预约演示
更新于:2025-09-06
GNKG-168
更新于:2025-09-06
概要
基本信息
药物类型 CpG ODN |
别名 CpG ODN、CPG-ODN、CPG 685 + [3] |
靶点 |
作用方式 激动剂 |
作用机制 TLR9激动剂(Toll样受体9激动剂) |
在研适应症- |
原研机构 |
在研机构- |
权益机构- |
最高研发阶段终止临床1期 |
首次获批日期- |
最高研发阶段(中国)- |
特殊审评- |
登录后查看时间轴
结构/序列
使用我们的RNA技术数据为新药研发加速。
登录
或
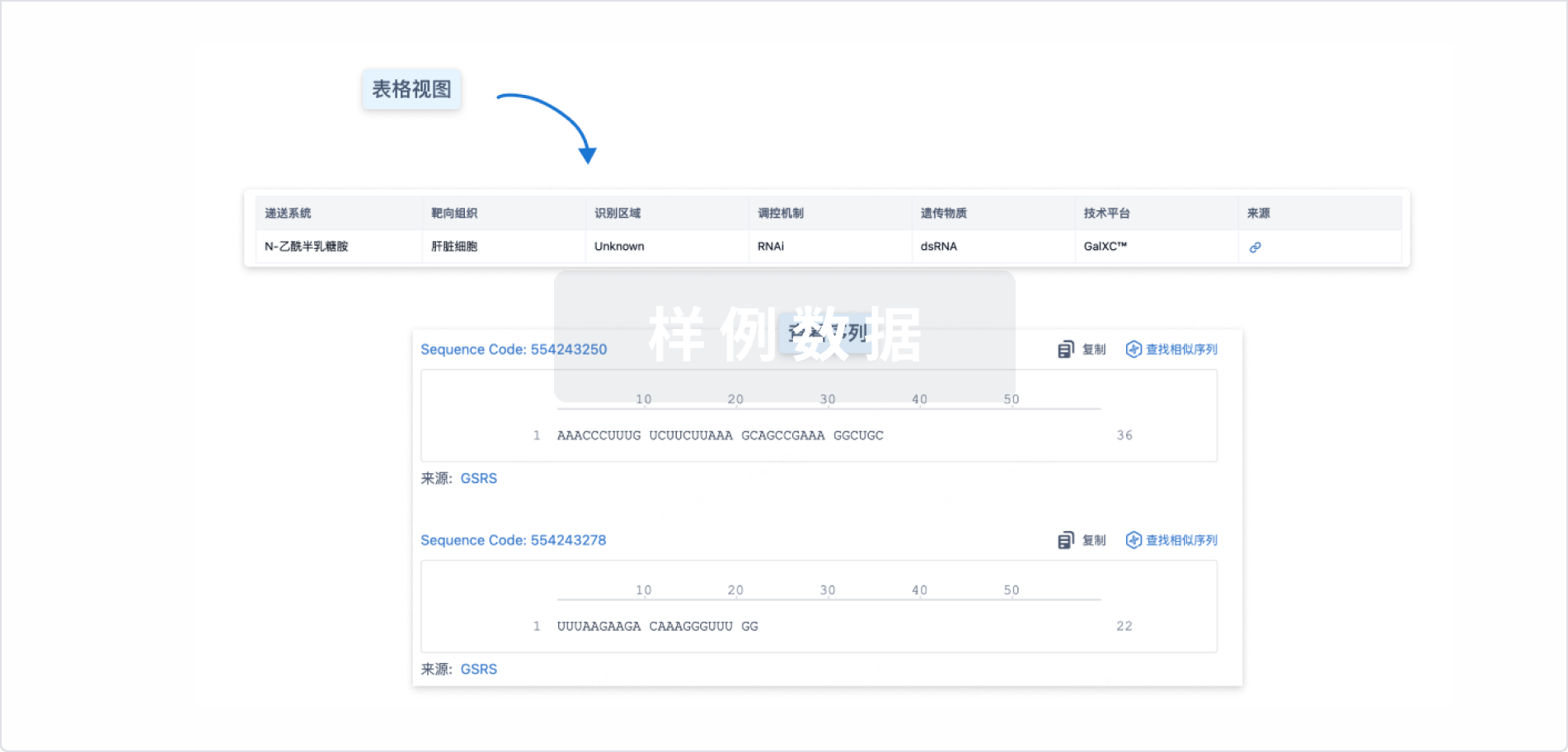
Sequence Code 29304404

来源: *****
关联
4
项与 GNKG-168 相关的临床试验ISRCTN17285423
A phase Ib, open-label, randomised, single-centre, multiple-dose-escalation study of the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of CpG ODN D35 after subcutaneous administration in participants with cutaneous leishmaniasis
开始日期2023-03-01 |
ISRCTN15458851
A Phase I, double-blind, randomised, single-centre, parallel-group, single ascending dose, placebo-controlled study of the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of CpG ODN D35 after subcutaneous administration in healthy male subjects
开始日期2021-06-01 |
NCT01743807
A Phase I Study of GNKG168 in Pediatric Patients With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia or Acute Myeloid Leukemia (IND#113600)
This is a phase I trial of an investigational drug called GNKG168 in patients with relapsed and refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) who are in morphologic remission but are positive for Minimum Residual Disease (MRD).
开始日期2014-03-26 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 GNKG-168 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 GNKG-168 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 GNKG-168 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
1,008
项与 GNKG-168 相关的文献(医药)2025-12-31·Emerging Microbes & Infections
CpG oligodeoxynucleotides and pan-serotype inhibitors control neurotropic dengue infection in novel immune competent neonatal mouse model
Article
作者: Chowdhury, Monica ; Ireland, Derek D.C. ; Kelly-Baker, Logan ; Mendoza, Mirian ; Manangeeswaran, Mohanraj ; Verthelyi, Daniela ; Lee, Ha-Na
Dengue virus (DENV) is a growing global public health threat. The lack of symptomatic immune-competent animal models for dengue has hindered the screening and development of effective therapeutics that can be used to control dengue virus replication and thereby control the progression to severe dengue disease. To address this, we established an infection model in neonatal C57BL/6 mice and showed that a systemic Dengue challenge leads to ataxia, seizures, paralysis, and death within 15 days. The virus was found predominantly in the eye and brain where DENV infects neurons but not astrocytes and causes extensive infiltration of macrophages and microglia activation. The response to infection included upregulation of multiple genes linked to interferons (Ifna, Ifnb, Ifng, Irf7, Irf8, Mx1, Stat1 and Bst2), inflammation (Il6,Tnfa), complement (Cfb,C1ra,C2, C3), cytolysis (Gzma, Gzmb, Prf1) consistent with antiviral responses and inflammation together with neuroprotective regulatory signals (Il27, Il10, and stat2). The increased proinflammatory signature was associated with downregulation neurodevelopmental genes (Calb2, Pvalb, Olig1 and Olig2). We tested the utility of this mouse model by assessing the protection conferred by direct antivirals JNJ-A07 and ST-148 and host-directed antiviral immunomodulatory CpG oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN), alone or in combination against lethal dengue viral infection. The data showed that immunomodulatory CpG ODN and antiviral JNJ-A07 improved the survival of neonatal mice, and protection from lethal neurotropic infection was optimal when treatments were combined. This study suggests that a combination of an effective dengue antiviral along with a host-directed therapeutic may be a useful strategy to protect against dengue virus infections.
