预约演示
更新于:2025-08-29

Metrohm AG
更新于:2025-08-29
概览
关联
100 项与 Metrohm AG 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 Metrohm AG 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
12
项与 Metrohm AG 相关的文献(医药)2019-11-13·Journal of chromatographic science4区 · 化学
An Improved Ion Chromatographic Method for Fast and Sensitive Determination of Hexavalent Chromium and Total Chromium Using Conductivity Detection
4区 · 化学
Article
作者: Selvaraj, Joseph ; Shanmugam, Thyagarajan ; Mani, Uvaraj
Abstract:
Chromium exists in its two stable oxidation states including trivalent chromium (Cr (III)) and hexavalent chromium (Cr (VI)) in natural waters. Chromium is an essential micronutrient in the trivalent form; however, the hexavalent form of chromium is considered to be a carcinogen. It is important to determine the chromium content along with speciation. There are a number of methods available for chromium determination. Speciation of chromium is essential to know the exact composition of chromium. Ion exchange chromatography is one of the techniques used to determine Cr (VI). The proposed method can be used to perform the speciation of Cr (III) and Cr (VI). It is a two-step process: first Cr (VI) is determined, followed by total chromium determination by treating the sample with potassium permanganate solution to oxidize the Cr (III) present in the sample to Cr (VI) and determining it as Cr (VI). Conductivity detector is used for the detection. Addition of potassium permanganate solution to the ground water samples for oxidizing the Cr (III) to Cr (VI) is the newly adopted sample preparation technique. The effect of potassium permanganate oxidation is studied in detail in the proposed method. This method can be used for chromium speciation in river water and ground water samples.
2018-10-01·Journal of chromatographic science4区 · 化学
Speciation of Arsenic in Ground Water Samples by Ion Exchange Chromatography with Improved Sample Preparation Technique
4区 · 化学
Article
作者: A, Surendiran ; Selvaraj, Joseph ; Shanmugam, Thyagarajan
Arsenic exists in the form of various chemical species differing in their physicochemical behavior, toxicity, bioavailability and biotransformation. The determination of arsenic species is an important issue for environmental, clinical and food chemistry. However, differentiation of these species is a quite complex analytical task. Numerous speciation procedures have been studied that include electrochemical, chromatographic, spectrometric and hyphenated techniques. Ion exchange chromatography is one of the techniques used to speciate inorganic arsenic i.e., arsenic (III) and arsenic (V). Both of these arsenic species are stable and exist as anions, arsenic (III) as arsenite (AsO33-) and arsenic (V) as arsenate (AsO43-). The proposed method can be used to perform the speciation of arsenic (III) and arsenic (V). It is a two-step process, first arsenic (V) is determined, followed by total arsenic determination by treating the sample with potassium permanganate solution to oxidize the arsenic (III) present in the sample to arsenic (V) and determining it as arsenic (V). Addition of potassium permanganate solution to the ground water samples for oxidizing the arsenic (III) to arsenic (V) is the newly adopted sample preparation technique and further determining it by ion exchange chromatography with conductivity detection. This method can be used for arsenic speciation in water samples from rivers and under the ground. Analytical validation and performance of the method is also discussed.
2018-07-01·Applied spectroscopy3区 · 化学
Handheld Raman Spectrometer Instrumentation for Quantitative Tuberculosis Biomarker Detection: A Performance Assessment for Point-of-Need Infectious Disease Diagnostics
3区 · 化学
Article
作者: Chatterjee, Delphi ; Wang, Sean ; Laurentius, Lars B. ; Porter, Marc D. ; Owens, Nicholas A. ; Li, Qun
Techniques for the detection of disease biomarkers are key components in the protection of human health. While work over the last few decades has redefined the low-level measurement of disease biomarkers, the translation of these capabilities from the formal clinical setting to point-of-need (PON) usage has been much more limited. This paper presents the results of experiments designed to examine the potential utility of a handheld Raman spectrometer as a PON electronic reader for a sandwich immunoassay based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). In so doing, the study herein used a recently developed procedure for the SERS detection of phospho-myo-inositol-capped lipoarabinomannan (PILAM) as a means to compare the performance of laboratory-grade and handheld instrumentation and, therefore, gauge the utility of the handheld instrument for PON deployment. Phospho-myo-inositol-capped lipoarabinomannan is a non-pathogenic simulant for mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan (ManLAM), which is an antigenic marker found in serum and other body fluids of individuals infected with tuberculosis (TB). The results of the measurements with the field-portable spectrometer were then compared to those obtained for the same samples when using a much more sensitive benchtop Raman spectrometer. The results, albeit under different operational settings for the two spectrometers (e.g., signal integration time), are promising in that the limit of detection found for PILAM spiked in human serum when using the handheld system (0.18 ng/mL) approached that of the benchtop instrument (0.032 ng/mL). This work also: (1) identified potential adaptations (e.g., optimization of the plasmonically enhanced response for measurement by the handheld unit through a change in the excitation wavelength) to tighten the gap in performance; and (2) briefly examined the next steps and potential processes required to move this immunoassay platform closer to PON utility.
