预约演示
更新于:2025-04-08
UDO(Vanderbilt University)
更新于:2025-04-08
概要
基本信息
非在研机构- |
最高研发阶段临床前 |
首次获批日期- |
最高研发阶段(中国)- |
特殊审评- |
结构/序列
分子式C24H21ClF3N3O |
InChIKeyOJFZYAQGMWSUID-QFIPXVFZSA-N |
CAS号1486506-92-6 |
关联
100 项与 UDO(Vanderbilt University) 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 UDO(Vanderbilt University) 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 UDO(Vanderbilt University) 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
18
项与 UDO(Vanderbilt University) 相关的文献(医药)2024-05-09·JOURNAL OF MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY
Identification of Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Acanthamoeba: Structural Insights into Sterol 14α-Demethylase as a Key Drug Target
Article
作者: Hargrove, Tatiana Y ; Wawrzak, Zdzislaw ; Lamb, David C ; Guengerich, F Peter ; Hull, Marcus ; Lepesheva, Galina I ; Kelly, Steven L
Acanthamoeba are free-living pathogenic protozoa that cause blinding keratitis, disseminated infection, and granulomatous amebic encephalitis, which is generally fatal. The development of efficient and safe drugs is a critical unmet need. Acanthamoeba sterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51) is an essential enzyme of the sterol biosynthetic pathway. Repurposing antifungal azoles for amoebic infections has been reported, but their inhibitory effects on Acanthamoeba CYP51 enzymatic activity have not been studied. Here, we report catalytic properties, inhibition, and structural characterization of CYP51 from Acanthamoeba castellanii. The enzyme displays a 100-fold substrate preference for obtusifoliol over lanosterol, supporting the plant-like cycloartenol-based pathway in the pathogen. The strongest inhibition was observed with voriconazole (1 h IC50 0.45 μM), VT1598 (0.25 μM), and VT1161 (0.20 μM). The crystal structures of A. castellanii CYP51 with bound VT1161 (2.24 Å) and without an inhibitor (1.95 Å), presented here, can be used in the development of azole-based scaffolds to achieve optimal amoebicidal effectiveness.
2024-05-08·JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURAL AND FOOD CHEMISTRY
14C-Isotope Use to Quantify Covalent Reactions between Flavor Compounds and β-Lactoglobulin
Article
作者: Reineccius, Gary A. ; Shepelev, Igor
A 14C-based method was developed to study the rate and extent of covalent bond formation between β-lactoglobulin and three model flavor compounds: a ketone (2-undecanone UDO), an aldehyde (decanal DAL), an isothiocyanate (2-phenylethyl isothiocyanate PEITC), and an unreactive "methods blank" (decane DEC). Aqueous protein solutions with one of the 14C-labeled model flavor compounds were placed in water baths at 25, 45, and 65 °C for 4 weeks measuring the amount of flavor: protein reaction at 1, 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28 days. UDO showed lowest reactivity (max of 0.9% of added compound reacted), DAL (max of 16.4% reacted), and PEITC (max of 71.8% reacted). All compounds showed a rapid initial reaction rate which slowed after ca. 7 days. It appears that only PEITC (at 65 °C) saturated all potential protein-reactive sites over the storage period.
2021-11-08·Optics express2区 · 物理与天体物理
Universal dwell time optimization for deterministic optics fabrication
2区 · 物理与天体物理
ArticleOA
作者: Choi, Heejoo ; Bouet, Nathalie ; Idir, Mourad ; Zhang, Zili ; Kuhne, Dennis ; Negi, Vipender S. ; Nakhoda, Kashmira ; Huang, Lei ; Ke, Xiaolong ; Wang, Chunjin ; Kim, Daewook ; Pullen, Weslin C. ; Vescovi, Matthew ; Wang, Tianyi ; Zhu, Yi ; Kemao, Qian
Computer-Controlled Optical Surfacing (CCOS) has been greatly developed and widely used for precision optical fabrication in the past three decades. It relies on robust dwell time solutions to determine how long the polishing tools must dwell at certain points over the surfaces to achieve the expected forms. However, as dwell time calculations are modeled as ill-posed deconvolution, it is always non-trivial to reach a reliable solution that 1) is non-negative, since CCOS systems are not capable of adding materials, 2) minimizes the residual in the clear aperture 3) minimizes the total dwell time to guarantee the stability and efficiency of CCOS processes, 4) can be flexibly adapted to different tool paths, 5) the parameter tuning of the algorithm is simple, and 6) the computational cost is reasonable. In this study, we propose a novel Universal Dwell time Optimization (UDO) model that universally satisfies these criteria. First, the matrix-based discretization of the convolutional polishing model is employed so that dwell time can be flexibly calculated for arbitrary dwell points. Second, UDO simplifies the inverse deconvolution as a forward scalar optimization for the first time, which drastically increases the solution stability and the computational efficiency. Finally, the dwell time solution is improved by a robust iterative refinement and a total dwell time reduction scheme. The superiority and general applicability of the proposed algorithm are verified on the simulations of different CCOS processes. A real application of UDO in improving a synchrotron X-ray mirror using Ion Beam Figuring (IBF) is then demonstrated. The simulation indicates that the estimated residual in the 92.3 mm × 15.7 mm CA can be reduced from 6.32 nm Root Mean Square (RMS) to 0.20 nm RMS in 3.37 min. After one IBF process, the measured residual in the CA converges to 0.19 nm RMS, which coincides with the simulation.
