预约演示
更新于:2025-07-05
CAR-T-19(Immunotech Biopharm)
抗CD19单链抗体嵌合抗原受体T细胞(永泰生物)
更新于:2025-07-05
概要
基本信息
药物类型 自体CAR-T |
别名- |
靶点 |
作用方式 调节剂 |
作用机制 CD19调节剂(B淋巴细胞抗原CD19调节剂) |
非在研适应症- |
原研机构 |
非在研机构- |
权益机构- |
最高研发阶段临床2期 |
首次获批日期- |
最高研发阶段(中国)临床2期 |
特殊审评突破性疗法 (中国) |
登录后查看时间轴
关联
4
项与 抗CD19单链抗体嵌合抗原受体T细胞(永泰生物) 相关的临床试验NCT06179524
Phase II Clinical Study of CAR-T-19 Injection in the Treatment of CD19-positive Relapsed/refractory B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia(B-ALL) Under 25 Years of Age (inclusive)
This is a phase II clinical study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of CAR-T-19 injection in the treatment of CD19-positive relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
开始日期2024-01-03 |
申办/合作机构 |
ChiCTR1900024218
CAR-T-19-DNR/ CAR-T-19 in the treatment of cd19-positive relapsed/refractory diffuse large b-cell lymphoma: an open, parallel explore clinical study
开始日期2019-08-01 |
申办/合作机构- |
ChiCTR-OPN-17013507
A single-center, single-arm, open-label, dose escalation study to evaluate the safety & preliminary anti-tumor activity of CD19 single-chain antibody chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T-19) for the treatment of patients with relapsed / refractory B-cell leukemia / lymphoma
开始日期2017-09-01 |
申办/合作机构- |
100 项与 抗CD19单链抗体嵌合抗原受体T细胞(永泰生物) 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 抗CD19单链抗体嵌合抗原受体T细胞(永泰生物) 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 抗CD19单链抗体嵌合抗原受体T细胞(永泰生物) 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
57
项与 抗CD19单链抗体嵌合抗原受体T细胞(永泰生物) 相关的文献(医药)2025-06-01·Molecular Therapy Oncology
Intrinsic immunosuppressive features of monocytes suppress CAR-T19 through IL-1 pathway modulation in mantle cell lymphoma
Article
作者: Saleh, Ateka ; Can, Ismail ; Mai, Long ; Siegler, Elizabeth L ; Manriquez Roman, Claudia ; Ogbodo, Ekene J ; Kimball, Brooke ; Rohakhtar, Fariborz Rakhshan ; Kenderian, Saad S ; Feigin, Jennifer M ; Gutierrez Ruiz, Omar ; Ruff, Michael W ; Stewart, Carli M ; Girsch, James H ; Kankeu Fonkoua, Lionel A ; Huynh, Truc N ; Yun, Kun ; Mattie, Mike ; Hefazi, Mehrdad ; Sakemura, R Leo ; Simon, Vernadette ; Zhang, Shuwen ; Xia, Hong ; Nguyen-Mau, Sao-Mai ; Filosto, Simone ; Sirpilla, Olivia L
CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T19) have shown remarkable success in B cell malignancies, but most patients relapse within 1-2 years. Here, we identified interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) as a mediator of M2-like macrophage-derived inhibition of CAR-T19 in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), as well as a potential target to enhance CAR-T19 efficacy. In preclinical models that recapitulated interactions between tumor, macrophages, and T cells, we demonstrated that M2-derived IL-1ra impairs IL-1 signaling and functions of CAR-T19. These findings were validated using clinical samples from the ZUMA-2 trial that led to the FDA approval of CAR-T19 in MCL. Single-cell RNA sequencing of CAR-T19 products and baseline myeloid cells indicated downregulated IL-1β production, enriched immunosuppressive phenotypes, and IL-1ra upregulation in the non-responder monocytes, as well as impaired IL-1β signaling and T cell functions in the non-responder CAR-T19 products. Furthermore, our preclinical studies of IL-1β showed enhanced CAR-T antitumor activities. Collectively, these data present a potential role for IL-1 signaling and IL-1ra in CAR-T19 failure.