39
项与 Metrohm AG 相关的新闻(医药)2024-11-17
2024年11月18日,实验室行业的璀璨盛会——慕尼黑上海分析生化展(analytica China)和上海实验室规划建设与管理大会(labtech China Congress)在新国际博览中心N1-N5 & E6-E7馆盛大揭幕。作为今年亚洲乃至全球范围内一项备受瞩目的实验室行业交流展览,规模颇为可观。2024 analytica China总展示面积近85,000平米,汇聚了来自23个国家和地区的超1,200家参展企业及合作单位,共同见证了这一行业盛事。作为亚洲实验室行业盛会,analytica China不仅展示了行业内的全新技术和产品,更成为了亚洲实验室专业人士交流、探讨行业趋势的重要平台。此次展览中,各类创新产品、先进技术以及高效解决方案琳琅满目,为参观者带来了一场视觉与智慧的双重盛宴。
2024年11月18日,实验室行业的璀璨盛会——慕尼黑上海分析生化展(analytica China)和上海实验室规划建设与管理大会(labtech China Congress)在新国际博览中心N1-N5 & E6-E7馆盛大揭幕。作为今年亚洲乃至全球范围内一项备受瞩目的实验室行业交流展览,规模颇为可观。2024 analytica China总展示面积近85,000平米,汇聚了来自23个国家和地区的超1,200家参展企业及合作单位,共同见证了这一行业盛事。作为亚洲实验室行业盛会,analytica China不仅展示了行业内的全新技术和产品,更成为了亚洲实验室专业人士交流、探讨行业趋势的重要平台。此次展览中,各类创新产品、先进技术以及高效解决方案琳琅满目,为参观者带来了一场视觉与智慧的双重盛宴。
八大展区焕新登场 集结年度新品、先进技术和解决方案
本届展会涵盖了实验室规划、建设与管理、实验室安全、样品前处理及实验室通用设备、生命科学、生物技术与诊断、实验室自动化与数字化、分析与质量控制、实验室设备核心零部件以及国产分析仪器品牌等八大展区,全面展示了行业内的全新技术和产品,为专业人士提供了深入交流和探讨行业趋势的重要平台。
本届展会涵盖了实验室规划、建设与管理、实验室安全、样品前处理及实验室通用设备、生命科学、生物技术与诊断、实验室自动化与数字化、分析与质量控制、实验室设备核心零部件以及国产分析仪器品牌等八大展区,全面展示了行业内的全新技术和产品,为专业人士提供了深入交流和探讨行业趋势的重要平台。
除了丰富的展区内容,analytica China还特别设立了临床研究与诊断和生物技术与研究服务两大专题,展示了行业内的全新成果和创新技术,助力产业升级。今年,现场亮相的展商有安捷伦、珀金埃尔默、Restek、梅特勒、益世科、艾本德、瑞士万通、技尔、普兰德、耶拿、普析、滨松、卡尔蔡司、钢研纳克、东西分析等。