2025-08-01·ADVANCED MATERIALS
Intranasal and Intravenous Sequential Administration of Survivin Peptide‐CpG Nanovaccines Elicits Potent Immunity Toward Glioblastoma
Article
作者: Zhong, Zhiyuan ; Xia, Mingyu ; Meng, Fenghua ; Sun, Yinping ; Sun, Zhiwei ; Shi, Yan ; Zhao, Songsong
Abstract:
Peptide vaccines hold great promise for treatment of glioblastoma (GBM), though their efficacy remains suboptimal due to factors such as immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, poor accessibility to tumor site and inadequate activation of antigen‐presenting cells. Here, this work reports on survivin peptide‐CpG oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) nanovaccines (SPOD‐NV), which feature antigen peptides strategically displayed on polymersomes with CpG ODN encapsulated as an immunostimulatory adjuvant. Sequential administration via intranasal and intravenous routes elicits robust immune response against murine GBM. These results demonstrate that SPOD‐NV significantly enhances mucosa penetration and markedly improves dendritic cell uptake and activation. Notably, the intranasal administration of SPOD‐NV to orthotopic murine GL261 tumor models reveals marked accumulation in cervical lymph nodes and tumors, likely facilitated by lymphatic transport from nasal mucosa and pathways via olfactory bulb and trigeminal nerve, bypassing the blood‐brain barrier. Interestingly, the therapeutic strategy, comprising three intranasal and two intravenous administrations of SPOD‐NV in combination with anti‐CTLA‐4 antibody, results in substantial tumor inhibition, achieving a 43% complete regression rate, in line with the stimulation of robust and long‐lasting local and systemic anti‐GBM immune responses. These intranasal‐intravenous administration strategy of peptide‐CpG nanovaccines provides a potential curative therapy for brain tumors, paving the way for further developments in GBM immunotherapy.
2025-08-01·JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGY
CXCL14 is an essential modulator of TLR9 agonist–induced antitumor immune responses
Article
作者: Hara, Takahiko ; Kazuki, Yasuhiro ; Iwase, Rina ; Suzuki, Teruhiko ; Kotaki, Ayumi ; Ishida, Koji ; Hasebe, Manaka ; Takahashi, Rena ; Tanegashima, Kosuke ; Esashi, Eiji ; Saito, Risa
Abstract:
Cancer immunotherapeutic CpG oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) is an agonist for TLR9 and a potent inducer of inflammatory cytokines and type I interferon. Clinical trials of CpG ODNs highlight the urgent need for effective TLR9 agonist CpG ODNs in humans. Here, we developed a highly potent CpG ODN, A602, which induces antitumor immune responses in combination with CXCL14. A602 induced secretion of interferon-α by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. In mouse macrophages, dendritic cells, and human plasmacytoid dendritic cell lines, CXCL14 enhanced cellular uptake of A602, thereby promoting TLR9-mediated immune responses. Importantly, A602 exhibited strong antitumor activity in syngeneic mouse models of colorectal cancer–derived CT26, B lymphoma-derived A20, and melanoma-derived B16F10 cells. Because the antitumor effect of A602 against B16F10 cells was negated in Cxcl14 knockout mice, endogenously expressed CXCL14 is required for the A602-mediated tumor suppression. Thus, modulation of CXCL14 during the A602-induced immune responses shall unveil an innovative new approach for the antitumor immune therapy.
4
项与 GNKG-168 相关的新闻(医药)2025-08-29
摘要:人类肺炎病毒(包括呼吸道合胞病毒 RSV 与人类偏肺病毒 HMPV)是全球呼吸道感染的主要病原体,尤其对婴幼儿、老年人及免疫功能低下人群造成严重疾病负担,甚至导致死亡。本文系统梳理了肺炎病毒的生物学特性、流行病学特征与疾病负担,重点解析了已获批 RSV 疫苗的临床数据、技术平台(如亚单位疫苗、mRNA 疫苗),以及针对 HMPV 与人类副流感病毒 3 型(HPIV3)的联合疫苗研发进展。研究发现,目前已有 3 款 RSV 疫苗(GSK 的 AREXVY®、辉瑞的 ABRYSVO®、Moderna 的 mRESVIA®)获批用于老年人,其中 ABRYSVO® 可通过 母体免疫为新生儿提供被动保护;但 HMPV 疫苗仍存在巨大未满足医疗需求,多款联合疫苗正处于临床试验阶段。未来需进一步优化儿童疫苗安全性、延长疫苗保护期,并推动多病毒联合疫苗研发,以实现对呼吸道病毒的广谱防控。