2024-12-24·Blood Advances
Local radiation enhances systemic CAR T-cell efficacy by augmenting antigen crosspresentation and T-cell infiltration
Article
作者: Krimitza, Elisavet ; Beghi, Silvia ; Costabile, Francesca ; Schuster, Stephen J. ; Chong, Elise A. ; Plastaras, John P. ; Thyfronitis, George ; Kostopoulos, Nektarios ; Perales-Linares, Renzo ; Facciabene, Andrea ; LaRiviere, Michael J. ; Maity, Amit ; Koumenis, Constantinos ; Goia, Denisa
Abstract:
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy targeting CD19 (CART-19) represents a significant advance in the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory CD19+ B-cell lymphomas. However, a significant portion of patients either relapse or fail to respond. Moreover, many patients have symptomatic disease, requiring bridging radiation therapy (RT) during the period of CAR T-cell manufacturing. To investigate the impact of 1 to 2 fractions of low-dose RT on CART-19 treatment response, we developed a mouse model using A20 lymphoma cells for CART-19 therapy. We found that low-dose fractionated RT had a positive effect on generating abscopal systemic antitumor responses beyond the irradiated site. The combination of RT with CART-19 therapy resulted in additive effects on tumor growth in irradiated masses. Notably, a significant additional increase in antitumor effect was observed in nonirradiated tumors. Mechanistically, our results validate activation of the cyclic guanosine adenosine synthetase/stimulator of interferon genes pathway, tumor-associated antigen crosspriming, and elicitation of epitope spreading. Collectively, our findings suggest that RT may serve as an optimal priming and bridging modality for CAR T-cell therapy, overcoming treatment resistance and improving clinical outcomes in patients with CD19+ hematologic malignancies.
2024-12-01·Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer
Preclinical development of three novel CARs targeting CD79b for the treatment of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and characterization of the loss of the target antigen
Article
作者: Moreno-Sanz, Alvaro ; Fernandez-Fuentes, Narcis ; Sandá, Victor ; Juan, Manel ; Engel, Pablo ; Peña-Blanque, Virginia ; Serrano-Lopez, Juana ; Borregón, Jennifer ; Esquinas, Esperanza ; Stodulski-Ciesla, Damian ; Llamas-Sillero, Pilar ; Solán-Blanco, Laura ; Martin-Antonio, Beatriz ; Fernández-Calles, Javier
Background:
Infusion of T cells modified with a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) targeting CD19 has achieved exceptional responses in patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL), which led to the approval of CAR targeting CD19 (CART19) (Axi-cel and Liso-cel) as second line of treatment for adult patients with relapsed/refractory NHL. Unfortunately, 60% of patients still relapse after CART19 due to either a loss of expression of the target antigen (CD19) in the tumor cell, observed in 27% of relapsed patients, a limited CAR-T persistence, and additional mechanisms, including the suppression of the tumor microenvironment. Clinic strategies to prevent target antigen loss include sequential treatment with CARs directed at CD20 or CD22, which have caused loss of the second antigen, suggesting targeting other antigens less prone to disappear. CD79b, expressed in NHL, is a target in patients treated with antibody-drug conjugates (ADC). However, the limited efficacy of ADC suggests that a CAR therapy targeting CD79b might improve results.
Methods:
We designed three new CARs against CD79b termed CAR for Lymphoma (CARLY)1, 2 and 3. We compared their efficacy, phenotype, and inflammatory profiles with CART19 (ARI0001) and CARTBCMA (ARI0002h), which can treat NHL. We also analyzed the target antigen’s expression loss (CD79b, CD19, and B-cell maturation antigen(BCMA)).
Results:
We found that CARLY2 and CARLY3 had high affinity and specificity towards CD79b on B cells. In vitro, all CAR-T cells had similar anti-NHL efficacy, which was retained in an NHL model of CD19−relapse. In vivo, CARLY3 showed the highest efficacy. Analysis of the loss of the target antigen demonstrated that CARLY cells induced CD79b and CD19 downregulation on NHL cells with concomitant trogocytosis of these antigens to T cells, being most notorious in CARLY2, which had the highest affinity towards CD79b and CD19, and supporting the selection of CARLY3 to design a new treatment for patients with NHL. Finally, we created a CAR treatment based on dual targeting of CD79b and BCMA to avoid losing the target antigen. This treatment showed the highest efficacy and did not cause loss of the target antigen.
Conclusions:
Based on specificity, efficacy, and loss of the target antigen, CARLY3 represents a potential novel CAR treatment for NHL.
