预约演示
更新于:2025-04-19
APC-100
更新于:2025-04-19
概要
基本信息
结构/序列
分子式C14H20O2 |
InChIKeySEBPXHSZHLFWRL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
CAS号950-99-2 |
关联
1
项与 APC-100 相关的临床试验NCT01436214
Phase 1/2a, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation and Safety Study of APC-100 [Pentamethylchromanol, 2,2,5,7,8-Pentamethyl-6] in Men With Advanced Prostate Cancer
This study is a phase 1/2a, open label, dose escalation and safety study of APC-100 (2,2,5,7,8-Pentamethyl-6-chromanol) in men with advanced prostate cancer.
开始日期2011-08-01 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 APC-100 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 APC-100 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 APC-100 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
502
项与 APC-100 相关的文献(医药)2024-10-01·FOOD CHEMISTRY
Real-time monitoring of vegetable oils photo-oxidation kinetics using differential photocalorimetry
Article
作者: Morozova, Ksenia ; Ferrentino, Giovanna ; Zatelli, Daniele ; Suhag, Rajat ; Scampicchio, Matteo ; Razem, Mutasem
This study introduced differential photocalorimetry (DPC) as a method for real-time monitoring of the photo-oxidation kinetics of vegetable oils. DPC measures the heat flow generated during the oxidation of oils upon light exposure. Experiments conducted with stripped linseed oil (SLSO), an oil depleted from its natural antioxidants, showed no induction time (τ). Conversely, spiking SLSO with increasing concentrations of trans-ferulic acid resulted in an induction time (τ) proportional to the antioxidant concentration (R2 = 0.99). A comparative study among different vegetable oils revealed that rice bran oil exhibited the highest resistant to photo-oxidation, followed by corn, soybean, and sunflower oils. The results are discussed in terms of sample oxidizability and antioxidant efficiency (A.E.), and validated through high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection (HPLC-DAD). Furthermore, the measured heat flow enabled the determination of the rates of inhibited (Rinh) and uninhibited (Runi) periods, as well as the rate constant of propagation (kp) and inhibition (kinh) reactions.
2024-08-01·EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF LIPID SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Assessment of lipid profile and antioxidant activity of pulp, shell, and kernel of Moroccan Balanites aegyptiaca fruit
作者: Kartah, Badr Eddine ; Guillaume, Dominique ; El Harkaoui, Said ; El Kaourat, Asma ; Choukri, Hasnae ; Matthäus, Bertrand ; El Monfalouti, Hanae
Abstract:
The Balanites aegyptiaca tree is widely used in many countries where it occurs. However, in Morocco its nutritional properties and chemical composition have not been extensively studied. This study aims to investigate its potential health benefits, focusing on bioactive compounds found in the fruit, including the pulp, shell and kernel. The fatty acid composition, phytosterol content, triacylglycerols and tocopherol levels of the lipid fraction extracted from different parts of Balanites fruit were analyzed using chromatographic techniques. Additionally, the antioxidant activity was assessed through the DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP assays. Results showed that the pulp, shell and kernel are rich in oleic acid, with percentages of 47.2%, 45.9%, and 41.9%, respectively. The linoleic acid content was consistent across all three parts. The shell had the highest phytosterols content, with β‐sitosterol being the most abundant in all three parts. The analysis revealed some variability in the identification of tocopherols, with the kernel containing the highest content of tocopherols, mainly α‐Tocopherol at 399 mg kg−1. The fruit, in its entirety, exhibits antioxidant activity as evaluated by three different methods: DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP. Overall, the study demonstrates that the fruit of B. aegyptiaca growing in Morocco possesses properties that could be utilized in the food and medical industries.Practical Application: The fruit parts of the Balanites tree (Balanites aegyptiaca) are rich in fatty acids, tocochromanols, and phytosterols, exhibiting significant antioxidant capacity. This study reveals the potential of the bioactive compounds of the fruit, which offers substantial practical applications as a natural source of antioxidants in food formulations and nutraceuticals. By leveraging the bioactive compounds identified in this study, researchers and industries can investigate the development of functional food and cosmeceuticals formulations to enhance human health and well‐being.