100 项与 UDO(Vanderbilt University) 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 棘阿米巴角膜炎 | 临床前 | 美国 | 2024-04-29 |
登录后查看更多信息
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
No Data | |||||||
登录后查看更多信息
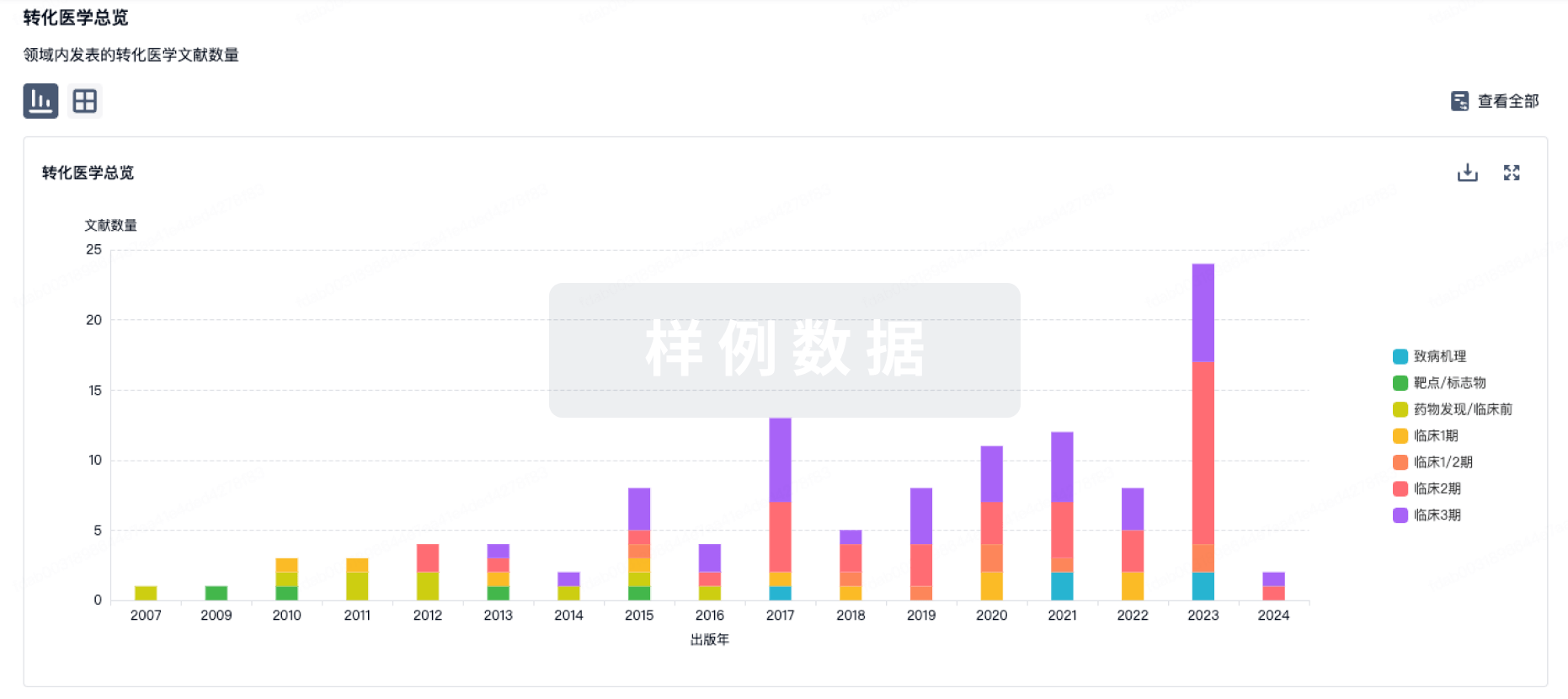
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
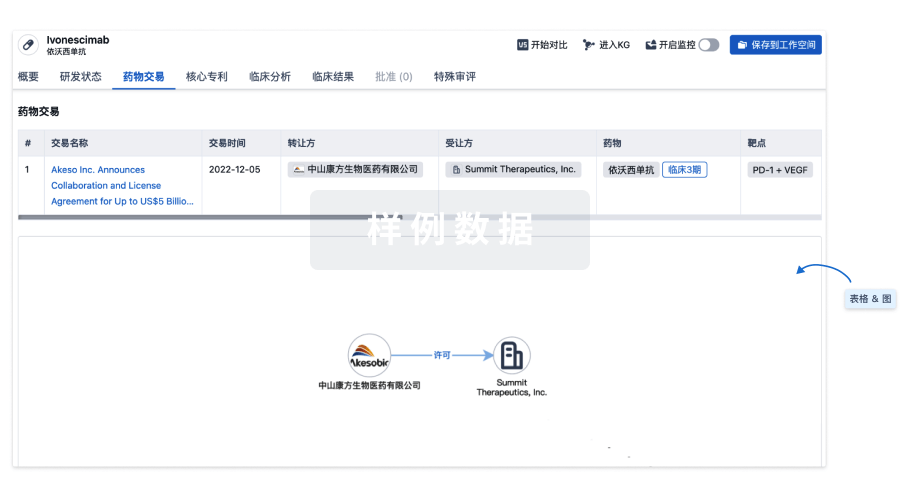
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