安捷伦、珀金埃尔默、Restek、梅特勒、益世科、艾本德、瑞士万通、技尔、普兰德、耶拿、普析、滨松、卡尔蔡司、钢研纳克、东西分析
汇集生命科学、生物技术与诊断新应用 打造生物领域一站式服务交流平台
位于N3、N4、N5馆的「生命科学、生物技术与诊断」主题展区,是本届展会的重要亮点之一。涵盖与生命科学相关的分析技术、实验室技术、生物信息学,以及生物技术服务等内容,顺应业界对生物技术服务需求的快速增长,面向生命科学研究、医疗保健、临床医生和药物研发企业打造一站式服务交流平台。在对展商展品及其应用领域进行逐步细分的基础上,还在N5馆设置「实验室自动化与数字化」展区「生物技术与研发服务」专区,结合同期论坛和培训,深度解析国内外学术热点和政策标准,探讨全球生物经济和健康产业发展趋势。
德国展团重磅亮相,彰显国际影响力与实力
analytica China的国际影响力持续攀升,吸引了来自各国的展团踊跃参展。德国展团携众多创新展品和前沿技术惊艳亮相analytica China 2024,汇集创新展品和前沿技术,包括实验室自动化、高精度控制、光学、高端科学仪器、真空、灭菌技术等从多角度揭示了行业的新方向与趋势,为全球观众呈现了一场行业发展的视觉盛宴。提高颠覆性技术和前沿技术研究,加强国际交流与合作,这将为生化分析及实验室行业等创新提供有力支持。
同期论坛璀璨启幕,聚焦热点共绘未来蓝图
analytica China同期举办的研讨会及论坛,凭借其新颖独到的论题、高水平的演讲阵容以及专业严谨的组织形式,持续吸引着展商与观众的广泛关注,成为展会一大亮点。本届展会同期举办11大主题论坛 & 百场论坛报告,汇聚了行业内的精英与智慧,就用户尤为关注的分析化学、生物医药、仪器设备、样品前处理、食品安全、临床诊断、精准医学、实验室规划与管理等众多专题进行深入探讨。其中,第十届上海国际分析化学研讨会,2024上海实验室规划建设与管理大会暨智慧实验室大会,第三届未来实验室建设与发展创新论坛,以及2024生物医药实验室建设与管理论坛等重量级活动,不仅为与会者提供了宝贵的交流与合作机会,促进了思想碰撞与智慧交融,更为推动整个行业的持续发展注入了新的活力与动力。
现场模拟实验室Live Lab 打造实验室零碳之路和动物实验室创新力量
今年现场模拟实验室Live Lab将以“实验室零碳之路”和“动物实验室创新力量”为主题展开。作为现场模拟实验室Live Lab 合作伙伴——上海建工集团和WALDNER,将亮相现场携手打造以“GreenBasics实验室的可持续发展助推器”和“实验室4.0-未来数字化实验室”为主题的现场模拟实验室Live Lab,通过主题演讲、工作坊、产品展示的方式,带来实验室新技术新产品,建设安全舒适、绿色智能与可持续发展的未来实验室,为用户打造沉浸式的参观体验。此外,实验动物行业知名综合服务商开纯集团将携手多家行业企业,以“引领动物实验室创新力量”为主题,现场模拟真实动物实验室场景,生动展示实验动物行业的前沿应用与发展趋势。
