更新于:2024-11-01
IBM Zurich Research Laboratory
私营公司|
Switzerland
私营公司|
Switzerland
更新于:2024-11-01
概览
关联
100 项与 IBM Zurich Research Laboratory 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 IBM Zurich Research Laboratory 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
273
项与 IBM Zurich Research Laboratory 相关的文献(医药)2024-02-01·Life Science Alliance
Proteomic-based stratification of intermediate-risk prostate cancer patients
Article
作者: Aref, Adel T ; Sun, Rui ; Wild, Peter J ; Poyet, Cédric ; Wang, Yingrui ; Hains, Peter G ; Robinson, Phillip J ; Lucas, Natasha ; Noor, Zainab ; Beyer, Andreas ; Hermanns, Thomas ; Chen, Guo-Bo ; Fankhauser, Christian ; Ding, Xuan ; Shao, Wenguang ; Zhong, Qing ; Poulos, Rebecca C ; Aebersold, Ruedi ; Neumann, Janis Frederick ; Zhu, Yi ; Reddel, Roger R ; Zhu, Tiansheng ; Guo, Tiannan ; Rutishauser, Dorothea ; Buljan, Marija ; Rueschoff, Jan H ; Rodríguez Martínez, María ; Lyu, Mengge ; Rupp, Niels J ; Anees, Asim
2023-02-19·2023 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference (ISSCC)
An 8b 1.0-to-1.25GS/s 0.7-to-0.8V Single-Stage Time-Based Gated-Ring-Oscillator ADC with $2\times$ Interpolating Sense-Amplifier-Latches
作者: Morf, Thomas ; Brändli, Matthias ; Ruffino, Andrea ; Kossel, Marcel ; Prathapan, Mridula ; Yonar, Abdullah Serdar ; Jang, Taekwang ; Francese, Pier Andrea
2022-09-19·ESSCIRC 2022- IEEE 48th European Solid State Circuits Conference (ESSCIRC)
A cryogenic SRAM based arbitrary waveform generator in 14 nm for spin qubit control
作者: Zota, Cezar ; Kossel, Marcel ; Brandli, Matthias ; Francese, Pier Andrea ; Heim, David ; Prathapan, Mridula ; Mueller, Peter ; Menolfi, Christian ; Ruffino, Andrea ; Morf, Thomas ; Oropallo, Maria Vittoria
1
项与 IBM Zurich Research Laboratory 相关的新闻(医药)2024-06-17
Google Research and Google DeepMind recently released a paper announcing the creation of a new LLM for drug discovery and therapeutic development dubbed Tx-LLM, fine-tuned from PaLM-2.
Tx-LLM utilizes the tech giant's PaLM-2, its generative AI technology that uses Google's LLMs to answer medical questions.
The drug discovery-focused LLM was trained using 709 datasets to target 66 tasks across the various stages of drug discovery, including evaluating efficacy and safety, predicting targets, and predicting ease of manufacturing.
The LLM constructs the Therapeutics instruction Tuning (TxT) collection by interleaving free-text instructions with representations of small molecules, such as SMILES strings for small molecules.
SMILES, or Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System, is a typographical method using printable characters that represent molecules and reactions.
TxT was then used to prompt and fine-tune Tx-LLM, the therapeutics large language model, to solve classification, regression and generation tasks involved with drug discovery and therapeutic development.
To use TxT to predict drug synergy, the researchers used prompts composed of instructions, context and a question.
Tx-LLM performed above or near the state of the art (SOTA) models for 43 out of 66 tasks, and exceeded SOTA models on 22 tasks.
"Interestingly, we find evidence of positive transfer between datasets with diverse drug types, as training on datasets including biological sequences improves performances on molecular datasets," the authors wrote.
"The proposed Tx-LLM shows promise as an end-to-end therapeutic development assist, allowing one to query a single model for multiple steps of the development pipeline."
THE LARGER TREND
Med-PaLM 2 was released in March of last year, and was found to generate more comprehensive answers to medical questions than the tech giant's original version, Med-PaLM.
Artificial intelligence capabilities are increasingly being used in drug discovery.
In December, Absci, a startup focused on developing generative AI antibody discovery technology, announced a potential $247 million partnership with pharma giant AstraZeneca to expedite the discovery of novel cancer treatments using genAI technology.
A month before, IBM and Boehringer Ingelheim, a German pharma company, announced a collaboration to harness the power of genAI and foundation models to further biologic drug discovery.
Other companies in the space include California-based AI drug-discovery startup Genesis, publicly listed Daewoong Pharmaceutical and Israel-based AION Labs, an AI-enabled drug-discovery partnership between global pharma and tech companies.
The HIMSS AI in Healthcare Forum is scheduled to take place September 5-6 in Boston. Learn more and register.