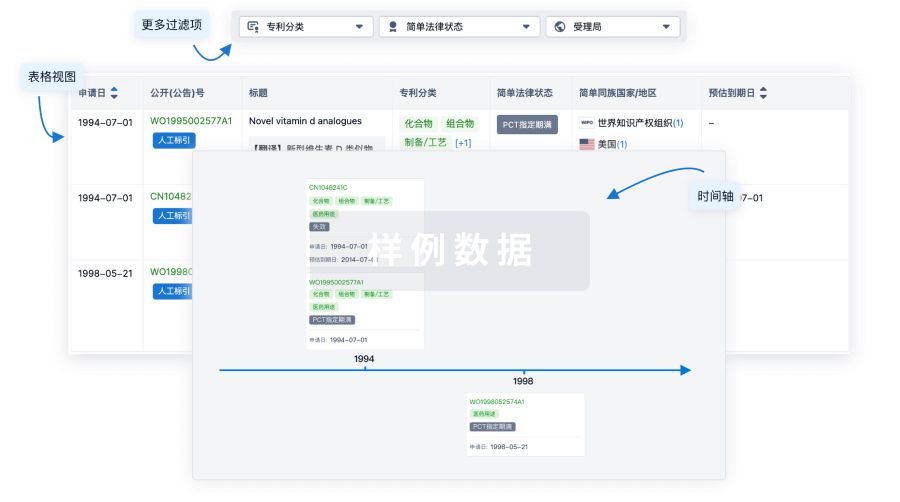
核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或
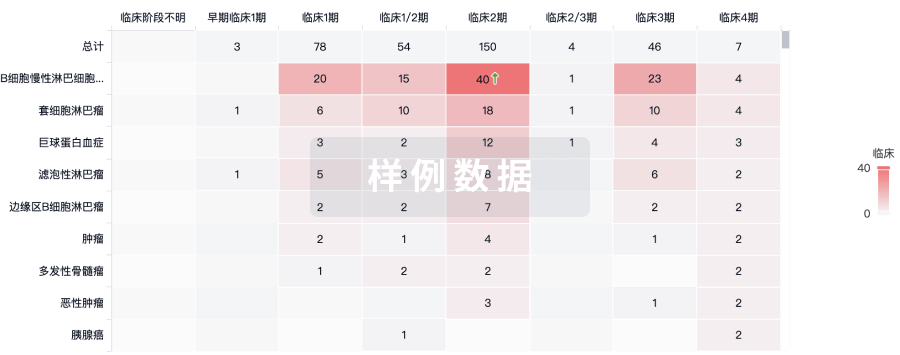
临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或
批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或
特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或
来和芽仔聊天吧
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用