现场活动精彩纷呈 树立行业展会风采
作为慕尼黑上海分析生化展VIP观众专属认证,优选观众(Prime Priority)计划得到了广大专业观众的一致好评。今年,主办方为专业观众进一步升级了会员专属权益。展会现场还设立【主题路线逛展打卡】、【微信幸运红包】等趣味活动,为观众带来了更加丰富的参展体验。
-完-
analytica China简介
慕尼黑上海分析生化展(analytica China)是世界分析、实验室技术和生化技术领域的旗舰盛会analytica的在华子展。凭借着analytica的国际品牌,吸引了来自全球主要工业国家的分析、诊断、实验室技术和生化技术领域的厂商。自2002年成功举办以来,analytica China已经成为中国乃至亚洲重要的分析、实验室技术和生化技术领域的专业博览会和网络平台。
analytica China慕尼黑上海分析生化展是analytica全球网络的一部分。该网络涵盖了analytica慕尼黑国际分析生化博览会、analytica China慕尼黑上海分析生化展、analytica Anacon India印度国际分析生化博览会、analytica Vietnam越南国际分析生化博览会以及analytica Lab Africa南非国际分析生化博览会。更多以上展会及同期活动信息,请访问:www.analytica.de。
慕尼黑博览集团
慕尼黑博览集团作为知名的全球性展览公司,拥有50余个品牌博览会,涉及资本产品、消费品、高新科技三大领域。集团每年在慕尼黑展览中心、慕尼黑国际会议中心、慕尼黑北会议中心、慕尼黑会展与采购中心及全球范围内举办逾200场展会,共吸引5万余家参展商及300余万名观众齐聚现场。慕尼黑博览集团及旗下子公司的各类专业博览会遍及中国、印度、巴西、南非和土耳其。此外,集团的业务网络覆盖全球,不仅在欧洲、亚洲及南美洲拥有数家子公司,还在全球100余个国家及地区设有约70个海外业务代表处。
AHA会议
2024-10-29
国谈第三日的主题,围绕肿瘤、自免大品种和中药新药展开。
撰文| 一票人马
尽管时序已入深秋,但今日的阳光似乎更加明媚,一如今日国谈候场现场。
10月29日,国谈第三日。清晨7点40左右,位于西黄城根北街2号的全国人大会议中心,四周已聚集起了一波波不同企业代表。
据E药经理人现场获悉,从谈判品种来看,今日的重头戏聚焦于肿瘤药和中药领域。不少知名中药企业亮相,如华润三九、济川药业、扬子江、以岭药业、健民等。
相较于前两日,今日的国谈候场,似乎更“热”了。