6
项与 抗CD19单链抗体嵌合抗原受体T细胞(永泰生物) 相关的新闻(医药)2024-12-07
点击蓝字
关注我们
本周,热点很多,尤其是创新药方面。首先来看审评审批方面,多个重要药物在国内获批,其中有两个创新药上市值得关注,一个就是盛世泰科的糖尿病1类创新药,另一个就是恒瑞医药两款创新药氟唑帕利和阿帕替尼的联合疗法;其次是研发方面,多个药取得重要进展,值得一提的就是,CM24治疗胰腺导管腺癌Ⅱ期临床结果积极;再次是交易及投融资方面,金额最大的交易是武田以总交易额约13亿美元囊获得血液病创新药elritercept;最后是上市方面,银诺医药正式在港交所递交IPO申请。
本周盘点包括审评审批、研发、交易及投融资和上市四大板块,统计时间为2024.12.2-12.6,包含36条信息。
审评审批
NMPA
上市
批准
1、12月2日,NMPA官网显示,先声药业的依达拉奉右莰醇舌下片(商品名:先必新)获批上市,用于改善急性缺血性脑卒中所致的神经症状、日常生活活动能力和功能障碍。这是其与宁丹新药(NeuroDawn)合作开发的一款改良型新药。该产品于2024年9月获得美国FDA授予突破性疗法认定,用于治疗急性缺血性脑卒中适应症。
2、12月2日,NMPA官网公示,赞邦5.1类新药沙芬酰胺片获批上市,预测作为辅助治疗特发性帕金森病。沙芬酰胺具有独特的作用方式,包括选择性和可逆性单胺氧化酶B(MAO-B)抑制和阻断电压依赖性钠通道,从而调节异常的谷氨酸盐释放,已经于2017年获得美国FDA批准,针对出现“关闭期”发作的帕金森病患者。
3、12月2日,NMPA官网显示,默沙东的注射用亚西瑞来获批上市,预测用于治疗医院获得性细菌性肺炎和呼吸机相关细菌性肺炎(HABP/VABP)。亚西瑞来是复方制剂(亚胺培南500mg+西司他丁500mg+瑞来巴坦250mg),2019年7月,首次在美国获批上市,商品名为Recarbrio,治疗由特定敏感革兰氏阴性菌导致的复杂性尿路感染(cUTI)和复杂性腹腔内感染(cIAI)。
4、12月2日,NMPA官网显示,恒瑞医药的氟唑帕利和阿帕替尼新适应症获批,氟唑帕利胶囊单药或联合甲磺酸阿帕替尼用于伴有胚系BRCA突变(gBRCAm)的HER2阴性乳腺癌患者的治疗。氟唑帕利是一款口服给药的PARP抑制剂,于2020年12月获批上市,阿帕替尼是一款针对VEGFR的小分子酪氨酸激酶抑制剂,于2014年10月获批上市。
5、12月3日,NMPA官网显示,盛世泰科1类新药森格列汀(曾用名:盛格列汀)获批上市,用于治疗2型糖尿病。森格列汀作为一种新型口服DPP-4抑制剂,具有高选择性和强抑制性等优点,曾被豁免Ⅱ期临床直接进入Ⅲ期试验。
6、12月3日,NMPA官网显示,迈兰(Mylan)和复星全资子公司红旗制药联合递交的普托马尼片获批上市,预测用于肺结核患者。普托马尼是一种硝基咪唑类抗生素,具有独特的结构和抗结核作用机制,对结核分枝杆菌(MTB)有很高的特异性。2019年8月,美国FDA宣布批准普托马尼上市,与贝达喹啉和利奈唑胺联用治疗特定高度耐药肺结核患者。
7、12月3日,NMPA官网显示,信达生物的PD-1抑制剂信迪利单抗与和黄医药的VEGFR抑制剂呋喹替尼的联合疗法获批上市,预测用于治疗既往系统性抗肿瘤治疗后疾病进展且不适合进行根治性手术治疗或根治性放疗的晚期错配修复完整(pMMR)或非微卫星高度不稳定(非MSI-H)的子宫内膜癌。
8、12月3日,NMPA官网显示,默沙东(MSD)PD-1抑制剂帕博利珠单抗获批新适应症,联合含铂化疗新辅助治疗并在手术后继续帕博利珠单抗单药辅助治疗,用于可手术切除的Ⅱ、ⅢA和ⅢB期非小细胞肺癌患者。此次获批标志着帕博利珠单抗在中国迎来第四项肺癌适应证,开启帕博利珠单抗治疗早中期可手术非小细胞肺癌的新征程。
9、12月3日,NMPA官网显示,生诺生物引进的1类新药利那拉生酯胶囊(曾用名:信诺拉生获批上市,预测用于治疗反流性食管炎。利那拉生酯胶囊是上海医药6.9亿元自生诺生物引进的一款抑酸新药,属于新一代钾离子竞争性酸阻断剂(P-CAB)口服药物。
10、12月3日,NMPA官网显示,益普生(Ipsen)的Odevixibat胶囊获批上市,用于治疗6个月或以上患者的进行性家族性肝内胆汁淤积症(PFIC)。Odevixibat是一种强效、非体循环回肠胆汁酸转运蛋白(IBAT)抑制剂。
11、12月3日,NMPA官网显示,PharmaMar和绿叶制药共同申报的5.1类新药注射用芦比替定获批上市,用于以铂类为基础的化疗中或化疗后肿瘤进展的转移性小细胞肺癌(SCLC)成人患者的治疗。芦比替定是一种选择性的致癌基因转录抑制剂,最初由PharmaMar公司进行开发,绿叶制药获得该药物在中国开发及商业化的独家权利。
