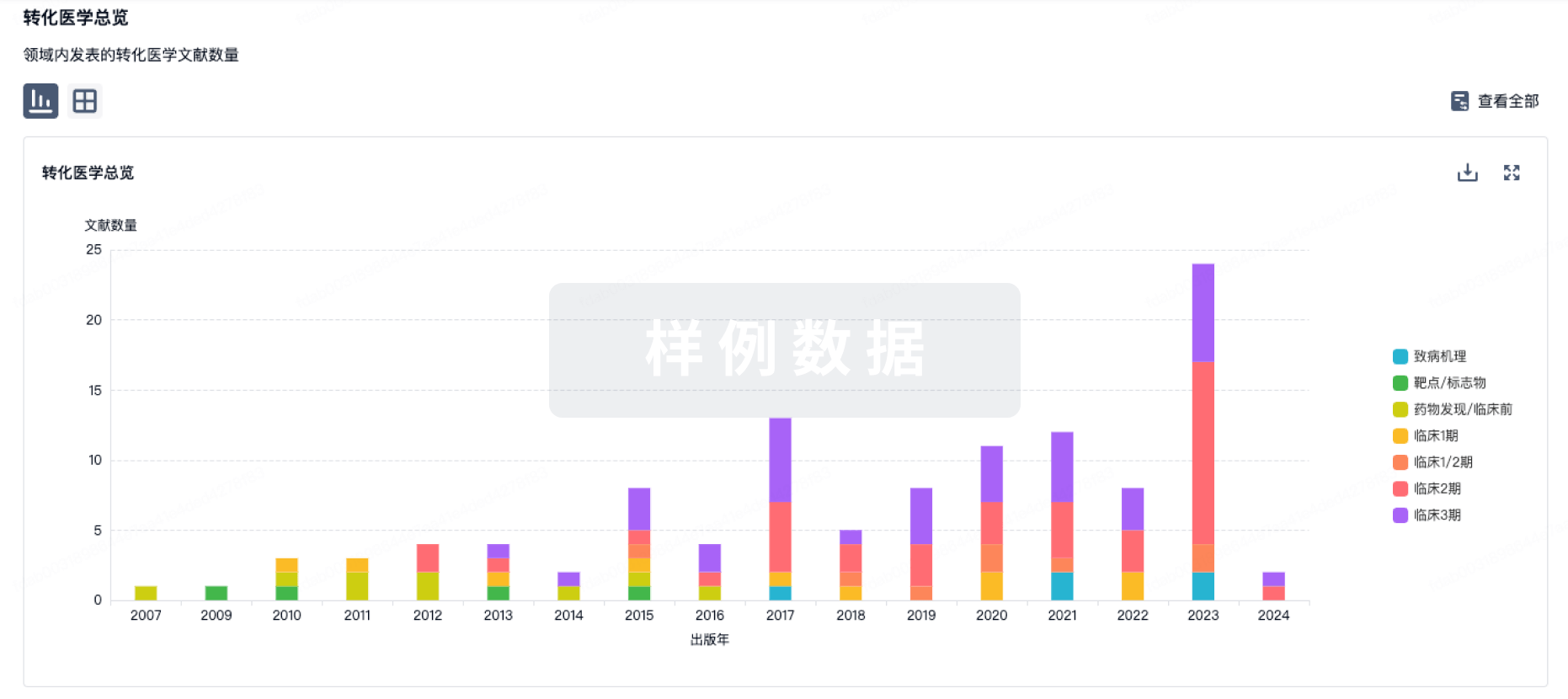
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the leading primary malignant tumor in the central nervous system. Current clinical therapeutics for treating GBM patients yield limited benefits. However, the development of new therapeutic methods is hindered because the blood-brain barrier (BBB) restricts drug penetration. The transferrin receptor (TfR) is highly expressed by brain endothelial cells and GBM cells, and it is considered a promising target for GBM drug delivery. Here, we modularly constructed a TfR-targeted aptamerdrug conjugate (ApDC) by linking a TfR aptamer (HG1-9) and a highly potent anti-tubulin drug, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), to cross the BBB and deliver GBM treatment. The targeting and BBB transport abilities of the TfR-targeted ApDC (HG1-9-MMAE) for GBM were evaluated in cultured vascular endothelial bEnd.3 cells and human GBM U-87 MG Luc2 cells, together with an in vitro transwell BBB model. Potent antitumor effects of HG1-9-MMAE were demonstrated by in vitro cellular proliferation assays and in vivo tumor inhibition in both subcutaneous and orthotopic GBM models. Our findings indicated that ApDC could be an efficient drug delivery strategy to treat GBM.