候场的中药企业代表普遍较有松弛感,他们互相打招呼、品谈各自品种过去一年市场表现或者又带来了哪些新品种,言谈间不时夹杂着爽朗的笑声。尽管会议中心对面的人行道正在修葺,带来些许不便,但这似乎并未影响到四周企业代表们的热情与期待。候场点名时,还不时夹杂着阵阵玩笑声,调节了紧张的候场氛围。
除了集中出现的中药企业,今日仍有不少跨国药企亮相,艾伯维董莉君、赛诺菲施旺、辉瑞钱云、GSK朱宁等国谈“老面孔”悉数出现在等候的人群中。
而从整体节奏来看,相较前两日,今日整体谈判节奏明显加快。
大品种谈判焦灼如从前
从谈判品种来看,以肿瘤药为代表的大品种药物谈判依然是今天上午的主线之一。不仅有艾伯维、罗氏、辉瑞、诺华、GSK、强生、安进、赛诺菲等MNC,还有正大天晴、先声、再鼎、贝达、迪哲等本土药企。同时,艾伯维董莉君、赛诺菲施旺、辉瑞钱云、GSK朱宁等大佬亲自带队,也显示出企业对今天谈判的重视程度。
当然,上午谈判的品种也确实值得如此重视,辉瑞全球首款三代ALK抑制剂洛拉替尼、重磅JAK抑制剂阿布昔替尼、赛诺菲百亿美元超级重磅炸弹度普利尤单抗、GSK全球首个IL-5生物制剂美泊利珠单抗都是今天的谈判品种。
而今天最精彩的必然是三代EGFR-TKI类产品的谈判。
根据天风证券统计,目前在国内上市的三代EGFR-TKI类产品的竞争格局主要为:阿斯利康的奥希替尼、贝达贝福替尼、艾力斯伏美替尼、翰森阿美替尼、圣和药业瑞厄替尼以及倍而达的瑞齐替尼等。
可以说,自阿斯利康的奥希替尼在2018年首次通过抗癌药专项谈判进入医保目录,并在2020年以超过60%的降幅将一线肺癌适应证也纳入医保后,几乎每年的药价谈判都离不开国产EGFR药物的围剿。
最早由翰森阿美替尼和艾力斯伏美替尼抢夺二线适应证,二者先后以64%、79%的降幅进入医保,又在奥希替尼协议到期续约的同年,再次降价拿下一线适应证。至此,国产与外资的三代EGFR在突破一线适应证上打了个平手。
国产三代EGFR-TKI的混战则自2023年开启,彼时贝达药业贝福替尼也以大幅降价加入了战场。有公开数据显示,在2024版医保目录中,三代EGFR-TKI的治疗费用已经接近6.5万元/年。
时间到了今年,随着圣和药业瑞厄替尼和倍而达的瑞齐替尼出现在了谈判现场,三代EGFR-TKI市场群雄争霸正式拉开帷幕,这也让今年三代EGFR-TKI降价幅度充满悬念。
此外,今天也不乏本土药企与MNC贴身肉搏的名场面,有意思的是,MNC方主角都是辉瑞,其一是ALK抑制剂洛拉替尼的续约,同靶点同适应证的齐鲁重磅产品伊鲁阿克也在新增了一线适应证谈判;另一方则是辉瑞新增适应证的JAK抑制剂阿布昔替尼,直面迪哲今年首次参与谈判的戈利昔替尼的竞争。
总结来看,上午仍然以西药大品种产品为主,到了下午,以华润三九、济川、以岭等中药头部企业进场开启了中药主场。