100 项与 IBM Zurich Research Laboratory 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
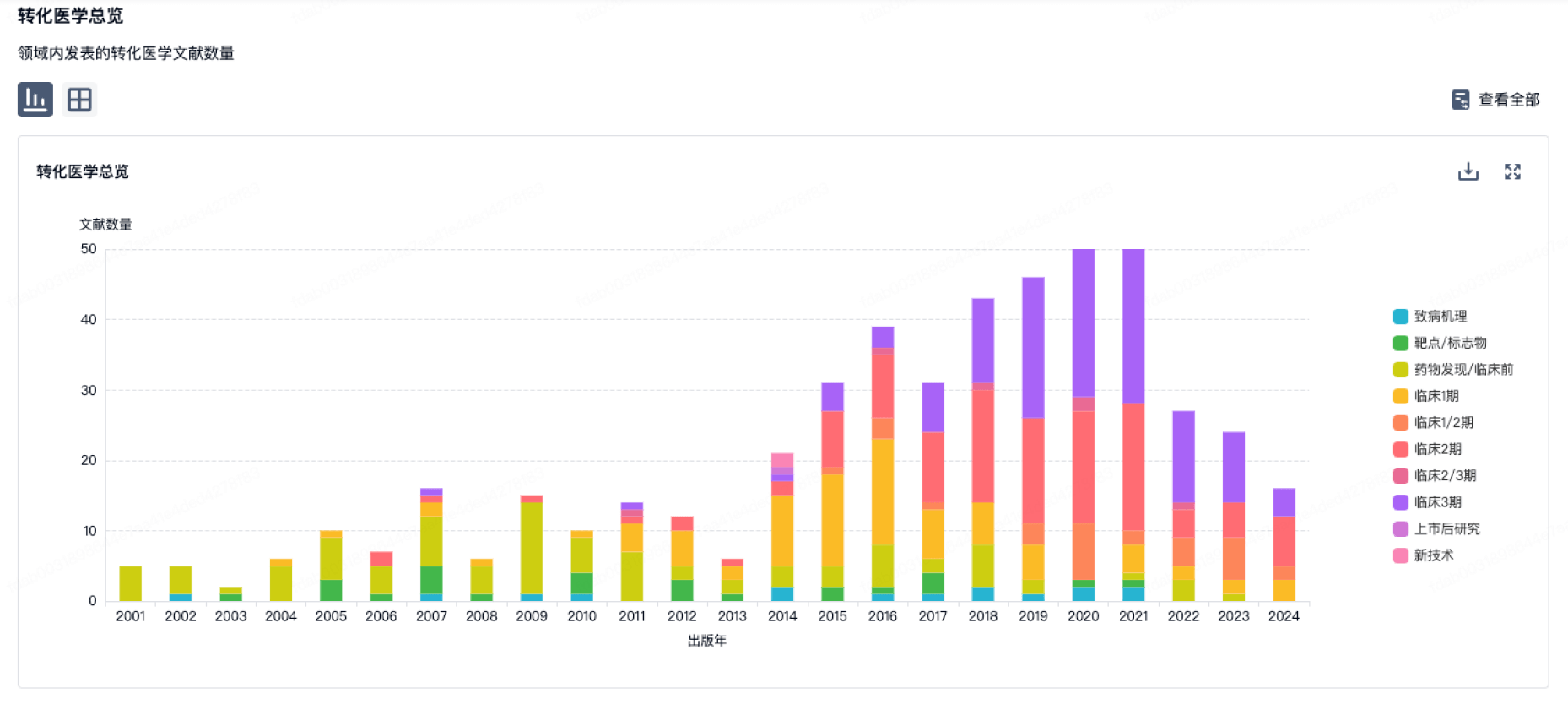
100 项与 IBM Zurich Research Laboratory 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
组织架构
使用我们的机构树数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

管线布局
2024年11月17日管线快照
无数据报导
登录后保持更新
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
营收
使用 Synapse 探索超过 36 万个组织的财务状况。
登录
或
科研基金(NIH)
访问超过 200 万项资助和基金信息,以提升您的研究之旅。
登录
或

投资
深入了解从初创企业到成熟企业的最新公司投资动态。
登录
或

融资
发掘融资趋势以验证和推进您的投资机会。
登录
或

标准版
¥16800
元/账号/年
新药情报库 | 省钱又好用!
立即使用
来和芽仔聊天吧
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用