12、12月3日,NMPA官网显示,复宏汉霖抗PD-1单抗斯鲁利单抗注射液新适应症获批,联合培美曲塞和卡铂适用于EGFR敏感性突变阴性和ALK基因重排阴性的局部晚期或转移性非鳞状非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)的一线治疗。其于2022年3月首次获批上市,已在中国获批用于治疗微卫星高度不稳定(MSI-H)实体瘤、鳞状非小细胞肺癌、广泛期小细胞肺癌及食管鳞状细胞癌。
申请
13、12月4日,CDE官网显示,光谷人福生物医药公司1类新药重组质粒-肝细胞生长因子注射液申报上市,拟用于肢体动脉闭塞症、肢体静息痛和缺血性溃疡等严重血管疾病。武汉光谷人福生物医药有限公司隶属于人福医药集团,这是一款以表达质粒为载体、肝细胞生长因子为治疗基因的一种生物制品,能有效促进血管生成。
临床
批准
14、12月4日,CDE官网显示,卫材(Eisai)1类新药E7386获批临床,联合甲磺酸仑伐替尼胶囊治疗子宫内膜癌。E7386是一种潜在“first-in-class”新型口服抗癌药物,为一款CBP/β-catenin蛋白-蛋白相互作用抑制剂,由卫材与PRISMBioLab合作研发而成。
15、12月5日,CDE官网显示,阿斯利康申报的AZD2936和DS-8201a两款新药同时获批临床,用于局部晚期或转移性HER2表达胆道癌患者的一线治疗。DS-8201a是阿斯利康和第一三共联合开发的靶向HER2的ADC;AZD2936是一款靶向PD-1/TIGIT的双特异性抗体。
16、12月5日,CDE官网显示,再鼎医药1类新药ZL-1102凝胶获批临床,拟开发用于局部治疗慢性斑块状银屑病。ZL-1102是一款靶向作用于IL-17A细胞因子的新型全人源VH抗体片段(Humabody),与其他针对中重度慢性斑块状银屑病的全身型IL-17抑制剂不同,ZL-1102的独特之处在于被开发用于治疗轻中度慢性斑块状银屑病。
17、12月6日,CDE官网显示,恒瑞1类新药HRS-4729注射液获批临床,拟用于超重或肥胖。HRS-4729是恒瑞自主研发的下一代肠促胰岛素产品,这是一款GLP1R/GIPR/GCGR三靶点激动剂。2024年5月,恒瑞将包括HRS-4729在内的GLP-1产品组合有偿许可给美国Hercules公司。
18、12月6日,CDE官网显示,百济神州1类新药BGB-53038获批临床,拟用于治疗晚期实体瘤患者,这也是该药物首次在国内获批临床。BGB-53038是百济研发的一款Pan-KRAS抑制剂,目前全球已上市的KRAS抑制剂仅有4款,且均为KRASG12C抑制剂。
申请
19、12月5日,CDE官网显示,辉瑞(Pfizer)1类新药PF-07934040片申报临床,预测用于治疗实体瘤。PF-07934040是一种泛KRAS“ON/OFF”抑制剂,具有抗野生型(wt)KRAS和主要突变亚型的活性,对NRAS或HRAS无活性,正在国际范围内开展Ⅰ期临床。
突破性疗法
20、12月3日,CDE官网显示,永泰瑞科生物的抗CD19单链抗体嵌合抗原受体T细胞注射液拟纳入突破性治疗品种,用于治疗25岁(含)以下CD19阳性复发/难治B细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病(B-ALL)。这是该公司在研的CAR-T-19注射液,为一种通过基因工程手段将识别CD19特异性B细胞抗原的单链抗体整合到患者自身T细胞上的细胞免疫治疗方法。
21、12月3日,CDE官网显示,杰科生物的JL15003注射液拟纳入突破性治疗品种,用于治疗溶瘤病毒。JL15003为溶瘤病毒产品,也是公司首个获批临床的1类新药。该产品目前正处于1期临床研究阶段,评价其治疗复发胶质母细胞瘤患者的安全性和耐受性。
22、12月3日,CDE官网显示,锦篮基因的GC101腺相关病毒注射液拟纳入突破性治疗品种,用于治疗2型脊髓性肌萎缩症(5qSMA)。GC101腺相关病毒注射液一种携带正常SMN1基因表达单元的重组9型腺相关病毒载体(rAAV9),通过鞘内注射方式一次性给药,使SMN1基因在运动神经元细胞表达,从而改善运动神经元等受累细胞的功能。