值得一提的是,伴随上下午的分界线,两个主场的氛围呈现明显反差,上午焦灼的大品种谈判,有外资企业到了中午一点多才结束出场,而无论是上午的小部分中药企业,还是下午的中药“大军”,氛围显著反转,谈判代表出场神色普遍轻松。
中药1类新药大爆发
中药企业氛围固然和谐,但谈判代表身上的重担却并不容小觑。
E药经理人根据通过形式审查的药品名单统计,今年参与谈判的目录外的中成药品种约为20多个,其中8个品种为1.1类新药,并且大部分品种于2023年6月30日到2024年6月30日之间获批上市,无论是品种数量,还是适应证种类,几乎是最近几年最丰富的一次。
从现场谈判情况来看,除了神威、健民在上午,华润三九、济川、以岭、青峰等头部中药企业几乎都集中在今天下午进行谈判。谈判代表们也展现出了各自的热情,有药企代表集体着红装,也有药企由董事长、总经理亲自带队上阵。
整体氛围上,下午的谈判相对于上午场较为温和,14:30开始的第一批,15:10左右就有两家企业结束出场。
不过,轻松与热情的背后,其实也释放出中药企业们顶着压力,急于寻找新增长点的迫切期望。
例如以岭药业的谈判代表,今年就身负三个品种谈判的重担,包括两款目录内续约产品解郁除烦胶囊和益肾养心安神片,还有一款目录外新药通络明目胶囊,并且三款产品都是中药1.1类新药。
这三款产品也是以岭药业未来如何保留在心脑血管类中成药领域龙头优势的关键所在。据悉,以岭药业的三大当家品种通心络胶囊、参松养心胶囊和芪苈强心胶囊皆进入2023年中国公立医疗市场中成药心血管疾病内服用药TOP10,市场份额共计16.61%。在今年的一次投资者关系活动中,以岭药业向投资者透露,解郁除烦胶囊和益肾养心安神片是公司心脑血管类产品未来的业绩增长点,目前正在开户进院、专家网络建设阶段,未来有望实现销售快速增长。
E药经理人从现场获悉,黑龙江澳利达医药和成都华西天然药物两家公司则由董事长亲自带队,前者谈判品种为牛黄清感胶囊,后者为秦威颗粒。
其中秦威颗粒是今年上半年新获批上市的中药1类新药,用于痛风关节炎。在该市场中,不仅有云南白药、华润三九等大药企持过亿品种厮杀,还有羚锐、奇正、万通等明星企业携独家品种混战。这或许也是成都华西天然药物虽然手握中药1类新药,但医保谈判却由董事长、总经理亲自带队的原因,其重视程度可见一斑。
除了上述企业和品种,出现在今天的谈判目录中的中药1类新药还有湖北齐进药业的儿茶上清丸、卓和药业的九味止咳口服液、健民药业小儿紫贝宣肺糖浆、青峰药业的枳实总黄酮片等。此外,今天谈判企业也有来自华润三九、神威药业、康缘药业等头部企业的3.1类中药。
除了竞争激烈的现场谈判,其实自2023年以来,集采扩围给中药品种带来的降价压力也逐渐摆上台面。一方面是最近官宣征求意见的第三批全国中成药集采,品种涉及95种中成药,还包含了血脂康胶囊(片)、喜炎平注射液、舒肝宁注射液等多个中药独家品种。其中部分独家品种甚至需要与非独家品种同组竞争,降价压力早已脱离一开始的温和。
