更新于:2024-11-01

Fakeeh Care Group
更新于:2024-11-01
概览
关联
100 项与 Fakeeh Care Group 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 Fakeeh Care Group 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
2
项与 Fakeeh Care Group 相关的文献(医药)2024-03-03·Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics
Investigation of Zika virus methyl transferase inhibitors using steered molecular dynamics
Article
作者: Alissa, Mohammed ; Alshamrani, Saleh A ; Alshengeti, Amer ; Al Fares, Mona A ; Alwashmi, Ameen S S ; Bajunaid, Huda A ; AlShehail, Bashayer M ; Rabaan, Ali A ; Garout, Mohammed ; Najim, Mustafa A ; Halwani, Muhammad A
Journal of Clinical Medicine
Tocilizumab Outcomes in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients Admitted to the ICU and the Role of Non-Tocilizumab COVID-19-Specific Medical Therapeutics
Article
作者: Azzam, Mohamed H ; Alharthy, Abdulrahman ; Alghamdi, Adnan ; Sallam, Hend ; Elhazmi, Alyaa ; Altalaq, Ali ; Al-Omari, Awad ; Tashkandi, Wail ; Melibari, Rami Ghazi ; Rabie, Ahmed A ; Alajmi, Saud A ; Alshahrani, Mohammed S ; Al-Aseri, Zohair A ; Almekhlafi, Ghaleb A ; Al-Tawfiq, Jaffar A ; Mufti, Hani N ; Mady, Ahmed ; Sindi, Anees ; Arabi, Yaseen M ; Faqihi, Fahad ; Kharaba, Ayman
100 项与 Fakeeh Care Group 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
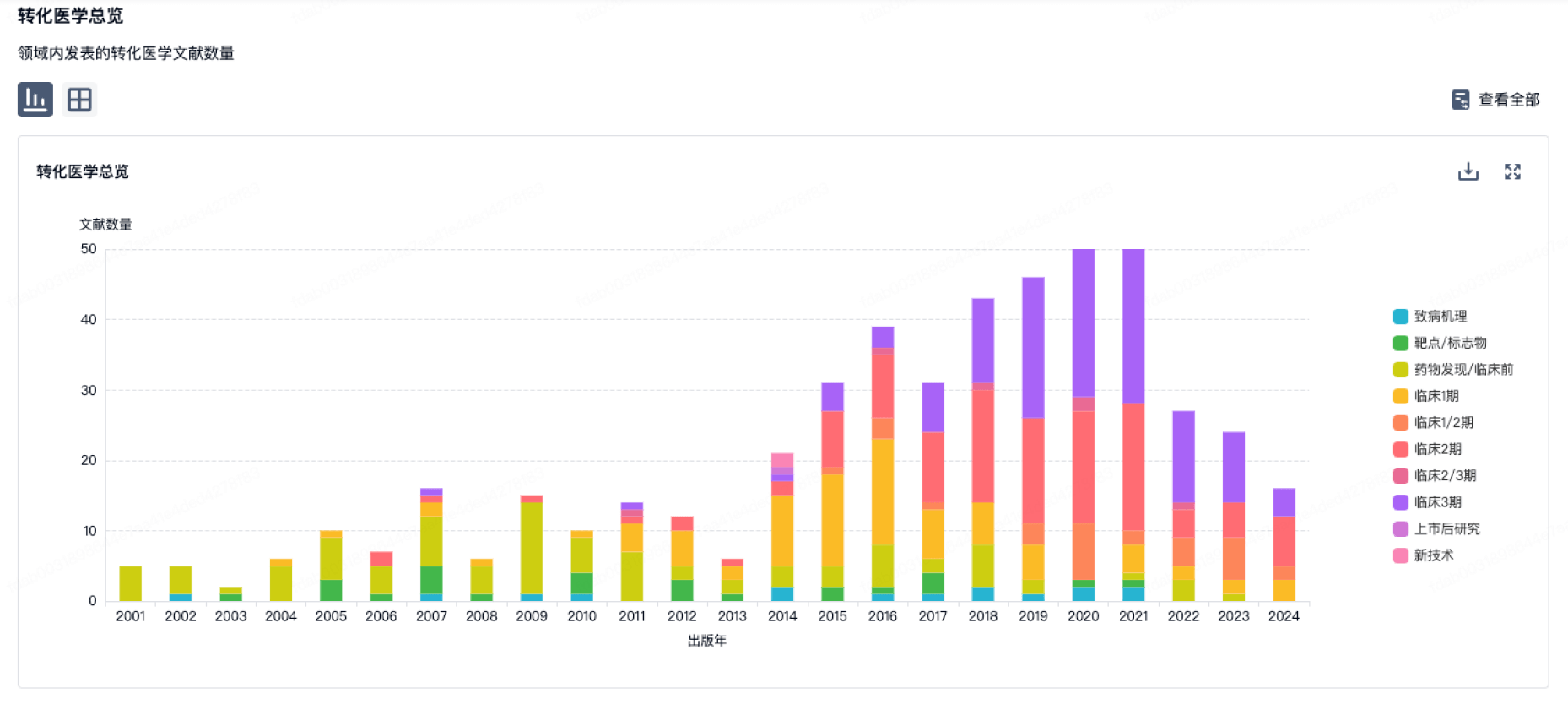
100 项与 Fakeeh Care Group 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
组织架构
使用我们的机构树数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

管线布局
2024年11月17日管线快照
无数据报导
登录后保持更新
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
营收
使用 Synapse 探索超过 36 万个组织的财务状况。
登录
或
科研基金(NIH)
访问超过 200 万项资助和基金信息,以提升您的研究之旅。
登录
或

投资
深入了解从初创企业到成熟企业的最新公司投资动态。
登录
或

融资
发掘融资趋势以验证和推进您的投资机会。
登录
或

标准版
¥16800
元/账号/年
新药情报库 | 省钱又好用!
立即使用
来和芽仔聊天吧
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用