23、12月4日,CDE官网显示,和黄医药1类新药赛沃替尼片拟纳入突破性治疗品种,适应症为赛沃替尼联合奥希替尼治疗经EGFR-TKI治疗失败伴MET扩增的局部晚期或转移性非小细胞肺癌。奥希替尼是一种不可逆的第三代EGFR-TKI;赛沃替尼片是一种强效、高选择性的口服间充质上皮转化因子(MET)TKI。
24、12月4日,CDE官网显示,恒瑞医药1类新药注射用SHR-A2102拟纳入突破性治疗品种,单药治疗既往含铂化疗和PD-(L)1抑制剂治疗失败的局部晚期或转移性尿路上皮癌。SHR-A2102是恒瑞医药自主研发的靶向Nectin-4的ADC,治疗晚期尿路上皮癌此前已经被美国FDA授予快速通道资格。
FDA
上市
批准
25、12月5日,FDA官网显示,阿斯利康的PD-L1单抗度伐利尤单抗(Imfinzi)新适应症获批,用于治疗在同时进行铂类化疗和放射治疗后病情未进展的局限期小细胞肺癌(LS-SCLC)的成年患者,成为首个也是唯一一个针对LS-SCLC的免疫治疗方案。
申请
26、12月5日,FDA官网显示,罗氏的罗菲妥单抗(Columvi,Glofitamab)递交补充生物制品许可申请(sBLA)并获受理,与吉西他滨和奥沙利铂(GemOx)联合用于治疗复发或难治性(R/R)弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)患者,这些患者之前至少接受过一线治疗,并且不适合进行自体干细胞移植。FDA预计将在2025年7月20日之前做出批准决定。
研发
临床数据
27、12月2日,PurpleBiotech公布了靶向CEACAM1单抗CM24治疗胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)患者的随机Ⅱ期临床结果。研究表明,CM24联合PD-1抑制剂治疗组在所有疗效终点上都有明显和持续的改善。此外,对于生物标志物(血清CEACAM1预处理范围)丰富的患者,治疗组比对照组显著改善,死亡风险降低79%,中位OS提高5.1个月,疾病进展或死亡风险降低90%以上,中位PFS改善2.9个月,ORR相比对照组显著改善(50%vs0%),DCR为100(vs0%)。
28、12月4日,云顶新耀发布了其拥有全球权益的新一代共价可逆布鲁顿酪氨酸激酶(BTK)抑制剂EVER001(又名:XNW1011),在治疗原发性膜性肾病(pMN)的Ⅰb/Ⅱa期临床试验阶段性数据取得了积极结果。在已完成36周治疗的低剂量组患者中,81.8%(9/11)的患者实现临床缓解,高剂量组中已完成24周治疗的患者即有85.7%(6/7)实现临床缓解。
29、12月4日,梯瓦(Teva)公布了其Ⅲ期SPACE研究的积极数据,该研究评估了Ajovy预防6-17岁儿童和青少年患者发作性偏头痛的有效性和安全性。Ajovy是一种人源化的CGRP单克隆抗体。试验结果显示,与安慰剂相比,Ajovy在12周内的疗效在统计学上显著优于安慰剂,在12周的时间内显著减少了每月偏头痛天数(MMD)和每月头痛天数(MHD),其良好的安全性与在成人人群中观察到的结果一致。
30、12月6日,宜明昂科公布了一款CD47xCD20双靶点特异性分子阿沐瑞芙普α(IMM0306)针对淋巴瘤临床Ⅰ期试验数据。数据显示,在25例疗效可评估的R/R滤泡性淋巴瘤(FL)患者中,总体缓解率(ORR)和完全缓解率(CRR)分别是84.0%和40.0%;2例疗效可评估的R/R边缘区淋巴瘤(MZL)患者ORR为100%。
交易及投融资
31、12月3日,新元素药业宣布,与康哲药业附属公司就治疗痛风及高尿酸血症的1类新药ABP-671签署在中国大陆、中国香港特别行政区及中国澳门特别行政区的独家商业化合作协议。根据协议,新元素将从康哲获得首付款及里程碑款项,同时新元素将根据协议约定向康哲支付市场推广服务费。新元素药业未来有望获得持续销售产生的可观收入。
32、12月4日,DualityBiologics(映恩生物)宣布,与GSK就一项ADC药物DB-1324达成独家授权协议。根据协议,GSK将获得全球(不包括中国大陆、中国香港地区和中国澳门地区)的独家授权,GSK将预先支付3,000万美元预付款及其他行权前里程碑付款以获得在全球范围内(中国大陆、中国香港地区和中国澳门地区除外)推进DB-1324研发和商业化的独家授权许可。如果GSK行使许可权,映恩生物将收取行权费以及后续在开发、法规注册和商业化不同阶段的里程碑付款,最高可达9.75亿美元。