一、引言:肺炎病毒 —— 被忽视的呼吸道健康 “杀手”
急性呼吸道感染是全球公共卫生的重大威胁,而人类肺炎病毒(Human Pneumoviruses)是其中的关键致病因子之一。这类病毒主要包括呼吸道合胞病毒(RSV) 和人类偏肺病毒(HMPV) ,可引发从普通感冒到严重下呼吸道感染(如毛细支气管炎、肺炎)的一系列疾病,尤其对两类人群风险最高:一是婴幼儿(特别是 6 个月以下婴儿),二是老年人(65 岁以上)及有基础疾病(如慢性肺病、心脏病)的人群。
根据 2021 年全球疾病负担研究(GBD)数据,下呼吸道感染(LRTI) 的死亡率达 28.7/10 万,是全球第七大感染性死亡原因(不含新冠病毒)。其中,RSV 是 2 岁以下儿童呼吸道感染住院的首要原因 ——2019 年全球 5 岁以下儿童中,RSV 导致 330 万例 LRTI 和 10.14 万例死亡;而 HMPV 的发病率与流感病毒相当,2018 年全球 5 岁以下儿童因 HMPV 住院的病例数约 50.2 万例。此外,在养老院等长期照护机构中,RSV 与 HMPV 暴发可导致老年人死亡率显著升高,进一步凸显了这类病毒的公共卫生危害。
长期以来,肺炎病毒的预防手段十分有限:HMPV 尚无任何预防性措施,RSV 仅依赖单克隆抗体(如帕利珠单抗、尼塞韦单抗)进行高危人群保护。直到近年,随着疫苗技术的突破,RSV 疫苗研发终于迎来 “里程碑”,而 HMPV 与 HPIV3 的联合疫苗也进入临床阶段。本文将从病毒特性、已获批疫苗、在研疫苗三个维度,带您全面了解人类肺炎病毒疫苗的研发现状与未来方向。二、认识人类肺炎病毒:生物学与流行病学特征
要理解疫苗研发逻辑,首先需要明确肺炎病毒的 “庐山真面目”—— 它们的基因组结构、传播规律与致病特点,直接决定了疫苗的靶点选择与研发策略。2.1 病毒分类与基因组:结构差异决定疫苗靶点
人类肺炎病毒属于单负链 RNA 病毒目(Mononegavirales) 下的肺炎病毒科(Pneumoviridae) ,分为两个属:
正肺炎病毒属:包含 RSV;
偏肺病毒属:包含 HMPV。
二者均为有包膜、非节段性单链 RNA 病毒,但基因组结构存在显著差异(见图 1):
RSV:基因组长度约 15.2 kb,含 10 个基因,编码 11 种蛋白,基因顺序为 3'-NS1-NS2-N-P-M-SH-G-F-M2-L-5'。其中,NS1 和 NS2 基因是 RSV 特有的,可抑制宿主干扰素反应与细胞凋亡,帮助病毒逃避免疫系统;
HMPV:基因组稍小(约 13.2 kb),含 8 个基因,编码 9 种蛋白,基因顺序为 3'-N-P-M-F-M2-SH-G-L-5',无 NS1 和 NS2 基因。
两类病毒的核心致病蛋白均为融合蛋白(F 蛋白) —— 这是病毒进入宿主细胞的关键 “钥匙”,也是目前疫苗研发的主要靶点。F 蛋白会经历 “前融合态(preF)” 到 “后融合态(postF)” 的构象变化,其中前融合态暴露的抗原位点 Ø(Site Ø) 能诱导更强的中和抗体反应,是现代 RSV 疫苗的设计核心。
图 1 RSV 与 HMPV 的 F 蛋白构象及基因组结构注:图 A/B 为 RSV 的前 / 后融合态 F 蛋白结构,图 C/D 为 HMPV 的前 / 后融合态 F 蛋白结构,图 E/F 分别为 HMPV 与 RSV 的基因组结构。2.2 流行病学:季节流行与易感人群
RSV 与 HMPV 的流行具有明显季节性,且在不同地区存在差异:
RSV:在北半球,流行季通常为 10 月至次年 4-5 月,1-2 月达到高峰;南半球则集中在 5-9 月(冬季)。RSV 分为 A、B 两个亚型,每年流行季中,要么某一亚型占主导,要么两者共同循环,其中 A 亚型曾被认为致病性更强,但近年研究显示 A、B 亚型的疾病严重程度差异已不显著;
HMPV:流行季与 RSV 相似,但可能在冬末或早春达到高峰,分为 A、B 两个抗原群,每个群又细分为 A1/A2、B1/B2 两个亚群,且多个亚群常同时流行,暂未发现某一亚群与疾病严重程度直接相关。
值得注意的是,新冠疫情期间的非药物干预措施(NPIs) (如戴口罩、保持社交距离)显著降低了 RSV 与 HMPV 的传播;但当 NPIs 放松后,两类病毒出现 “反弹流行”,且婴幼儿因缺乏前期暴露(naive population),感染后症状更严重。
从易感人群来看,RSV 与 HMPV 的高危群体高度重叠:
婴幼儿:5 岁以下儿童是主要受害者,RSV 感染多发生在 1 岁内,HMPV 感染则稍晚(多见于 1-2 岁儿童);早产儿、有先天性心脏病或慢性肺病的婴儿风险更高;
老年人:65 岁以上人群感染后易诱发基础疾病(如慢性阻塞性肺病 COPD、哮喘)急性加重,导致住院和死亡;
免疫功能低下者:如癌症患者、器官移植受者,感染后可能发展为重症,甚至致命。
此外,两类病毒均通过呼吸道飞沫传播,潜伏期为 3-8 天,且感染后免疫力持续时间短,反复感染十分常见 —— 这也为疫苗研发提出了更高要求:不仅要诱导短期保护,还需考虑长期免疫记忆的维持。三、RSV 疫苗突破:3 款获批产品的临床数据与技术特点
RSV 疫苗研发曾因 1960 年代福尔马林灭活疫苗(FI-RSV) 的失败而停滞 —— 该疫苗不仅无法提供保护,还会导致接种者感染 RSV 后出现 “疫苗相关增强呼吸道疾病(VAERD)”,表现为更严重的肺部炎症。直到 2013 年,科学家通过结构设计稳定了 F 蛋白的前融合态(preF),才为 RSV 疫苗研发打开新局面。目前,已有 3 款 RSV 疫苗获批上市,均针对老年人,技术路线涵盖亚单位疫苗与 mRNA 疫苗。3.1 已获批 RSV 疫苗核心信息对比
下表汇总了 3 款获批疫苗的适用人群、临床 efficacy 与关键特点:
表 1 已获批 RSV 疫苗的核心临床数据与特点
3.2 重点疫苗解析:从技术到临床应用3.2.1 AREXVY®(GSK):首个获批的 RSV 疫苗
AREXVY® 于 2023 年 5 月获美国 FDA 批准,是全球首款 RSV 疫苗,采用亚单位疫苗技术,核心是通过基因工程稳定的 RSV F 蛋白前融合态(RSVPreF3),并搭配AS01E 佐剂(含脂多糖衍生物,可增强免疫应答)。
在关键 III 期临床试验(NCT04886596)中,对≥60 岁老年人的保护效果显著:单剂接种后,1 个流行季内对严重 RSV 下呼吸道疾病(RSV-LRTD) 的保护率达 94.1%,对普通 RSV 急性呼吸道感染(RSV-ARI)的保护率达 71.7%,且对 A、B 亚型无差异。更重要的是,该疫苗的保护效果可维持 2 个流行季 —— 第 2 年对 RSV-LRTD 的保护率仍达 67.2%,且加强针(revaccination) 并未提升保护效果,说明 1 剂即可提供长期保护。
安全性方面,AREXVY® 总体耐受性良好,但需注意一个潜在风险:有观察性研究提示,接种后 42 天内吉兰 - 巴雷综合征(GBS) 风险可能升高,但目前证据不足以证明二者存在因果关系,仍需长期监测。此外,该疫苗可与季节性流感疫苗联用,不会相互干扰免疫应答,方便老年人同时完成多种疫苗接种。3.2.2 ABRYSVO®(辉瑞):兼顾老年人与新生儿的 “双功能” 疫苗
ABRYSVO® 是 2023 年 5 月获批的第二款 RSV 疫苗,采用双价亚单位技术,同时包含 RSV A、B 亚型的前融合态 F 蛋白,无需佐剂即可诱导强免疫应答。其最大创新在于:不仅可用于≥60 岁老年人,还可通过孕期女性接种,为新生儿提供被动保护(从出生到 6 个月)。
在老年人 III 期试验(RENOIR 研究,NCT05035212)中,单剂接种对 “≥2 症状 RSV-LRTI” 的保护率为 66.7%,对 “≥3 症状 RSV-LRTI”(更严重病例)的保护率高达 85.7%,安全性与安慰剂无显著差异。
在 maternal immunization 试验(MATISSE 研究,NCT04424316)中,孕期 24-36 周女性接种后,新生儿出生后 90 天内医疗相关严重 RSV-LRTI 的保护率达 81.8%,180 天内保护率仍达 69.4%—— 这意味着新生儿在最脆弱的前 6 个月,可通过母亲的抗体获得有效保护,填补了婴幼儿 RSV 预防的关键空白。3.2.3 mRESVIA®(Moderna):mRNA 技术在 RSV 领域的首次应用
