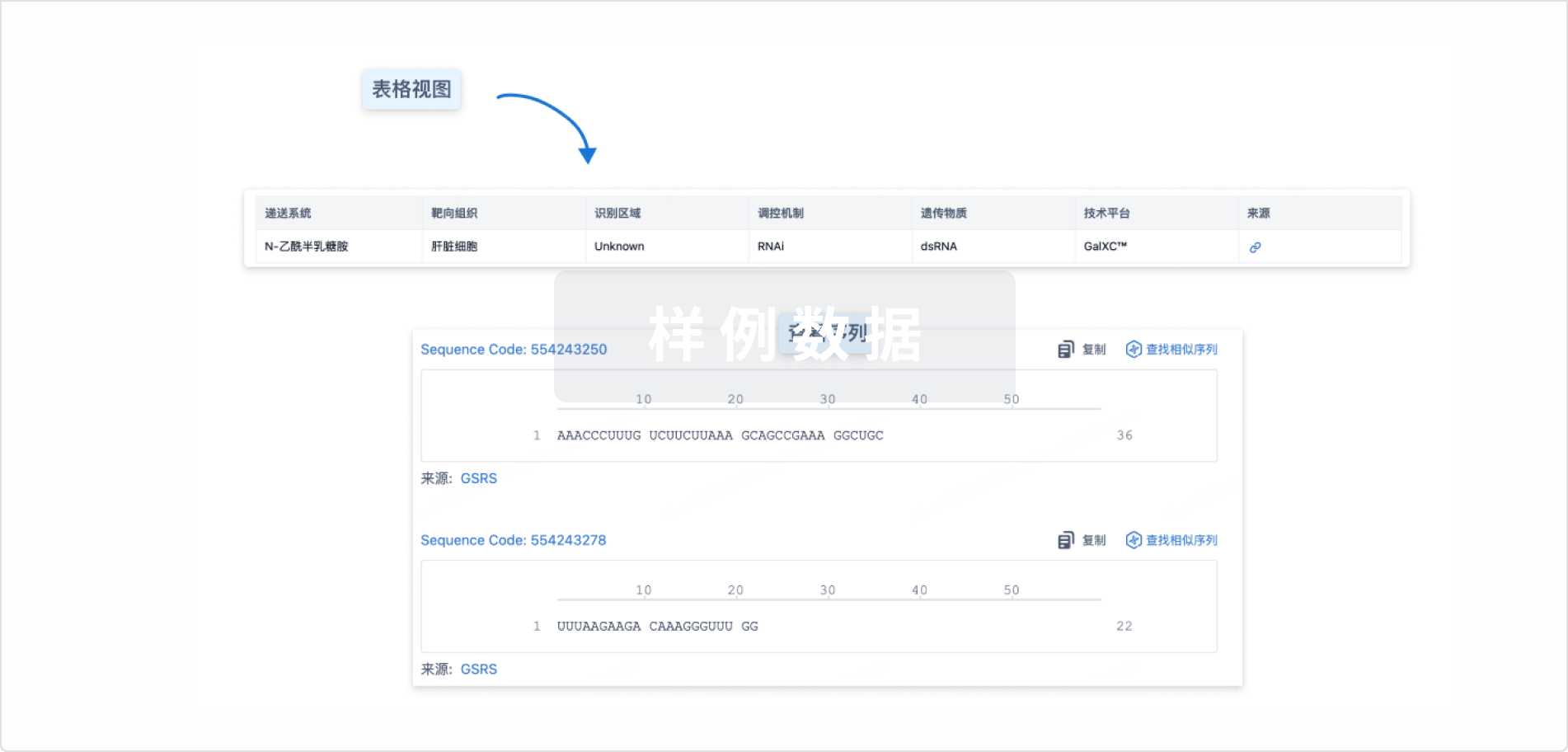
100 项与 LPA siRNA(赛诺菲) 相关的临床结果
100 项与 LPA siRNA(赛诺菲) 相关的转化医学
100 项与 LPA siRNA(赛诺菲) 相关的专利(医药)
2
项与 LPA siRNA(赛诺菲) 相关的新闻(医药)▎Armstrong2024年4月30日,礼来发布一季度财报,营业收入87.68亿美元,同比大增26%,净利润22.43亿美元,同比大增60%。替尔泊肽减重版Mounjaro销售额18.07亿美元替尔泊肽减重版去年11月刚刚获批,今年一季度销售5.17亿美元。替尔泊肽合计销售额23.24亿美元,预计全年将突破100亿美元。度拉糖肽销售额14.56亿美元,同比下降26%,市场快速切换到新一代的替尔泊肽。在GLP-1类药物的加持下,礼来一季度糖尿病业务收入实现54.93亿美元收入,同比增加31%。肿瘤药收入18.1亿美元,同比增长31%,主要驱动力源自Verzenio的快速放量,一季度销售额10.5亿美元。礼来盘前股价大涨近6%,市值达到7400亿美元。总结礼来在2024年还将迎来多个催化剂时间,包括GLP-1R/GIPR/GCGR三靶点激动剂Retatrutide降糖三期临床,Lpa siRNA三期临床、替尔泊肽心衰三期临床以及头对头司美格鲁肽三期临床等。Armstrong技术全梳理系列GPRC5D靶点全梳理;CD40靶点全梳理;CD47靶点全梳理;补体靶向药物技术全梳理;补体药物:眼科治疗的重要方向;Claudin 6靶点全梳理;Claudin 18.2靶点全梳理;靶点冷暖,行业自知;中国大分子新药研发格局;被炮轰的“me too”;佐剂百年史;胰岛素百年传奇;CUSBEA:风雨四十载;中国新药研发的焦虑;中国生物医药企业的研发竞争;中国双抗竞争格局;中国ADC竞争格局;中国双抗技术全梳理;中国ADC技术全梳理;Ambrx技术全梳理;Vir Biotech技术全梳理;Immune-Onc技术全梳理;亘喜生物技术全梳理;康哲药业技术全梳理;科济药业技术全梳理;恺佧生物技术全梳理;同宜医药技术全梳理;百奥赛图技术全梳理;腾盛博药技术全梳理;创胜集团技术全梳理;永泰生物技术全梳理;中国抗体技术全梳理;德琪医药技术全梳理;德琪医药技术全梳理2.0;和铂医药技术全梳理;荣昌生物技术全梳理;再鼎医药技术全梳理;药明生物技术全梳理;恒瑞医药技术全梳理;豪森药业技术全梳理;正大天晴技术全梳理;吉凯基因技术全梳理;基石药业技术全梳理;百济神州技术全梳理;百济神州技术全梳理第2版;信达生物技术全梳理;信达生物技术全梳理第2版;中山康方技术全梳理;复宏汉霖技术全梳理;先声药业技术全梳理;君实生物技术全梳理;嘉和生物技术全梳理;志道生物技术全梳理;道尔生物技术全梳理;尚健生物技术全梳理;康宁杰瑞技术全梳理;科望医药技术全梳理;科望医药技术全梳理2.0;岸迈生物技术全梳理;礼进生物技术全梳理;康桥资本技术全梳理;余国良的抗体药布局;荃信生物技术全梳理;安源医药技术全梳理;三生国健技术全梳理;仁会生物技术全梳理;乐普生物技术全梳理;同润生物技术全梳理;宜明昂科技术全梳理;派格生物技术全梳理;迈威生物技术全梳理;Momenta技术全梳理;NGM技术全梳理;普米斯生物技术全梳理;普米斯生物技术全梳理2.0;三叶草生物技术全梳理;贝达药业抗体药全梳理;泽璟制药抗体药全梳理;恒瑞医药抗体药全梳理;齐鲁制药抗体药全梳理;石药集团抗体药全梳理;豪森药业抗体药全梳理;华海药业抗体药全梳理;科伦药业抗体药全梳理;百奥泰技术全梳理;凡恩世技术全梳理。