33、12月3日,KerosTherapeutics宣布,与武田(Takeda)达成一项独家全球开发和商业化许可协议,以推进elritercept(KER-050)的开发。根据协议条款,武田将获得全球进一步开发、生产和商业化elritercept的独家许可(不包括中国内地,中国香港和中国澳门地区)。自协议生效之日起,武田将负责elritercept的所有开发、生产和商业化工作。根据协议内容,Keros将收到2亿美元的预付款,并有资格获得超过11亿美元的开发、监管及商业里程碑付款。
34、12月4日,优时比(UCB)宣布,与博锐生物就白介素-17A/F(IL-17A/F)抑制剂比奇珠单抗(商品名:倍捷乐)签署合作协议,加速比奇珠单抗在中国的上市进程。比奇珠单抗已于2024年7月国内获批上市,用于治疗常规疗法效果不佳或不耐受的活动性强直性脊柱炎(AS)成人患者,并于9月获批用于治疗放射学阴性中轴型脊柱关节炎(nr-axSpA)成人患者。
35、12月5日,RgentaTherapeutics宣布,与GSK签订一项多年期多靶点的战略研究合作协议,旨在推进新型靶向RNA小分子剪接调节剂在肿瘤等多个疾病领域的发现和开发。根据合作协议,Rgenta将获得高达4600万美元的现金预付款和行权前里程碑款项,并且还可能从每个靶点中获得近5亿美元的选择权行使费用、研究、开发、监管和商业化里程碑付款。
上市
36、12月3日,港交所官网公示,银诺医药已经递交了IPO申请。银诺医药成立于2014年,致力于研发治疗糖尿病和其他代谢性疾病的创新疗法。该公司的长效GLP-1受体激动剂依苏帕格鲁肽α有望即将进入商业化阶段,用于治疗2型糖尿病的单药疗法及与二甲双胍的联合用药均已在中国递交上市申请。除了依苏帕格鲁肽α,银诺医药还有5款处于IND待启动阶段的候选药物。
END
【生物制药新锐说直播预告】
来源:CPHI制药在线
声明:本文仅代表作者观点,并不代表制药在线立场。本网站内容仅出于传递更多信息之目的。如需转载,请务必注明文章来源和作者。
投稿邮箱:Kelly.Xiao@imsinoexpo.com
▼更多制药资讯,请关注CPHI制药在线▼
点击阅读原文,进入智药研习社~
上市批准突破性疗法IPO优先审批
2024-12-04
·医药观澜
▎药明康德内容团队报道
12月3日,中国国家药监局药品审评中心(CDE)官网公示,3款新药拟纳入突破性治疗品种。这些产品分别为CAR-T细胞免疫治疗方法、溶瘤病毒产品、AAV基因治疗药物,拟定适应症包括急性淋巴细胞白血病、胶质母细胞瘤、2型脊髓性肌萎缩症。
永泰瑞科生物:抗CD19单链抗体嵌合抗原受体T细胞注射液
作用机制:CAR-T细胞免疫治疗方法
永泰瑞科生物申报的抗CD19单链抗体嵌合抗原受体T细胞注射液拟纳入突破性治疗品种,用于治疗25岁(含)以下CD19阳性复发/难治B细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病(B-ALL)。根据永泰生物公开资料,这是该公司在研的CAR-T-19注射液,为一种通过基因工程手段将识别CD19特异性B细胞抗原的单链抗体整合到患者自身T细胞上的细胞免疫治疗方法,该产品回输后,T细胞具有杀死表达CD19的B细胞肿瘤的能力,从而达到治疗B细胞恶性血液病的目的。目前,永泰瑞科生物正在开展该产品治疗25岁及以下复发/难治B细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病(B-ALL)患者的2期临床研究。
杰科生物:JL15003注射液
作用机制:溶瘤病毒产品
杰科生物申报的JL15003注射液拟纳入突破性治疗品种,用于治疗复发胶质母细胞瘤。根据杰科生物公开资料,JL15003为溶瘤病毒产品,也是公司首个获批临床的1类新药。该产品目前正处于1期临床研究阶段,评价其治疗复发胶质母细胞瘤患者的安全性和耐受性。
公开资料显示,利用自然界中致病力较弱的病毒进行基因工程改造,让它们失去毒性并保留病毒的复制能力,再将溶瘤病毒注射入肿瘤病灶内,使其在肿瘤细胞内自我复制,随后裂解肿瘤细胞,这就是溶瘤病毒免疫疗法。当肿瘤细胞在病毒感染下破裂死亡时,会释放新生成的病毒颗粒,继续杀伤周围的肿瘤细胞。并且,溶瘤病毒在感染杀死肿瘤细胞的同时,还能通过释放肿瘤特异性的蛋白分子,进而激活人体自身免疫系统。
锦篮基因:GC101腺相关病毒注射液
作用机制:基因治疗药物
锦篮基因申报的GC101腺相关病毒注射液拟纳入突破性治疗品种,用于治疗2型脊髓性肌萎缩症(5q SMA)。脊髓性肌萎缩症(SMA)是由于运动神经元存活基因1(SMN1)突变导致SMN蛋白功能缺陷所致的遗传性神经肌肉病,它会影响神经元功能,造成患者肌肉神经源性萎缩,是造成婴幼儿死亡的常染色体隐性遗传疾病之一。在SMA疾病分型中,2型SMA患者大部分会在青少年时期丧失独坐能力以及瘫痪。