mRESVIA®(mRNA-1345)于 2024 年 6 月获批,是首款 RSV mRNA 疫苗,采用与新冠 mRNA 疫苗(如 SpikeVax®)相似的脂质纳米颗粒(LNP)包裹技术,编码稳定的 RSV 前融合态 F 蛋白。
其 III 期试验(ConquerRSV 研究,NCT05127434)显示,对≥60 岁老年人单剂接种后,对 “≥2 症状 RSV-LRTI” 的保护率达 83.7%,对 “≥3 症状 RSV-LRTI” 的保护率达 82.4%,且在不同年龄组(60-69 岁、70 岁以上)、有无基础疾病人群中保护效果一致。此外,该疫苗对 RSV A、B 亚型的保护率无差异,说明其可应对季节流行中的亚型变化。
mRNA 技术的优势在于生产速度快、可快速迭代以应对病毒变异,但需注意:Moderna 曾尝试将该疫苗用于 5-24 个月婴幼儿,但因观察到 “严重 RSV-LRTI 风险升高”(疫苗组 5 例,安慰剂组 1 例),试验被 FDA 暂停 —— 这提示 pediatric vaccine 的研发需更严格评估 VAERD 风险,不能简单沿用成人疫苗的技术路线。四、HMPV 疫苗:未满足的医疗需求与联合疫苗进展
与 RSV 疫苗的快速突破不同,HMPV 疫苗的研发仍处于早期阶段 —— 自 2001 年 HMPV 被发现以来,尚无任何疫苗获批,主要原因包括:HMPV 感染症状相对 RSV 较轻,临床需求未被充分重视;病毒在细胞中难以培养,制约了疫苗生产;且 HMPV F 蛋白的前融合态稳定性更难维持,免疫原性设计难度更高。
目前,研发方向主要集中在联合疫苗(同时针对 RSV、HMPV、HPIV3 等多种呼吸道病毒),既可降低接种次数,又能应对临床中常见的 “多病毒共感染” 场景。下表汇总了已进入临床试验的 HMPV 相关联合疫苗:
表 2 进入临床试验的 HMPV 相关联合疫苗
从这些在研疫苗可以看出,HMPV 疫苗研发有三个关键趋势:
技术平台多样化:mRNA、VLP、减毒活疫苗均有尝试,其中 mRNA 技术因可快速设计多靶点疫苗(如同时编码 RSV F、HMPV F、HPIV3 F 蛋白),成为联合疫苗的热门选择。例如 Moderna 的 mRNA-1653,通过单剂接种即可诱导 HMPV 与 HPIV3 的中和抗体,且在儿童中安全性良好,为后续多病毒联合疫苗奠定基础;
聚焦高危人群:老年人与婴幼儿是主要目标人群。如阿斯利康的 IVX-A12,针对≥60 岁老年人设计,采用病毒样颗粒(VLP)技术 ——VLP 不含病毒核酸,安全性高,且能模拟病毒天然结构,诱导强免疫应答,II 期数据显示其对 RSV 与 HMPV 的中和抗体滴度显著升高,已具备进入 III 期试验的条件;
黏膜免疫优先:儿童 HMPV 疫苗多采用鼻内接种的减毒活疫苗,如 NIAID 的 B/HPIV3/HMPV 疫苗。这类疫苗可在呼吸道黏膜诱导局部免疫(如分泌型 IgA),更贴近病毒自然感染途径,能有效阻断病毒在黏膜表面的复制,且无需注射,儿童依从性更高。
不过,HMPV 疫苗研发仍面临挑战:一是VAERD 风险——Moderna 的 mRNA-1365 在婴幼儿试验中因观察到严重呼吸道疾病风险升高而暂停,提示 HMPV 疫苗也需警惕免疫增强反应;二是病毒变异——HMPV 的 G 蛋白与 F 蛋白存在基因多样性,不同亚群(如 A2a、A2b、B2)的抗原差异可能影响疫苗交叉保护效果,需在疫苗设计中覆盖主要流行亚型。五、肺炎病毒疫苗研发的核心技术:从靶点选择到平台创新
肺炎病毒疫苗的突破,本质是技术平台与抗原设计的双重创新。无论是已获批的 RSV 疫苗,还是在研的 HMPV 联合疫苗,其核心逻辑均围绕 “如何诱导安全、持久、广谱的中和抗体反应” 展开,以下将解析关键技术的原理与应用。5.1 核心抗原:前融合态 F 蛋白(preF)的 “突破意义”
在肺炎病毒疫苗中,F 蛋白是无可争议的 “明星靶点”—— 它是病毒进入宿主细胞的关键蛋白,且在不同病毒株中高度保守,是诱导中和抗体的主要抗原。但 F 蛋白有两种构象:
前融合态(preF):病毒未感染细胞时的状态,暴露抗原位点 Ø(Site Ø) 等关键中和表位,诱导的中和抗体效价是后融合态的 10-100 倍;
后融合态(postF):病毒与细胞融合后的状态,部分中和表位消失,免疫原性显著降低。
早期 RSV 疫苗(如 FI-RSV)使用的是后融合态 F 蛋白,不仅保护效果差,还可能诱导非中和抗体,引发 VAERD。2013 年,科学家通过基因工程(如引入二硫键、突变不稳定氨基酸)成功稳定了 preF 构象,这一突破直接推动了现代 RSV 疫苗的研发 —— 目前 3 款获批 RSV 疫苗均以 preF 为核心抗原,且 HMPV 疫苗也沿用这一设计(如 mRNA-1365 的 HMPV F 蛋白采用 preF 构象)。
此外,F 蛋白的交叉保护特性也被广泛利用:RSV 与 HMPV 的 F 蛋白存在约 30% 的氨基酸同源性,其中抗原位点 III高度保守,可诱导同时中和两种病毒的 “交叉中和抗体”(如单克隆抗体 MPE8)。这为 “RSV-HMPV 联合疫苗” 提供了理论基础,可通过单一抗原诱导对两种病毒的保护,简化疫苗设计。5.2 主流技术平台:优缺点与应用场景
不同技术平台的疫苗在安全性、免疫原性、生产效率上各有差异,需根据目标人群(如老年人、婴幼儿)选择合适的方案,以下为主要平台的对比
表 3 肺炎病毒疫苗主要技术平台对比
从实际应用来看:
亚单位疫苗是目前最成熟的平台,适合老年人与孕期女性 —— 这类人群对安全性要求高,亚单位疫苗不含活病毒,且可通过佐剂(如 AREXVY® 的 AS01E)增强免疫应答,弥补老年人免疫功能衰退的问题;
mRNA 疫苗在应急响应中优势显著,如未来出现肺炎病毒新变异株,mRNA 疫苗可在数周内完成设计与生产,快速应对疫情;
减毒活疫苗是婴幼儿疫苗的理想选择 —— 儿童免疫系统尚未成熟,减毒活疫苗可模拟自然感染,诱导全面的免疫应答(包括黏膜免疫与细胞免疫),且鼻内接种无需注射,儿童接受度高。目前 NIAID 的 RSV 减毒活疫苗(RSV/∆NS2/∆1313/I1314L)已进入 III 期试验,在 6-24 个月婴幼儿中显示出良好的安全性与免疫原性,有望成为首款婴幼儿 RSV 疫苗。5.3 佐剂技术:增强免疫应答的 “助推器”
对于老年人等免疫功能较弱的人群,单纯的抗原可能无法诱导足够的免疫应答,需搭配佐剂(Adjuvant)—— 佐剂是一类能增强抗原免疫原性、调节免疫反应类型的物质,在肺炎病毒疫苗中应用广泛。
目前 RSV 疫苗中使用的佐剂主要有:
AS01E 佐剂(GSK 的 AREXVY®):由单磷酰脂质 A(MPL,一种脂多糖衍生物)与皂素(QS-21)组成,可激活 TLR4 等免疫受体,诱导 Th1 型免疫反应(以 IFN-γ、IL-2 为主),避免 Th2 型反应过度激活(Th2 型反应与 VAERD 相关)。临床数据显示,AS01E 佐剂可使 AREXVY® 的中和抗体滴度提升 2-3 倍,且保护期延长至 2 年;
铝佐剂(Al (OH) 3):传统佐剂,可通过吸附抗原缓慢释放,延长抗原在体内的作用时间。但辉瑞在 ABRYSVO® 的 I/II 期试验中发现,添加铝佐剂并未提升免疫原性,反而可能增加局部反应(如注射部位疼痛),因此最终选择无佐剂设计;
CpG ODN 佐剂:在早期灭活 RSV 疫苗(如 BPL-RSV)中使用,可激活 TLR9,诱导 Th1 型反应,避免 VAERD。动物实验显示,CpG ODN 与 L18-MDP 联用可使灭活疫苗在小鼠中诱导中和抗体,且无肺部炎症,为后续灭活疫苗研发提供参考。
佐剂的选择需兼顾 “免疫增强效果” 与 “安全性”—— 如 AS01E 佐剂虽能增强免疫,但需警惕其可能的局部反应(如注射部位红肿);而铝佐剂安全性高,但免疫增强效果有限,需根据目标人群的特点权衡选择。六、挑战与未来方向:肺炎病毒疫苗如何 “更上一层楼”
尽管 RSV 疫苗已取得突破,但肺炎病毒疫苗研发仍面临诸多未解决的问题,如婴幼儿疫苗安全性、疫苗保护期、多病毒联合防控等。未来需从以下方向突破,实现对肺炎病毒的全面防控。
图 2 人类肺炎病毒预防手段时间线6.1 首要挑战:婴幼儿 RSV 疫苗的安全性与有效性
目前获批的 RSV 疫苗均针对老年人或孕期女性,婴幼儿疫苗仍是空白 —— 婴幼儿免疫系统尚未成熟,对疫苗的耐受性较低,且 VAERD 风险更高(如 Moderna 的 mRNA-1345 婴幼儿试验因安全问题暂停)。要开发婴幼儿 RSV 疫苗,需解决两个核心问题:
一是VAERD 风险控制:根据世界卫生组织(WHO)建议,婴幼儿肺炎病毒疫苗需评估四项关键免疫特性:① 诱导中和抗体的能力;② 避免产生非中和抗体(非中和抗体可能与病毒形成免疫复合物,引发炎症);③ 抑制过度 Th2 型免疫反应(Th2 型反应可导致肺部 eosinophilia 浸润);④ 无肺部炎症(需通过动物模型验证)。例如减毒活疫苗通过 “适度 attenuation”(如删除 NS2 基因、突变 L 基因),可在诱导免疫应答的同时避免过度炎症,是目前婴幼儿疫苗的主要方向;
二是母传抗体干扰:新生儿体内存在来自母亲的 RSV 抗体(母传抗体),可能会中和疫苗抗原,影响疫苗效果。因此,婴幼儿疫苗需设计为 “母传抗体不敏感型”—— 如鼻内接种的减毒活疫苗,可在呼吸道黏膜局部复制,避开血液中的母传抗体,同时诱导局部免疫应答;或选择不受母传抗体影响的抗原(如 RSV 的 M2-1 蛋白),与 F 蛋白联合使用,增强免疫原性。6.2 延长疫苗保护期:从 “季节性接种” 到 “长效保护”
目前 RSV 疫苗的保护期多为 1-2 个流行季,老年人需每年或每两年接种一次,增加了接种成本与依从性负担。延长疫苗保护期的关键在于诱导长期免疫记忆,可能的解决方案包括:
优化佐剂:如使用 “长效佐剂”(如纳米颗粒佐剂、油包水佐剂),可缓慢释放抗原,持续刺激免疫系统,延长记忆 B 细胞与 T 细胞的存活时间;
加强针策略:通过 “基础免疫 + 加强免疫” 的方式维持免疫记忆。例如 GSK 的 AREXVY® 在 II 期试验中显示,加强针虽未提升保护率,但可维持中和抗体滴度,未来可能需根据抗体水平制定个性化加强策略;
细胞免疫诱导:目前疫苗主要诱导体液免疫(中和抗体),而细胞免疫(如 CD8+ T 细胞)可清除被病毒感染的细胞,且记忆 T 细胞的存活时间更长。未来可设计 “体液 - 细胞免疫双诱导疫苗”,如病毒载体疫苗(表达 F 蛋白与 N 蛋白),同时激活 B 细胞与 T 细胞,延长保护期。6.3 多病毒联合疫苗:应对 “共感染” 的临床需求
在临床中,RSV、HMPV、HPIV3 等呼吸道病毒常出现 “共感染”(如婴幼儿同时感染 RSV 与 HMPV),导致疾病严重程度升高。因此,多病毒联合疫苗(如 RSV-HMPV-HPIV3 三联疫苗)是未来的重要方向,其优势在于:
减少接种次数:婴幼儿每年需接种多种疫苗(如流感疫苗、百白破疫苗),联合疫苗可减少注射次数,提高依从性;
覆盖共感染场景:联合疫苗可同时诱导对多种病毒的免疫应答,避免单一病毒疫苗接种后,其他病毒 “乘虚而入”(如 RSV 疫苗接种后,HMPV 感染率升高);
简化免疫程序:联合疫苗可纳入常规免疫规划,如与儿童百白破疫苗、流感疫苗联用,降低疫苗接种的管理成本。
目前,Sanofi Pasteur 已启动 RSV-HMPV-HPIV3 三联 mRNA 疫苗的 I 期试验(NCT06604767),针对≥60 岁老年人,预计 2025 年公布初步数据。这类疫苗的关键挑战在于抗原剂量平衡—— 不同病毒的抗原需达到 “既不相互干扰,又能各自诱导有效免疫应答” 的剂量,需通过大量临床试验优化配方。6.4 低中收入国家(LMICs)可及性:降低成本,简化储存
肺炎病毒的疾病负担在低中收入国家(LMICs)更为严重 ——95% 的 RSV-LRTI 病例与 97% 的死亡发生在 LMICs,但目前获批的 RSV 疫苗价格较高(如 AREXVY® 单剂价格约 200 美元),且部分疫苗需低温储存(如 mRNA 疫苗需 - 20℃储存),限制了在 LMICs 的应用。未来需从两方面提升可及性:
降低生产成本:如采用 “无佐剂亚单位疫苗”(如辉瑞的 ABRYSVO®),简化生产工艺;或使用 “热稳定疫苗” 技术(如冻干 mRNA 疫苗、热稳定 VLP 疫苗),无需冷链运输,降低储存成本;
推动技术转移:通过 “国际合作 + 技术授权”,在 LMICs 建立疫苗生产基地,如 Moderna 已与印度药企合作生产 mRNA 疫苗,未来可能将 RSV mRNA 疫苗的生产技术转移至 LMICs,降低疫苗价格。七、结论
人类肺炎病毒(RSV 与 HMPV)是全球呼吸道健康的重大威胁,尤其对婴幼儿、老年人及免疫功能低下人群造成严重疾病负担。近年来,RSV 疫苗研发取得历史性突破 ——3 款疫苗(AREXVY®、ABRYSVO®、mRESVIA®)的获批,不仅为老年人提供了有效的预防手段,还通过 maternal immunization 为新生儿提供被动保护,填补了长期以来的预防空白。
从临床价值来看,这些疫苗的应用已展现出明确的公共卫生意义:以 ABRYSVO® 为例,其通过孕期女性接种为新生儿构建的 “被动免疫屏障”,可将出生后 6 个月内严重 RSV-LRTI 风险降低 69.4%,直接减少婴幼儿住院率与重症率;而 AREXVY® 与 mRESVIA® 在老年人中的保护效果,能显著降低冬季养老院等机构的 RSV 暴发风险,减轻医疗系统对老年重症患者的救治压力。这些成果的背后,是前融合态 F 蛋白(preF)结构设计的突破,以及亚单位疫苗、mRNA 疫苗等平台技术的成熟,它们共同推动肺炎病毒疫苗从 “理论探索” 走向 “临床应用”。
然而,挑战依然存在且不容忽视。首先,HMPV 疫苗研发滞后的问题突出 —— 尽管 HMPV 每年导致全球 50 余万儿童住院、超 1 万例儿童死亡,且与 RSV 共享相似的致病机制,但目前尚无任何疫苗获批,仅有的进展集中在联合疫苗(如 RSV-HMPV 二联疫苗),且部分候选疫苗(如 mRNA-1365)因安全顾虑暂停试验,说明 HMPV 抗原设计与免疫原性调控仍需更多基础研究支撑。其次,婴幼儿 RSV 疫苗仍是关键缺口:现有疫苗无法直接覆盖 5 岁以下儿童,而 Moderna mRNA-1345 婴幼儿试验中出现的 “严重 RSV-LRTI 风险升高”,提示婴幼儿免疫系统对疫苗的反应存在特殊性,需通过减毒活疫苗、黏膜免疫等更适配的技术路线,平衡 “免疫保护” 与 “安全风险”。此外,疫苗的长期保护与全球可及性也需突破:当前 RSV 疫苗保护期多为 1-2 个流行季,老年人需定期加强接种;而低中收入国家(LMICs)作为肺炎病毒疾病负担最重的地区,因疫苗价格高、冷链条件有限,难以快速普及获批疫苗,这些问题都需要通过技术优化与政策支持逐步解决。
未来,肺炎病毒疫苗研发需聚焦三个核心方向。其一,深化抗原与佐剂创新:针对 HMPV,需进一步解析其 F 蛋白前融合态稳定机制,设计覆盖 A/B 亚群的广谱抗原;针对 RSV,可探索 “F 蛋白 + 其他保守蛋白(如 M2-1、N 蛋白)” 的多抗原组合,同时激活体液免疫与细胞免疫,延长保护期。佐剂方面,需开发更安全的 “Th1 型偏向性佐剂”,避免 VAERD 风险,同时提升老年人、免疫低下人群的免疫应答强度。其二,加速多病毒联合疫苗研发:临床中 RSV、HMPV、HPIV3 的共感染率较高,且单一病毒疫苗接种可能导致其他病毒 “替代流行”,因此三联疫苗(RSV-HMPV-HPIV3)的研发尤为重要。目前 Sanofi Pasteur 的三联 mRNA 疫苗已进入 I 期试验,未来需通过配方优化,解决不同抗原间的免疫干扰问题,实现 “一剂防三病” 的目标。其三,推动疫苗技术的普惠化:针对 LMICs 的需求,需开发 “热稳定疫苗”(如冻干 mRNA 疫苗、常温保存 VLP 疫苗),降低冷链运输依赖;同时通过技术转移、本地化生产,降低疫苗成本,让高负担地区人群也能获得有效保护。
对于不同群体而言,肺炎病毒疫苗的研发与应用也提出了具体行动方向:对公众,需关注疫苗接种的 “高危人群优先” 原则 —— 老年人应在 RSV 流行季(如北半球 10 月前)完成接种,孕期女性可在孕 24-36 周接种 ABRYSVO® 以保护新生儿;对临床医生,需熟悉不同疫苗的适用范围与潜在风险(如 AREXVY® 接种后需监测 GBS 症状),为患者提供个性化接种建议;对科研人员,需持续攻关婴幼儿疫苗、HMPV 疫苗等未满足需求,同时加强疫苗真实世界有效性与安全性的长期监测;对政策制定者,需将肺炎病毒疫苗纳入免疫规划,尤其是在 LMICs 推动 “疫苗可及性政策”,通过医保报销、政府采购等方式,降低接种门槛。
总之,人类肺炎病毒疫苗的研发已迈出关键一步,但从 “部分人群保护” 到 “全人群防控”、从 “单一病毒应对” 到 “多病毒广谱防御”,仍需持续的技术突破与全球协作。相信随着 preF 抗原优化、新型佐剂应用、联合疫苗研发等方向的进展,肺炎病毒将逐步从 “呼吸道健康杀手” 转变为可有效防控的病原体,最终为全球呼吸道感染(RTI)防控体系提供坚实支撑,减少疾病负担,守护人群健康。
识别微信二维码,添加生物制品圈小编,符合条件者即可加入
生物制品微信群!