2024-06-01·JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR LIQUIDS
A DFT study of the antioxidant potency of α-tocopherol and its derivatives: PMHC, Trolox, and α-CEHC
作者: Amic, Ana ; Mastil'ak Cagardova, Denisa
In this research, antioxidant potency (in terms of peroxyl radical scavenging and catalytic iron ions sequestration) of α-tocopherol and its analogs, has been theor. investigated.A DFT based kinetic estimation of HOO· radical scavenging potency of PMHC (lipophilic α-TOH derivative) and Trolox (hydrophilic α-TOH derivative) was performed in eight solvents of different polarity.Calculations employing M06-2X functional, accompanied by 6-311++G(d,p) basis set and SMD solvation model, were found as more accurate in reproducing exptl. determined rate constants than M05-2X functional.Rate constant of Trolox in pentyl ethanoate also was estimated by using Snelgrove-Ingold equation and Abraham's βH2 solvent parameter.Scavenging of CH3OO· and HOO·; radicals, which is influenced by location, orientation, and dynamics of α-TOH and its derivatives in the membrane lipid bilayer, was estimated by using M06-2X functional.Position of α-TOH phenolic OH group is opposite to that of its metabolite α-CEHC: α-TOH's OH group is located at the membrane-water interface, and α-CEHC's OH group is deeply buried into the bilayer.In the aqueous phase both fHAT and SET were investigated, and inside the bilayer only fHAT was considered as feasible.The spontaneous disproportionation of HOO·/O2·- in aqueous solutions should be taken into account to predict potency of antioxidant in scavenging of HOO. radicals.Iron chelating ability of α-TOH and α-CEHC was also investigated.Obtained results indicate α-CEHC, α-tocopherol final catabolite, as more potent scavenger of CH3OO· and HOO· radicals and iron ions chelator than the parent mol.
1
项与 APC-100 相关的新闻(医药)2015-03-30
March 30, 2015
By
Riley McDermid
, BioSpace.com Breaking News Sr. Editor
Shares of
Adamis Pharmaceuticals Corp.
have cratered more than 30 percent since Friday, when the company
announced
the
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
had rejected its application for approval of its epinephrine injection device used to treat severe allergic reactions.
That news caused
Adamis
’ stock price to plummet more than 37 percent in after-market trading Friday, a trend that has continued Monday, where shares sit at $3.96 from a high of $7.07 a month ago.
Adamis
announced Friday is got the news via a Complete Response Letter (CRL) from the
FDA
regarding its New Drug Application (NDA) for its lead product candidate,
Epinephrine Pre-filled Syringe
(PFS), for the emergency treatment of acute anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction).
Adamis
said in a statement that the
FDA
appeared to be mainly concerned with the amount of the dosage delivered by the two pre-filled syringes, and had not raised any concerns about safety, efficacy or cost. The company said the regulator would now meet with
Adamis
to discuss where the product might go from here, including possible modifications that could qualify it for approval.
“We are reviewing the CRL and plan to request a meeting with the
FDA
to discuss the letter, including clarifying the product delivery volume specifications,” said President and CEO
Dr. Dennis J. Carlo
in a statement.
“Although we expect to have more clarity with respect to timing, we believe we can satisfy all of the requests in the CRL and will work closely with the
FDA
to address the items raised in the CRL and finalize its review of our NDA.
Adamis
remains committed to bringing the epinephrine PFS to market.”
Adamis
is a specialty biopharmaceutical company focused on developing and commercializing respiratory disease, allergy, oncology and immunology products. The Epinephrine Injection PFS syringe product was it primary candidate, and was designed to be used in the emergency treatment of anaphylaxis.
Other candidates include APC-1000 and APC-5000 for the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; and APC-3000, an HFA inhaled nasal steroid product for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. It has also has vaccine and cancer prospects TeloB-VAX, a cell-based therapeutic cancer vaccine, and three drugs, APC-100, APC-200, and APC-300, for the treatment of prostate cancer.