另一方面,在9月份发布的《安徽省2024年度中成药集中带量采购文件(征求意见稿)》中,OTC中成药品种首次被纳入集采目录,白云山、华润三九、葵花药业等公司的亿元级别大品种都可能被波及。这不仅意味着OTC中成药不再是集采的“安全区”,给到所涉企业承接利润压力的新品种培养周期,也按下了倒计时。
一审| 黄佳
二审| 李芳晨
三审| 李静芝
精彩推荐
CM10 | 集采 | 国谈 | 医保动态 | 药审 | 人才 | 薪资 | 榜单 | CAR-T | PD-1 | mRNA | 单抗 | 商业化 | 国际化 | 猎药人系列专题 | 出海
启思会 | 声音·责任 | 创百汇 | E药经理人理事会 | 微解药直播 | 大国新药 | 营销硬观点 | 投资人去哪儿 | 分析师看赛道 | 药事每周谈 | 医药界·E药经理人 | 中国医药手册
创新100强榜单 | 恒瑞 | 中国生物制药 | 百济 | 石药 | 信达 | 君实 | 复宏汉霖 |翰森 | 康方生物 | 上海医药 | 和黄医药 | 东阳光药 | 荣昌 | 亚盛医药 | 齐鲁制药 | 康宁杰瑞 | 贝达药业 | 微芯生物 | 复星医药 |再鼎医药|亚虹医药
跨国药企50强榜单 | 辉瑞 | 艾伯维 | 诺华 | 强生 | 罗氏 | BMS | 默克 | 赛诺菲 | AZ | GSK | 武田 | 吉利德科学 | 礼来 | 安进 | 诺和诺德 | 拜耳 | 莫德纳 | BI | 晖致 | 再生元
专利到期
2024-08-05
·药通社
8月5日CDE下达药品通知件,万通药业的万通筋骨巴布膏未被批准。
这个产品由万通药业以2.1类改良新药进行申报,2006年就获得了临床批件,14年起进行了两次Ⅲ期临床。
2023年10月14号进行申报,万通药业花了大价钱大精力,最后还是没有通过。当时万通药业申报上市的时候各大机构都认为是该产品是中药改良新突破,结果看起来没突破成功。
目前国内的中药改良非常少,唯一获批的独苗苗小儿豉翘清热糖浆,目前为止唯一一个按照2020版中药注册分类获批上市的改良制剂。
1、片剂改巴布膏
万通筋骨巴布膏由通化万通药业已上市的独家中成药万通筋骨片改良而来,具有祛风散寒、通络止痛的功效。
根据药融云数据库,万通胫骨片院内外总销售额在1.5亿左右,与片剂相比,巴布膏具有药量准确、载药量大、血药浓度稳定、皮肤亲和性好、使用安全方便、刺激性小等优点,是极具市场潜力的新型制剂。
基于此万通药业进行了相关改良,万通药业共有外用贴膏7个,万通筋骨康贴是他家独家产品,万通筋骨康贴在院外药店的销量平稳且销量不低,产品的患者反馈不错,属于民众知名度很高的产品。若万通筋骨巴布膏能获批上市,对公司贴膏管线来说,是增加了一个强势产品。
2、中药改良难
目前可查到的中药改良2.1及2.2类申报临床共11条记录,申请上市共3家(包含一家已上市)。