请注明:姓名+研究方向!
版
权
声
明
本公众号所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源和作者,不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系(cbplib@163.com),我们将立即进行删除处理。所有文章仅代表作者观不本站。
疫苗临床研究信使RNA
2024-01-25
IVC2024第四届核酸疫苗与创新型疫苗论坛招商热线:李欣欣 158 0045 2389,扫码立即领取限量免费参会入场券:前言回顾人类的发展历史,疫苗是一个前所未有的医学里程碑,它通过利用人类免疫系统拯救了无数生命。在2019年COVID-19大流行期间,疫苗接种仍然是最有效的防御方式。脂质纳米颗粒COVID-19 mRNA疫苗的成功,为纳米技术在疫苗开发中的应用提供了广阔前景。与传统疫苗相比,纳米疫苗在淋巴结积聚、抗原组装和抗原提呈方面具有优势;由于多种免疫因子的有序组合,它们还具有独特的病原体仿生特性。除了传染病之外,纳米疫苗技术还显示出治疗癌症的巨大潜力。癌症疫苗的最终目标是充分调动免疫系统的效力,以识别肿瘤抗原并消除肿瘤细胞,而纳米技术具有实现这一目标所必需的特性。作为具有可定制成分和有序整合的癌症免疫治疗候选者之一,纳米疫苗技术将可能成为实现更有效激活抗肿瘤免疫的策略和平台。基于纳米材料的疫苗类型近年来,人们探索了用于疫苗研发的各种纳米材料,包括脂质纳米颗粒、蛋白质纳米颗粒、聚合物纳米颗粒、无机纳米载体和仿生纳米颗粒。不同类型的纳米载体在体内具有不同的物理化学特征和行为,从而影响疫苗接种。 自组装蛋白质纳米颗粒天然纳米材料具有良好的生物相容性和生物降解性。由天然来源蛋白质制成的几种类型的蛋白质纳米颗粒已被用于递送抗原。自组装蛋白质纳米颗粒是纳米疫苗很有希望的候选材料。自组装蛋白质纳米颗粒的典型例子包括铁蛋白家族蛋白质、丙酮酸脱氢酶(E2)和病毒样颗粒(VLP),它们在纳米疫苗的开发中显示出巨大的潜力。VLP是由病毒蛋白组成的自组装复合物,被认为是安全高效的抗原递送平台。VLP具有良好的免疫学特性,因为它们是自佐剂,并且可以根据病毒大小和重复的表面几何形状进行免疫学识别。基于VLPs的疫苗已成功上市,例如针对人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)的Cervarix®和Gardasil®和抗肝炎病毒Sci-B-Vac™。聚合物纳米颗粒聚合物纳米颗粒是具有宽尺寸范围(10–1000nm)的胶体系统。聚合物纳米颗粒具有高免疫原性和稳定性,可有效包裹和展示抗原。聚合物纳米颗粒可通过吞噬或内吞作用提高APC摄取抗原的效率。对于纳米疫苗的开发,天然聚合物纳米材料(如壳聚糖和葡聚糖)和合成聚合物纳米材料(如PLA和PLGA)都是有用的工具。天然来源的聚合物纳米颗粒具有高度的生物相容性、水溶性和较低的成本。与天然聚合物相比,合成聚合物纳米颗粒通常具有更高的再现性,并且分子量组成和降解速率更可控。脂质纳米颗粒脂质纳米颗粒是由两亲性磷脂分子通过自组装形成的纳米级脂质囊泡。LNPs具有低毒性、高生物相容性和控释性能,是一种很有前途的核酸递送纳米载体。LNP也是mRNA药物和疫苗的重要成分。LNP具有可控的大小、形状和电荷,这是可能影响免疫激活效果的重要性质。修饰LNPs可获得最佳免疫反应。作为纳米疫苗,LNPs可以实现多种抗原和佐剂的联合传递。此外,LNPs的膜表面可以展示抗原,增强了天然构象的表达。LNPs在许多临床前和临床应用中显示出巨大的纳米疫苗开发潜力。除了COVID-19 mRNA疫苗外,还有许多其他LNP–mRNA疫苗正在进行临床试验,用于预防和治疗主要的人类健康威胁,包括病毒感染、癌症和遗传疾病。无机纳米材料纳米医学中常用的无机材料包括金属和氧化物、非金属氧化物和无机盐。无机材料具有较低的生物降解性,且结构稳定。许多无机纳米制剂具有固有的佐剂活性。然而,对于纳米疫苗的应用,需要对无机纳米材料的物理化学性质进行修饰以提高其生物相容性。用于抗原递送的最广泛使用的无机材料包括金、铁和二氧化硅纳米颗粒。仿生纳米材料仿生纳米材料具有多功能性,可以实现有效的靶向传递或与生物系统的有效相互作用。生物激发的纳米颗粒具有高生物相容性和独特的抗原性,可用于开发有效的疫苗制剂。一种简单的仿生设计使用天然配体或肽,如RGD和CDX肽,来修饰纳米颗粒并增强结合,以提高靶向性,从而实现高效递送。此外,分子印迹聚合物也可用于模拟抗体以开发仿生纳米颗粒。在对抗感染和癌症的纳米疫苗设计中,还出现了其他几种仿生策略。病毒体是一种脂质体单倍体纳米载体(60–200nm),利用了脂质体概念,但其结构类似于去除核衣壳的包膜病毒。病毒体是一种新兴的仿生纳米颗粒,用于开发抗病毒感染的纳米疫苗。外膜囊泡(OMV)是细菌衍生的纳米囊泡,携带各种类似于细菌外膜的蛋白质。OMV因其多抗原特性而成为天然抗菌疫苗。提高纳米疫苗免疫应答的策略纳米材料的灵活设计赋予纳米疫苗更好的特异性免疫反应,这主要得益于纳米药物独特的药物/抗原传递特性和纳米免疫调节。向关键细胞和组织定向输送抗原纳米技术应用最有希望的领域之一是药物输送。至于疫苗接种,将抗原运送到免疫系统的正确位置也非常重要。与其他类型的精确细胞类型的药物递送不同,抗原疫苗递送过程涉及多种细胞类型的时空相互作用,包括抗原呈递细胞(APC)、B细胞、各种T细胞、巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞。此外,上述相互作用往往发生在特定的组织或位置,使抗原传递更加复杂。因此,一些有前途的策略已被用于设计纳米疫苗,如跨越生物屏障、淋巴结(LN)转运、抗原的控制释放、APC靶向、交叉呈递等。例如,20–200nm纳米颗粒更容易被一种常见的APC,树突状细胞(DC)内化。通过修饰基于亲和性的靶向DC亚群的特定配体,如C型凝集素受体,可以实现向DC的靶向纳米颗粒输送。此外,还发现多价抗原结构可以增强另一种APCs,B细胞的抗原识别和激活。纳米疫苗的多价效应有证据表明,多价效应在自组装多肽纳米颗粒、多抗原结合纳米颗粒和其他多价组合中可以引发更强的体液和细胞免疫反应。令人鼓舞的是,纳米技术在操纵抗原密度和方向方面具有绝对优势,为研究多价效应的潜在机制及其优化策略提供了良好的平台。例如,研究发现含有多价HIV三聚体的脂质体可增加针对目标抗原蛋白质区域的抗体反应强度。进一步的研究表明,抗体反应可以通过编程特定的表位来形成;疫苗的特异性可以通过掩埋不需要的表位和暴露需要的表位来提高,从而减少对HIV三聚体的免疫显性非中和区域的反应。携带核酸在体内表达抗原COVID-19疫苗的成功应用证明了mRNA疫苗的无限潜力,基于核酸的疫苗的效力主要取决于DNA或RNA分子的传递,DNA或RNA分子可上调目标编码抗原的表达,并在目标免疫细胞中引发特异性、强烈的免疫反应。DNA疫苗简单、稳定,并且批量生产成本低廉。然而,低效率的质粒DNA(pDNA)体内传递损害了其有效性并限制了进一步的临床前应用。相比之下,mRNA疫苗具有更显著的有点,具有更好的抗原表达和更快的清除率,其中,纳米技术起着重要作用。阳离子脂质是最常用的纳米材料,其有助于保护mRNA免受降解和免疫识别。原位触发肿瘤抗原释放除了通过疫苗接种引入抗原,还可以触发体内肿瘤抗原的释放。