▎Armstrong2023年8月3日,Ionis Pharmaceuticals宣布与诺华达成合作协议,开发新一代Lpa靶向药物,诺华支付6000万美元预付款,未披露的里程碑金额和一定比例的销售分成。Ionis与诺华合作开发的Lpa靶向寡核苷酸药物Pelacarsen已经处于三期临床阶段,预计2025年获得临床数据。此次新协议将采用Ionis新技术开发新一代Lpa靶向药物。总结近年来,小核酸药物在常见病领域尤其是心血管领域取得诸多临床突破,包括PCSK9 siRNA、Lpa siRNA等,此外AGT siRNA也取得优异的初步临床数据,非肝靶向的小核酸药物也处在积极开发中,如CNS递送初步初步临床概念验证。Armstrong技术全梳理系列GPRC5D靶点全梳理;CD40靶点全梳理;CD47靶点全梳理;补体靶向药物技术全梳理;补体药物:眼科治疗的重要方向;Claudin 6靶点全梳理;Claudin 18.2靶点全梳理;靶点冷暖,行业自知;中国大分子新药研发格局;被炮轰的“me too”;佐剂百年史;胰岛素百年传奇;CUSBEA:风雨四十载;中国新药研发的焦虑;中国生物医药企业的研发竞争;中国双抗竞争格局;中国ADC竞争格局;中国双抗技术全梳理;中国ADC技术全梳理;Ambrx技术全梳理;Vir Biotech技术全梳理;Immune-Onc技术全梳理;康哲药业技术全梳理;科济药业技术全梳理;恺佧生物技术全梳理;同宜医药技术全梳理;百奥赛图技术全梳理;腾盛博药技术全梳理;创胜集团技术全梳理;永泰生物技术全梳理;中国抗体技术全梳理;德琪医药技术全梳理;德琪医药技术全梳理2.0;和铂医药技术全梳理;荣昌生物技术全梳理;再鼎医药技术全梳理;药明生物技术全梳理;恒瑞医药技术全梳理;豪森药业技术全梳理;正大天晴技术全梳理;吉凯基因技术全梳理;基石药业技术全梳理;百济神州技术全梳理;百济神州技术全梳理第2版;信达生物技术全梳理;信达生物技术全梳理第2版;中山康方技术全梳理;复宏汉霖技术全梳理;先声药业技术全梳理;君实生物技术全梳理;嘉和生物技术全梳理;志道生物技术全梳理;道尔生物技术全梳理;尚健生物技术全梳理;康宁杰瑞技术全梳理;科望医药技术全梳理;科望医药技术全梳理2.0;岸迈生物技术全梳理;礼进生物技术全梳理;康桥资本技术全梳理;余国良的抗体药布局;荃信生物技术全梳理;安源医药技术全梳理;三生国健技术全梳理;仁会生物技术全梳理;乐普生物技术全梳理;同润生物技术全梳理;宜明昂科技术全梳理;派格生物技术全梳理;迈威生物技术全梳理;Momenta技术全梳理;NGM技术全梳理;普米斯生物技术全梳理;普米斯生物技术全梳理2.0;三叶草生物技术全梳理;贝达药业抗体药全梳理;泽璟制药抗体药全梳理;恒瑞医药抗体药全梳理;齐鲁制药抗体药全梳理;石药集团抗体药全梳理;豪森药业抗体药全梳理;华海药业抗体药全梳理;科伦药业抗体药全梳理;百奥泰技术全梳理;凡恩世技术全梳理。
100 项与 LPA siRNA(赛诺菲) 相关的药物交易