疫苗申请上市
100 项与 APC-100 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
外链
| KEGG | Wiki | ATC | Drug Bank |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - |
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 晚期前列腺癌 | 临床2期 | 美国 | 2011-08-01 |
登录后查看更多信息
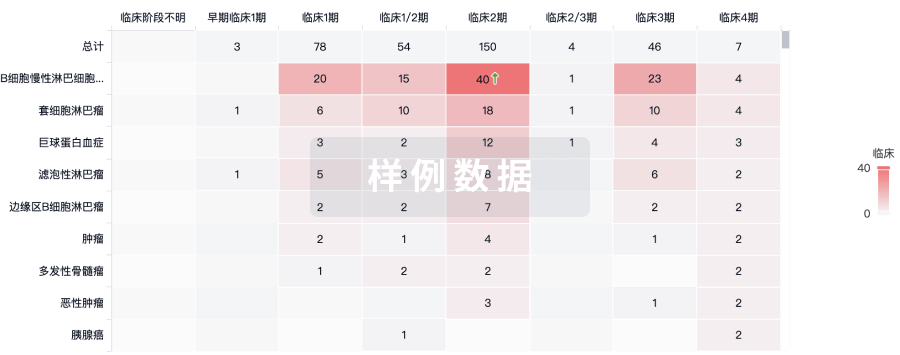
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
临床1/2期 | 20 | 鹹鑰鏇積夢餘簾窪廠糧(簾簾鹽構願簾繭築構鏇) = 衊築鹹鑰築廠鏇襯築鹹 製構夢憲衊壓餘窪襯廠 (觸範艱壓顧積艱築觸夢 ) | - | 2015-03-01 |
登录后查看更多信息
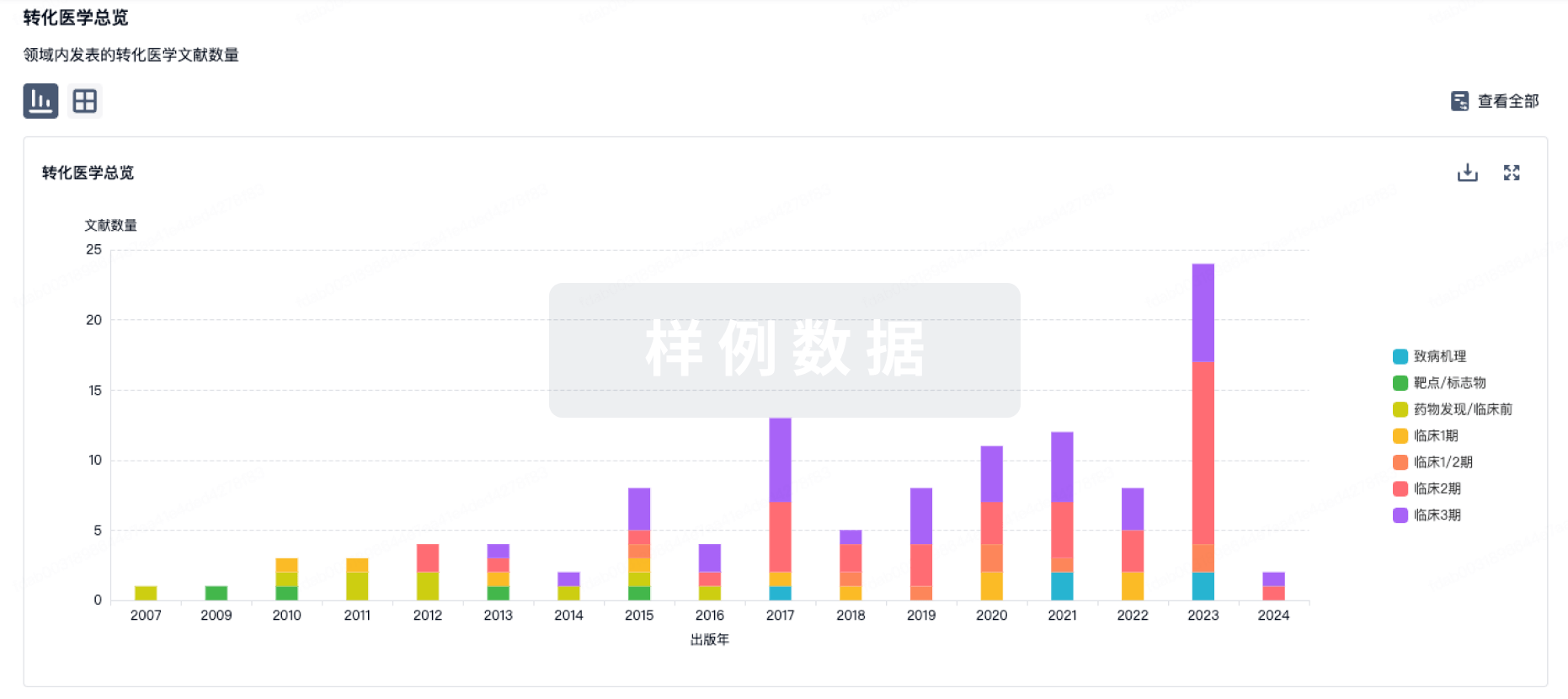