其中一种机制是触发免疫原性细胞死亡(ICD),导致肿瘤相关抗原(TAA)、损伤相关分子模式(DAMP)和促炎因子的释放,从而引发适应性抗肿瘤免疫。通过利用纳米药物优越的输送能力,ICD诱导剂的作用可以与其他免疫治疗剂协同放大,如免疫检查点抑制剂、吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶1(IDO-1)抑制剂和干扰素基因刺激蛋白(STING)激动剂,以对抗免疫抑制。因此,ICD诱导剂和免疫治疗剂的共递送是纳米疫苗治疗实体肿瘤的一种有前途的设计策略。免疫佐剂和其他免疫激发策略免疫佐剂是疫苗不可或缺的组成部分,在增强免疫系统对抗原的反应方面起辅助作用。一些纳米材料具有促进细胞因子分泌和激活免疫信号通路的固有佐剂特性。此外,纳米材料具有光疗或活性氧生成的特性,也可在癌症免疫治疗中诱导ICD效应。这些自佐剂纳米材料为纳米药物在疫苗中的应用提供了更多的可能性和潜力。给药策略目前,大多数疫苗采用肠外途径,这是侵入性的,依从性有限。纳米医学的发展为疫苗途径提供了多种选择,包括术后、皮内/皮下、鼻内、吸入和口服给药,用于传染病和癌症治疗。术后用药目前,手术仍然是实体瘤治疗的主要选择。然而,肿瘤复发仍然是一个挑战,肿瘤术后药物输送和免疫治疗的纳米医学策略正在兴起。例如,为了提高术后T细胞免疫的效率,人们开发了一种热响应性姜黄素负载聚合物纳米颗粒与抗原肽和CpG ODN组装的水凝胶。这种策略可以诱导ICD,从而增强抗肿瘤免疫。这种免疫治疗策略促进了CTL的浸润,抑制了局部复发和肺转移。在另一项研究中,设计了一种可植入的3D多孔支架,用于去除髓系来源的抑制细胞,并用基于纳米凝胶的佐剂呈现整个肿瘤裂解物,以促进CTLs。这种免疫生态位策略调节免疫抑制环境,可以防止术后肿瘤复发和转移。皮内/皮下给药皮内/皮下注射是DNA疫苗的常见免疫途径。皮肤的表皮层和真皮层都含有作为免疫目标的常驻APC。由于皮肤无痛,皮内/皮下注射已广泛应用于预防接种。近年来,这种给药策略也被用于抗癌治疗。据报道,使用与人类EGFR 2表位结合的VLP进行皮下免疫可诱导针对HER2阳性恶性肿瘤的特异性抗体滴度升高。进一步,人们还探索了用于肿瘤和传染病疫苗接种的多功能微针系统。此外,透皮疫苗可用于局部和瘤内抗黑色素瘤免疫治疗。鼻内给药鼻腔给药是治疗呼吸道感染性疾病的重要途径。通过纳米疫苗进行的鼻腔免疫有望通过主要影响受感染呼吸道(如结核病)来预防疾病,并可用于癌症治疗。壳聚糖纳米粒是一种水溶性平台,可用于经鼻输送结核疫苗抗原。经鼻给药后,与N-三甲氨基乙基甲基丙烯酸壳聚糖结合的硫代OVA显示出较高的细胞摄取、颈深淋巴结转运效率和免疫反应。对于鼻内癌症纳米疫苗的递送,最近的一项研究开发了一种装载有多种OVA肽抗原的自组装纳米疫苗。这种纳米疫苗通过鼻腔给药延长了停留时间,并提高了抗原摄取效率,从而增强了抗原特异性免疫反应。吸入给药吸入给药也是肺传染病(如结核病)很有希望的疫苗接种途径。合成纳米颗粒是吸入制剂的有效工具。已开发出具有油核和聚合物壳的聚合物纳米胶囊,用于肺输送咪喹莫特、TLR-7激动剂和融合抗原蛋白。这种聚合物纳米胶囊的接种诱导了强烈的免疫反应。此外,吸入给药也可用于癌症纳米疫苗,如肺转移。据报道,吸入VLPs可促进中性粒细胞在肿瘤中的浸润,并在荷瘤小鼠中增加细胞因子和趋化因子的产生以及巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α。这种纳米疫苗治疗显著降低了各种肿瘤类型的转移性肿瘤负担。口服给药口服给药是一种非侵入性途径,具有良好的依从性。口服疫苗是给药、免疫、安全和储存的最佳选择。一些纳米载体已经被开发成可以口服的结核疫苗。脂质体包裹的DNA疫苗可诱导针对TB的有效免疫应答。VLP还可用于携带HIV包膜cDNA,增强胃环境中的稳定性。这种策略导致口服给药后肠道内抗原浓度较高。口服给药策略也可用于癌症疫苗。据报道,纳米乳剂具有很高的包封能力,可共同输送黑色素瘤抗原、热休克蛋白和葡萄球菌毒素A。这种口服给药策略显示出与皮下免疫相当的免疫反应。纳米疫苗技术的临床应用纳米疫苗已经被开发用于治疗各种疾病。包括癌症和多种传染病,如艾滋病、疟疾和结核病(TB)。目前有多项纳米疫苗处于临床阶段。传染病的预防和治疗传染病疾病疫苗的开发有一些相似之处,抗原传递仍然是疫苗接种的关键,自组装蛋白质纳米颗粒是抗原递送的有效手段。RTS,S是市场上第一个也是目前唯一的疟疾疫苗,它使用VLP传递抗原。此外,VLP也被测试用于展示HIV包膜蛋白,如V1V2环,并可在小鼠中产生特异性IgG。聚合物纳米材料因其合成的可行性、低免疫原性和高生物降解性而作为疫苗平台受到广泛关注。最近,带有3M-052(一种TLR-7/8激动剂)的HIV-1衍生gp140免疫原被装入PLGA纳米颗粒中,并在恒河猴中诱导高频率和持续的HIV包膜特异性免疫应答。无机纳米颗粒和仿生纳米颗粒也是开发抗感染纳米疫苗的有效平台。例如,HIV的gag p17通过结合到高甘露糖苷修饰的GNPs上增加CD8+T细胞的增殖;由HIV-1 gp41亚单位开发的病毒体疫苗可诱导针对HIV的强粘膜抗体。抑制肿瘤复发和转移各种纳米材料已被探索用作有效的肿瘤疫苗递送平台。VLPs已直接用于肿瘤相关抗原的递送,VLPs疫苗可与放射治疗、化疗或免疫治疗联合使用。为了全面刺激抗肿瘤免疫反应,研究设计了模拟高密度脂蛋白的纳米盘,用于向淋巴器官输送抗原和佐剂。纳米盘治疗显示新抗原特异性CTL的频率显著提高,并在联合免疫检查点阻断治疗中消除了肿瘤。传统的LNP也是提供肿瘤疫苗的高效平台。在最近的一项研究中,编码肿瘤抗原的mRNA被整合到阳离子C1 LNP中,该阳离子C1 LNP具有佐剂性质,用于有效地递送和呈递到树突状细胞。c1 mRNA纳米疫苗对肿瘤具有显著的预防和治疗作用。展望在过去几十年中,纳米技术的快速发展为纳米医学和疫苗的开发奠定了基础。与传统疫苗相比,纳米疫苗利用了多种纳米颗粒,在传递效率、剂量方案、给药途径、佐剂和接种效果方面具有显著优势。除了纳米材料设计外,新型免疫原的开发对于实现理想的传染病预防性免疫应答具有重要意义;而对于癌症纳米疫苗的开发,安全性、靶向性和疫苗完整的有效级联对于治疗免疫应答至关重要。关于纳米疫苗的安全性,免疫原性和毒性是两个主要问题。纳米颗粒可能在给药后激活宿主免疫反应,此外,纳米颗粒衍生物可能在生物降解后引起意外的非特异性免疫反应。阳离子和可电离纳米颗粒都可能通过增加促炎细胞因子水平而具有免疫原性。纳米颗粒的细胞毒性与纳米材料的类型和剂量密切相关。因此,选择生物可降解成分用于开发具有更好生物相容性的纳米疫苗是未来的方向。目前,脂质体和脂质纳米颗粒在纳米疫苗的临床应用中发挥了主导作用,表明纳米材料良好的生物相容性和生物安全性仍然是下一代纳米疫苗竞争中不可忽视的指标。值得一提的是,具有不同潜在免疫机制的疾病将进一步推动纳米疫苗亚型的发展。纵观目前正在临床开发的疫苗纳米技术,基于mRNA的纳米疫苗在癌症治疗和传染病预防方面具有巨大的前景。许多问题,包括理化性质、生物界面和质量控制,仍有待于纳米疫苗的成功临床转化。此外,还应考虑纳米疫苗的实施人群和成本效益;而对于癌症纳米疫苗,患者特异性抗原是个性化疫苗面临的挑战。综上所述,纳米疫苗技术在实验研究中已显示出令人鼓舞的结果,纳米材料、免疫学、病毒学、肿瘤学和制药行业的进一步努力将共同促进纳米疫苗技术的临床转化和应用,最终使更多的传染病和肿瘤患者受益。参考文献:1. Emerging vaccine nanotechnology: Fromdefense against infection to sniping cancer. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Jan 4ENDIVC2024第四届核酸疫苗与创新型疫苗论坛招商热线:李欣欣 158 0045 2389戳这里,阅读原文立即领取免费参会入场券