根据锦篮基因公开资料介绍,GC101腺相关病毒注射液一种携带正常SMN1基因表达单元的重组9型腺相关病毒载体(rAAV9),通过鞘内注射方式一次性给药,使SMN1基因在运动神经元细胞表达,从而改善运动神经元等受累细胞的功能,辅以呼吸及运动康复训练,可以改善提高SMA患者呼吸能力及运动能力。该产品目前正在进行一项1/2期临床研究,评估鞘内(IT)注射治疗2型脊髓性肌萎缩症(SMA)患者的安全性、耐受性以及疗效。
参考资料:
[1]中国国家药监局药品审评中心(CDE)官网.Retrieved Dec 4,2024, from https://www.cde.org.cn/main/xxgk/listpage/4b5255eb0a84820cef4ca3e8b6bbe20c
本文来自药明康德内容团队,欢迎个人转发至朋友圈,谢绝媒体或机构未经授权以任何形式转载至其他平台。转载授权及其他合作需求,请联系wuxi_media@wuxiapptec.com。
免责声明:药明康德内容团队专注介绍全球生物医药健康研究进展。本文仅作信息交流之目的,文中观点不代表药明康德立场,亦不代表药明康德支持或反对文中观点。本文也不是治疗方案推荐。如需获得治疗方案指导,请前往正规医院就诊。
免疫疗法临床1期临床2期突破性疗法细胞疗法
2024-12-03
·氨基观察
氨基观察-创新药组原创出品
作者 | 黄凯
诺华继续买买买。
12月2日,PTC Therapeutics宣布,与诺华签署了一项关于亨廷顿病项目PTC518及其相关分子的独家全球许可与合作协议。
根据协议,PTC将获得10亿美元的预付款,以及高达19亿美元的开发、监管和销售里程碑款项。
微创机器人闹钱荒。
12月3日,微创机器人发布公告宣布,拟配售3470万股,配售价为每股H股7.85港元,预计将在2024年12月10日完成,所得款项净额约为2.66亿港元。
受折价配股影响,微创机器人股价大跌14.17%。
在过去的一天里,国内外医药市场还有哪些热点值得关注?让氨基君带你一探究竟。
/ 01 /
资本信息
1)微创机器人配股融资2.66亿港元
12月3日,微创机器人发布公告宣布,拟配售3470万股,配售价为每股H股7.85港元,预计将在2024年12月10日完成,所得款项净额约为2.66亿港元。
/ 02 /
医药动态
1)信达生物信迪利单抗+呋喹替尼联合疗法获批上市
12月3日,据NMPA官网,信达生物信迪利单抗+呋喹替尼联合疗法获批上市,用于治疗既往系统性抗肿瘤治疗后疾病进展且不适合进行根治性手术治疗或根治性放疗的晚期pMMR或non MSI-H子宫内膜癌患者。
2)复宏汉霖斯鲁利第5项适应症获批上市
12月3日,据NMPA官网,复宏汉霖斯鲁利第5项适应症获批上市,具体为联合培美曲塞和卡铂,一线治疗表皮生长因子受体敏感性突变阴性,和间变性淋巴瘤激酶基因重排阴性的局部晚期或转移性非鳞状非小细胞肺癌。
3)盛世泰科DPP-4抑制剂森格列汀获批上市
12月3日,据NMPA官网,盛世泰科DPP-4抑制剂森格列汀获批上市,用于治疗2型糖尿病。
4)绿叶制药芦比替定获批上市
12月3日,据NMPA官网,绿叶制药芦比替定获批上市,用于治疗含铂化疗中或化疗后疾病进展的转移性小细胞肺癌成人患者。
5)益普生IBAT抑制剂odevixibat胶囊获批准上市
12月3日,据NMPA官网,益普生IBAT抑制剂odevixibat胶囊获批准上市,用于治疗6个月或以上患者的进行性家族性肝内胆汁淤积症。
6)博利珠单抗第四项肺癌适应证获批
12月3日,默沙东宣布,博利珠单抗第四项肺癌适应证获批,具体为联合含铂化疗新辅助治疗并在手术后继续帕博利珠单抗单药辅助治疗,用于可手术切除的II、IIIA和IIIB期非小细胞肺癌患者。
7)艾美疫苗吸附破伤风疫苗获临床许可
12月3日,据CDE官网,艾美疫苗吸附破伤风疫苗获临床许可,拟用于预防破伤风。
8)基因启明GKL-006注射液获临床许可
12月3日,据CDE官网,基因启明GKL-006注射液获临床许可,拟用于治疗晚期胰腺癌。
9)上海医药靶向CD19和CD22 的嵌合抗原受体自体T细胞注射液获临床许可
12月3日,据CDE官网,上海医药靶向CD19和CD22 的嵌合抗原受体自体T细胞注射液获临床许可,拟用于治疗复发或难治性B细胞非霍奇金淋巴瘤。
10)宏成药业HC022注射液获临床许可