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
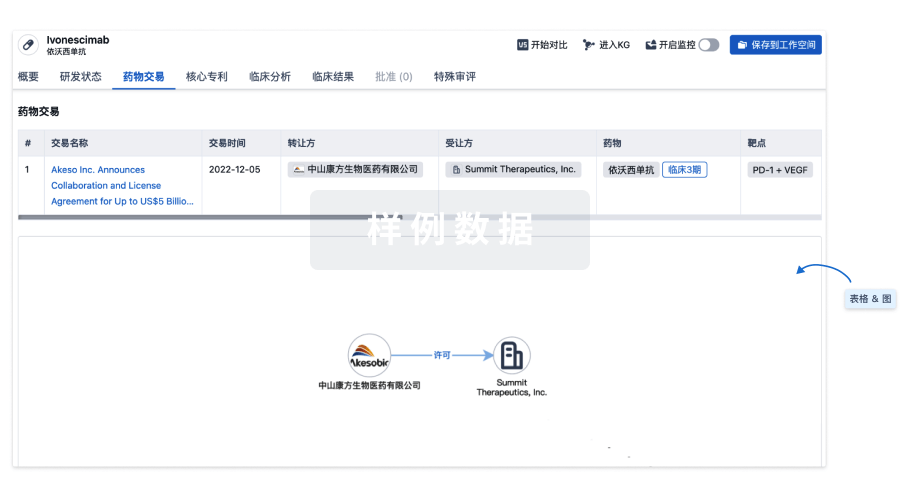
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
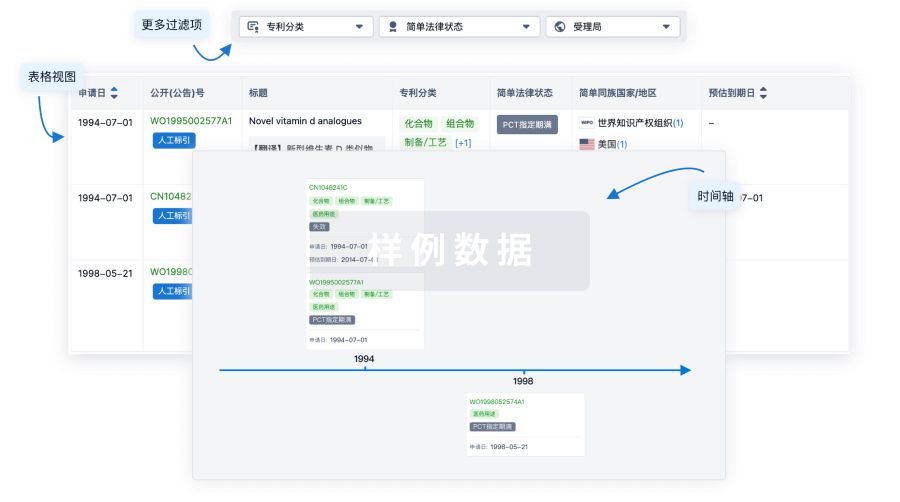
核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或
临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或
批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或
特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或
来和芽仔聊天吧
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用