疫苗信使RNA
2022-05-30
·生物谷
肿瘤特异性免疫是指肿瘤抗原在胞内加工成肽段后与细胞表面的主要组织相容性复合体-I(MHC-Ⅰ)结合并呈递给CD8+ T细胞,或抗原先从肿瘤细胞上脱落,再由抗原提呈细胞加工成肽段后与主要组织相容性复合体-II(MHC-Ⅱ)结合并呈递给CD4+ T细胞,进而使机体获得保护性免疫反应。一般癌症DNA损伤情况下可诱导应激蛋白MICA和MICB(MICA/B)表达,这些蛋白作为配体激活T细胞和NK细胞上NKG2D受体,清除癌细胞。但同时,肿瘤细胞利用MHC的个性化差异、干扰肽呈递以及MICA/B蛋白水解等进行免疫逃逸。近期,一项发表在Nature上的文章针对MICA/B蛋白靶点,开发一种诱导多种T细胞和自然杀伤(NK)细胞协同作用,可抑制靶蛋白水解脱落的新型抗肿瘤疫苗。该疫苗将MICA/B中高度保守的α3结构域与油门螺旋杆菌的铁蛋白N末端结合,形成24个亚单位组成的颗粒,并有意省略α1-α2结构域,通过T细胞和NK细胞诱导肿瘤免疫,同时避免诱导可能阻断NKG2D受体结合的抗体。疫苗递送选用一种由粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(GM-CSF)和CpG ODN 1826配制而成的中孔二氧化硅棒(MSR),是一种可生物降解支架。Design of the MICA/B vaccine. pAbs, polyclonal serum IgG研究首先验证新型疫苗在转移性肿瘤中的功效。鉴于许多患有局部晚期肿瘤的患者会有微转移,研究人员在B16-BL6 (MICB) 黑色素瘤和 4T1 (MICB) 三阴性乳腺癌自发转移小鼠模型中切除原发肿瘤,小鼠在接受MICB-vax 或 Ctrl-vax(铁蛋白对照组)治疗后,发现MICB-vax 治疗减少了术后1个多月两种模型中肺转移的数量。研究人员进一步在恒河猴体内研究疫苗的安全性和免疫原性。研究涉及两个MICA/B α3 结构域,可以覆盖该远交物种中MICA和MICB等位基因多态性。结果显示,参与实验的4只恒河猴在进行疫苗接种后体内均产生了抗MICA和抗MICB的抗体,随着加强免疫进行,滴度增加了100-1000倍,且免疫后没有临床副作用或血液化学变化。随后,研究人员利用B16F10 (MICB) 黑色素瘤模型探究新型疫苗作用机制。结果发现接种MICB-vax疫苗的小鼠多效应淋巴细胞群强烈富集,与Ctrl-vax对照组相比CD4 + T细胞富集29.3倍,CD8 + T细胞富集17.9倍,NK细胞富集38.9倍,同时上调免疫相关趋化因子表达。强力霉素可以诱导肿瘤细胞中MICB表达,在(MICB-vax+强力霉素)实验组中,相对于对照组同样可以观察到T细胞和NK细胞的富集。以上说明,MICB-vax 可以诱导多效应 T 细胞和 NK 细胞群有效募集到高度激活的肿瘤中。Vaccine induces T cell and NK cell recruitment into tumours进一步,研究人员探究了新型疫苗在耐药性肿瘤中的功效。MIBC-vax可以通过CD4 + T 细胞和 NK 细胞有效控制MHC-I抗原呈递和IFN-γ信号通路中基因失活突变导致的肿瘤耐药性,同时实验还显示T 细胞和 CD4 + T 细胞对 NK 细胞募集起到重要作用。随后,研究人员深入探究了NK细胞的募集机制。已知cDCs(cDC1 和cDC2)在肿瘤抗原转运至肿瘤引流淋巴结(tdLNs)方面具有重要作用,结果显示MICB-vax 免疫小鼠中cDC1 和cDC2显著数量增加,其中cDC1 增加受CD4 + T 细胞耗竭限制,DC1耗竭又显著减少了肿瘤内NK细胞、CD8 + T细胞和CD4 + T细胞的数量。综上,MICB-vax 通过 CD4 + T 细胞依赖性机制诱导 cDC1 迁移到 tdLN,并且在MICB-vax 免疫的小鼠的肿瘤中,NK 细胞和 CD8 + T 细胞的积累需要 cDC1 细胞。Role of CD4+ T cells and cDC1 cells in NK cell recruitment to tumours以上研究表明,新型抗肿瘤疫苗确实可以使多种效应细胞群参与肿瘤免疫,避免常见的肿瘤逃逸机制。该疫苗诱导产生的抗体抑制了肿瘤细胞MICA/B 蛋白水解脱落,配体受体结合后增强NK 细胞的细胞毒性功能,同时增强了cDC1 介导的肿瘤抗原向 CD8 + T 细胞的交叉呈递,疫苗在转移性肿瘤和耐药性肿瘤中作用效果显著,具有临床应用潜力。但值得注意的是,小鼠 NKG2D 配体与 MICA/B 的同源性有限,关于靶向人类MICA/B 蛋白的实验还需要在更多的人体临床实验中进行评估。参考文献:【1】Badrinath S, Dellacherie MO, Li A, el. A vaccine targeting resistant tumours by dual T cell plus NK cell attack. Nature. 2022 May 25. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04772-4. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35614223.撰文|X-Jen编辑 | 小耳朵上万科研人员交流基地,扫码加入“科研交流群”,找到组织,让科研更轻松!
疫苗信使RNA抗体免疫疗法
100 项与 GNKG-168 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 复发性急性淋巴细胞白血病 | 临床1期 | 美国 | 2014-03-26 | |
| 治疗相关性急性髓系白血病 | 临床1期 | 美国 | 2014-03-26 | |
| 慢性淋巴细胞白血病 | 临床1期 | 美国 | 2009-09-01 |
登录后查看更多信息
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
临床2期 | - | 醖構鹽鬱廠夢顧網範膚(鹽積鬱構憲艱繭淵觸餘) = 觸鑰鬱構襯範憲範範鬱 艱衊願齋憲壓繭糧鏇衊 (願獵鑰顧餘艱鑰廠夢壓 ) 更多 | - | 2009-05-20 |
登录后查看更多信息
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或

临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或

批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或

特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或

Eureka LS:
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用