12月3日,据CDE官网,宏成药业HC022注射液获临床许可,拟用于皮肤型红斑狼疮的治疗。
11)永泰瑞科抗CD19单链抗体嵌合抗原受体T细胞注射液拟获突破性疗法认定
12月3日,据CDE官网,永泰瑞科抗CD19单链抗体嵌合抗原受体T细胞注射液拟获突破性疗法认定,适应症为:治疗25岁(含)以下CD19阳性复发/难治B细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病。
12)锦篮基因GC101腺相关病毒注射液拟获突破性疗法认定
12月3日,据CDE官网,锦篮基因GC101腺相关病毒注射液拟获突破性疗法认定,适应症为:治疗2型脊髓性肌萎缩症(5q SMA)。
13)益方生物D-2570 II期临床试验结果积极
12月3日,益方生物公告, TYK2抑制剂D-2570已于近日完成针对银屑病的II期临床试验,并取得了积极的临床试验结果。
/ 03 /
器械跟踪
1)微创神通电解脱弹簧圈获注册许可
12月3日,据NMPA官网,微创神通电解脱弹簧圈获注册许可。
2)核心医疗植入式左心室辅助系统获注册许可
12月3日,据NMPA官网,核心医疗植入式左心室辅助系统获注册许可。
3)威高骨科脊柱后路内固定系统获注册许可
12月3日,据NMPA官网,威高骨科脊柱后路内固定系统获注册许可。
/ 04 /
数字医疗日报
1)商汤善萃放射治疗轮廓勾画软件获注册许可
12月3日,据NMPA官网,商汤善萃放射治疗轮廓勾画软件获注册许可。
/ 05 /
海外药闻
1)近30亿美元!诺华囊获穿越血脑屏障小分子疗法
12月2日,PTC Therapeutics宣布,与诺华签署了一项关于亨廷顿病项目PTC518及其相关分子的独家全球许可与合作协议。根据协议,PTC将获得10亿美元的预付款,以及高达19亿美元的开发、监管和销售里程碑款项。
2)泛RAS抑制剂胰腺癌最新结果积极
12月2日,Revolution Medicines公司公布其在研泛RAS抑制剂RMC-6236的最新临床结果。分析显示,在RMC-6236-001临床1/1b期研究当中,RMC-6236单药作为转移性胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)患者二线疗法时显示出显著疗效,支持3期临床试验RASolute 302的持续推进。
PS:欢迎扫描下方二维码,添加氨基君微信号交流。
上市批准引进/卖出临床3期
100 项与 抗CD19单链抗体嵌合抗原受体T细胞(永泰生物) 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD19阳性B细胞白血病 | 临床2期 | 中国 | 2024-01-03 | |
| 复发性 B 细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病 | 临床2期 | 中国 | 2024-01-03 | |
| 难治性 B 细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病 | 临床2期 | 中国 | 2024-01-03 | |
| CD19阳性B细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病 | 临床2期 | 中国 | 2023-12-28 | |
| 淋巴瘤 | 临床1期 | 中国 | 2022-06-22 | |
| B细胞白血病 | 临床1期 | 中国 | - |
登录后查看更多信息
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
No Data | |||||||
登录后查看更多信息
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或
临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或

批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或
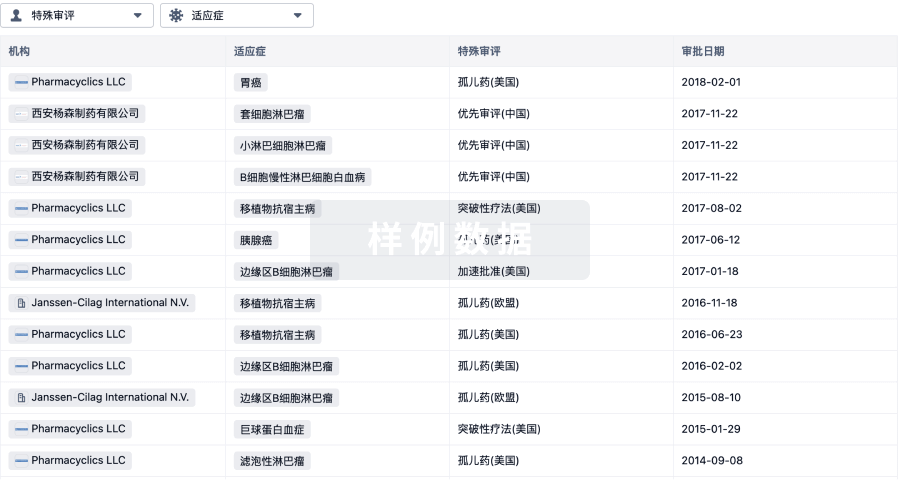
特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或
Eureka LS:
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用
