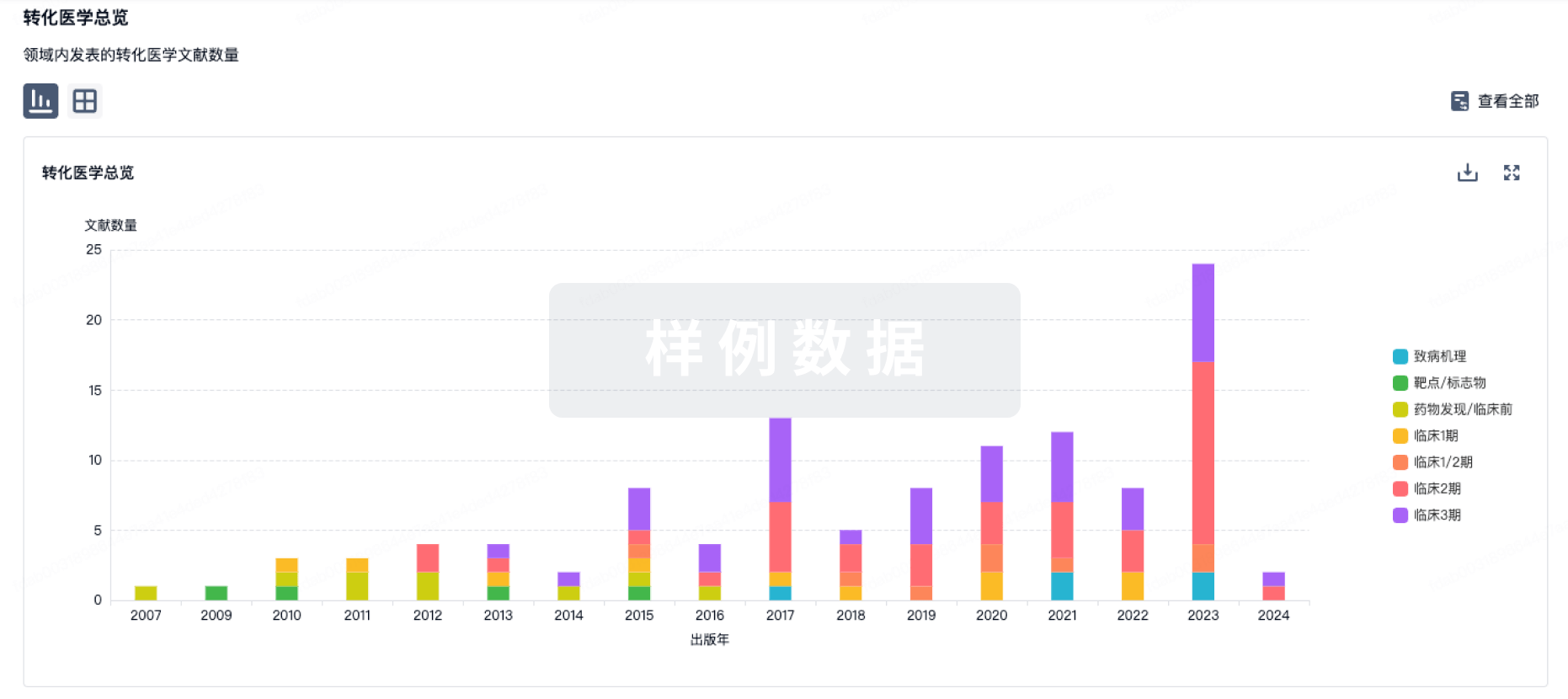
To further pursue potent Bax activators with better safety profiles for the treatment of breast cancer, structural optimization was conducted based on lead compound CYD-4-61 through several strategies, including scaffold hopping on the 2-nitro-fluorene ring, replacement of the nitro group with bioisosteres to avoid potential toxicity, and further optimization on the upper pyridine by exploring diverse alkylamine linkers as a tail or replacing the pyridine with bioisosteric heterocycles. F-containing compound 22d (GL0388) exhibited a good balance between the activity and toxicity, displaying submicromolar activities against a variety of cancer cell lines with 5.8-10.7-fold selectivity of decreased activity to MCF-10A human mammary epithelial cell line. Compound 22d dose-dependently blocked colony formation of breast cancer cells and prevented the migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells. Mechanism of action studies indicate that 22d activated Bax, rendering its insertion into mitochondrial membrane, thereby leading to cytochrome c release from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm, subsequently inducing release of apoptotic biomarkers. Further in vivo efficacy studies of 22d in human breast cancer xenografts arisen from MDA-MB-231 cells demonstrated that this drug candidate significantly suppressed tumor growth, indicating the therapeutic promise of this class of compounds for the treatment of breast cancer as well as the potential for developing F-radiolabeled imaging ligands as anticancer chemical probes.