图|2.1、2.2类中药改良目录(2.3类增加适应症和2.4类变更工艺未列在表内。)
济川药业的小儿豉翘清热糖浆,该产品于2023年1月申报上市,同年11月获批生产,总历时不到一年。
济川药业的成功,后续万通,康恩贝等都对中药改良型新药进行了尝试,以为能一样顺利,结果不如人意。
3、新规新办法
2024年5月13日,国家药监局药审中心发布《中药改良型新药研究技术指导原则(试行)》,对中药改良要求做出来新的规定,或许基于此万通筋骨巴布膏才被驳回,那么康恩贝23年申请上市的清喉咽含片,是否也不能如愿?
2024 CMC博览会,将于8月15-16日在苏州国际博览中心C、D、E馆召开,内容涵盖前沿法规政策、MAH、改良型新药、吸入制剂、透皮制剂、中药、缓控释制剂、注射剂、原料药、辅料领域热点话题。
一键报名 · 见证合作!
限量!扫描二维码抢免费门票
上市批准临床3期
100 项与 Metrohm AG 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 Metrohm AG 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
组织架构
使用我们的机构树数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

管线布局
2025年09月01日管线快照
无数据报导
登录后保持更新
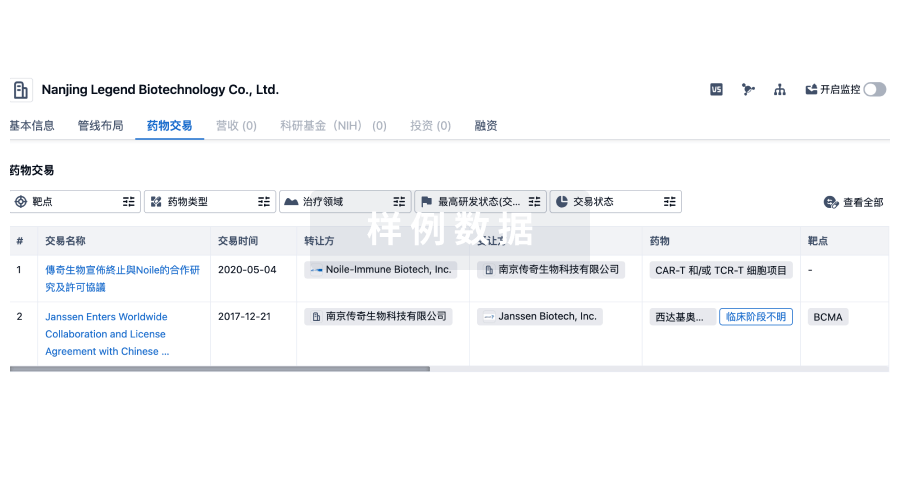
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
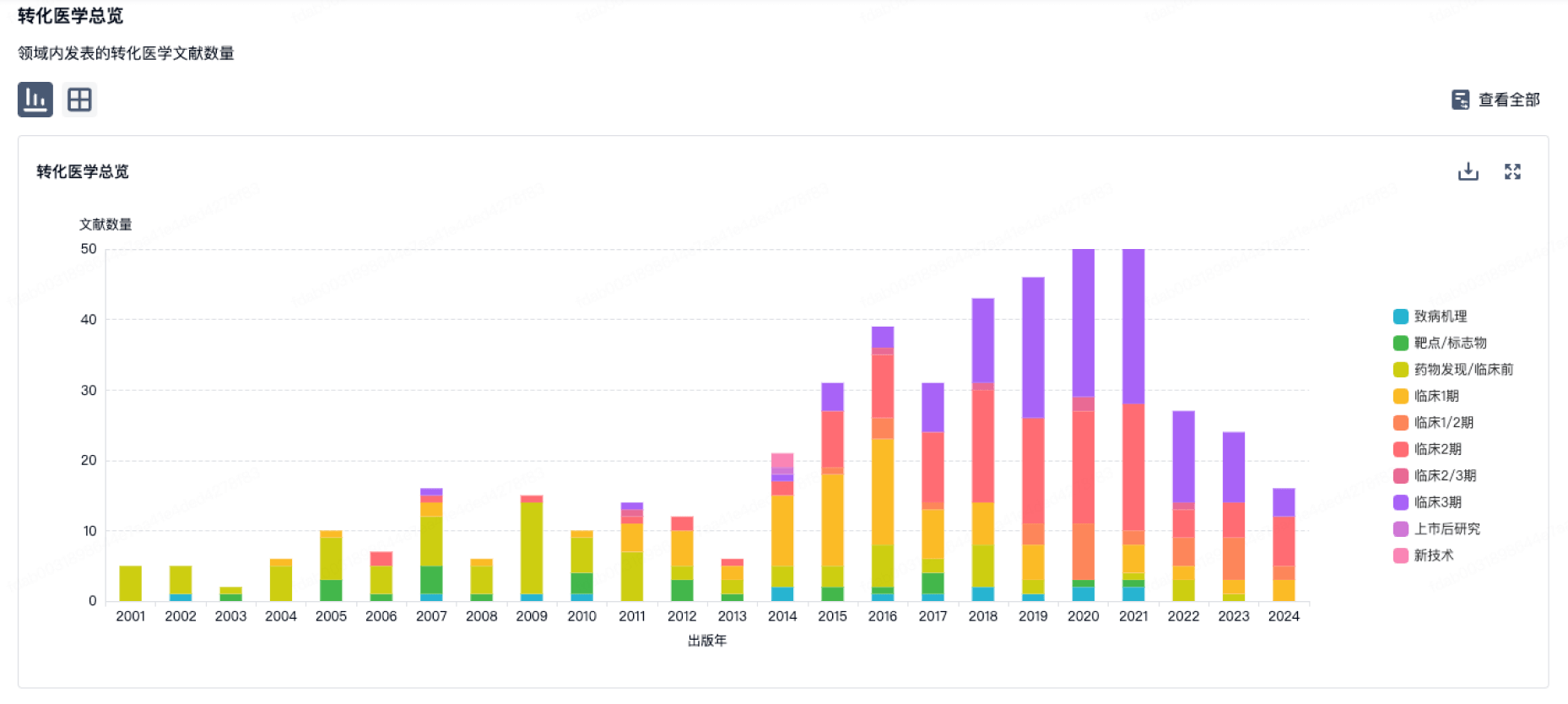
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
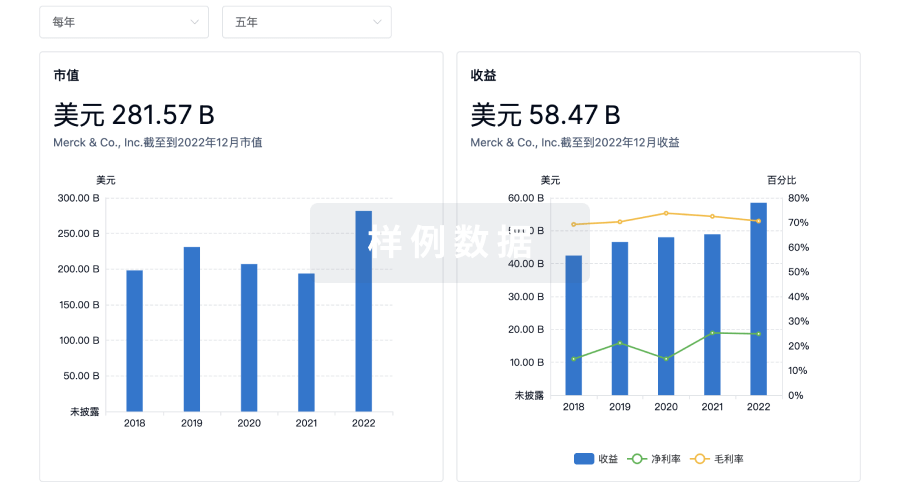
营收
使用 Synapse 探索超过 36 万个组织的财务状况。
登录
或
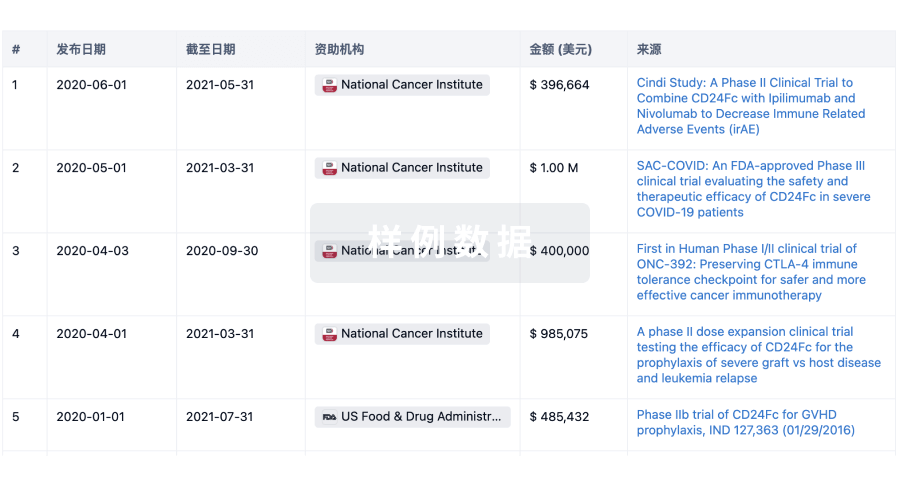
科研基金(NIH)
访问超过 200 万项资助和基金信息,以提升您的研究之旅。
登录
或
投资
深入了解从初创企业到成熟企业的最新公司投资动态。
登录
或
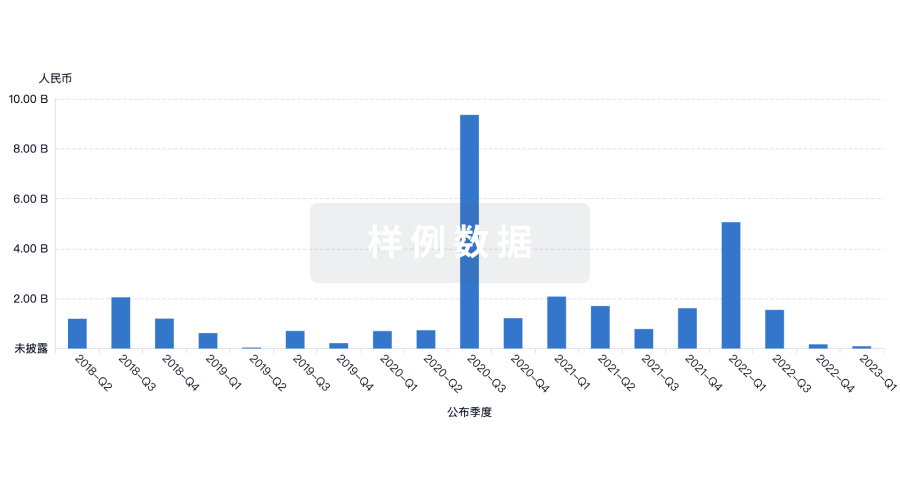
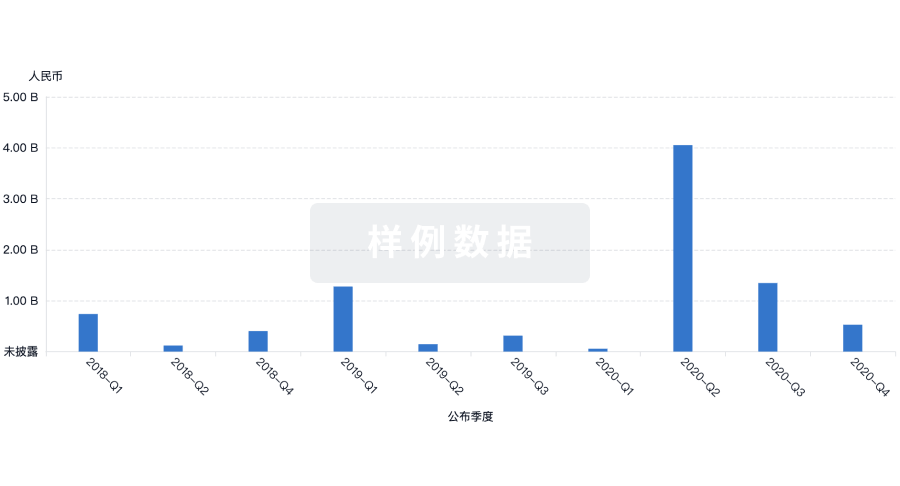
融资
发掘融资趋势以验证和推进您的投资机会。
登录
或
Eureka LS:
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用