预约演示
更新于:2025-09-02
GNR-084
更新于:2025-09-02
概要
基本信息
药物类型 双特异性T细胞结合器 |
别名 CD3/CD19 bispecific antibody、GNR 084、GNR084 |
作用方式 调节剂、刺激剂 |
作用机制 CD19调节剂(B淋巴细胞抗原CD19调节剂)、CD3刺激剂(T细胞表面糖蛋白CD3复合体刺激剂) |
非在研适应症- |
原研机构- |
在研机构 |
非在研机构- |
最高研发阶段临床1/2期 |
首次获批日期- |
最高研发阶段(中国)- |
特殊审评- |
登录后查看时间轴
关联
1
项与 GNR-084 相关的临床试验NCT04601584
Dose-escalation Sequention Cohort Study of Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of GNR-084 in Patients With Refractory or Relapse Acute Lymphoblastic B-cell Precursor Leukemia.
It is an open-label dose-escalating study in sequential cohorts to assess safety and pharmacokinetics of GNR-084.
开始日期2020-10-15 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 GNR-084 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 GNR-084 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 GNR-084 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
6
项与 GNR-084 相关的文献(医药)2022-02-01·Frontiers of medicine3区 · 医学
Preclinical characterization and comparison between CD3/CD19 bispecific and novel CD3/CD19/CD20 trispecific antibodies against B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: targeted immunotherapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia
3区 · 医学
Article
作者: Zhou, Yuebo ; Xu, Wenqian ; Wang, Jin ; Wang, Sisi ; Leung, Stewart ; Peng, Lijun ; Mi, Jian-Qing ; Zhu, Ziyan ; Yan, Xiaoqiang ; Kong, Yushan
The CD19-targeting bispecific T-cell engager blinatumomab has shown remarkable efficacy in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. However, several studies showed that blinatumomab has a short plasma half-life due to its low molecular weight, and thus its clinical use is limited. Furthermore, multiple trials have shown that approximately 30% of blinatumomab-relapsed cases are characterized by CD19 negative leukemic cells. Here, we design and characterize two novel antibodies, A-319 and A-2019. Blinatumomab and A-319 are CD3/CD19 bispecific antibodies with different molecular sizes and structures, and A-2019 is a novel CD3/CD19/CD20 trispecific antibody with an additional anti-CD20 function. Our in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo experiments demonstrated that A-319 and A-2019 are potent antitumor agents and capable of recruiting CD3 positive T cells, enhancing T-cell function, mediating B-cell depletion, and eventually inhibiting tumor growth in Raji xenograft models. The two molecules are complementary in terms of efficacy and specificity profile. The activity of A-319 demonstrated superior to that of A-2019, whereas A-2019 has an additional capability to target CD20 in cells missing CD19, suggesting its potential function against CD19 weak or negative CD20 positive leukemic cells.
2020-06-01·Biology of blood and marrow transplantation : journal of the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation2区 · 医学
Outcomes of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation after Salvage Therapy with Blinatumomab in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
2区 · 医学
Article
作者: Stein, Anthony ; Salhotra, Amandeep ; Marcucci, Guido ; Malki, Monzr M Al ; Ali, Haris ; Aribi, Ahmed ; Pullarkat, Vinod ; Mei, Matthew ; Nakamura, Ryotaro ; Sandhu, Karamjeet S ; Snyder, David ; Cao, Thai ; Spielberger, Ricardo ; Yang, Dongyun ; Mokhtari, Sally ; Khaled, Samer ; Aldoss, Ibrahim ; Budde, Elizabeth ; Forman, Stephen J
Historically, outcomes of adult patients with relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who fail to enter remission with conventional chemotherapy are very poor. Blinatumomab, a bispecific CD3/CD19 antibody, has shown remarkable activity in relapsed/refractory (r/r) ALL. Although allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) is the recommended consolidation therapy for patients with r/r ALL who respond to salvage therapy, HCT and toxicity outcomes for those who received blinatumomab salvage and HCT remain largely unknown. We treated 89 patients with r/r ALL with blinatumomab, of whom 43 patients (48%) achieved remission. Here we describe our single-center experience in the subset of patients who responded to blinatumomab salvage therapy for eradication of either gross (n = 24) or minimal residual disease (n = 11) before HCT. Overall survival at 1 and 2 years after allogeneic HCT was 77% and 52%, respectively. Leukemia-free survival at 1 and 2 years were 65% and 40%, respectively. Additionally, with blinatumomab administration pre-HCT, no unusual toxicities such as delayed neutrophil/platelet engraftment or graft failure were observed. Acute grades II to IV graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) at day +100 post-HCT was at 43% and 2-year chronic GVHD was 36%, both comparable with historic control subjects. Finally, results of our subset analysis based on pre-HCT minimal residual disease (MRD) status indicated no significant difference in survival outcomes among patients undergoing transplant in MRD-negative status and the entire cohort. In conclusion, based on results of this study, blinatumomab may be considered as a safe and effective agent for r/r ALL patients before HCT.
2019-06-07·Leukemia & lymphoma4区 · 医学
Antibody-based therapy in acute leukemia - beware the risks
4区 · 医学
Article
作者: Stahl, Maximilian ; Tallman, Martin S.
Antibody-based therapy has started to revolutionize the treatment of acute leukemia. The CD3/CD19 bispecific antibody blinatumomab [1] and inotuzumab ozogamicin (IO), an anti-CD22 antibody conjugat...
1
项与 GNR-084 相关的新闻(医药)2022-06-12
2022年6月8日,罗氏宣布Lunsumio® (mosunetuzumab)获得欧盟附加条件上市许可,成为全球第一个上市的CD3/CD20双抗,获批是基于其phase I/II GO29781 study(NCT02500407),CR为60%,ORR为80%。除此之外,Roche还手握另外一个基于2:1 CrossMab 的CD3/CD20双抗,Glofitamab (RO7082859)。具体可以阅读:Roche 2022有望上市抗体药,多为免疫靶点。血液肿瘤除去CD20之外,尚有10个热门靶点,就其TCE双抗项目进展稍作梳理。01GPRC5D(多发性骨髓瘤)GPRC5D(GPCR class C group 5 member D)分子量39kDa,孤儿G蛋白偶联受体,通常只在毛囊中表达。GPRC5D在多发性骨髓瘤中过表达,且不太可能从细胞膜上脱落,可以避免因脱落引起的疗效下降。Talquetamab(JNJ-64407564)Janssen Talquetamab(GPRC5D/CD3),采用Genmab的Duobody双抗技术平台构建(immunoglobulin G4 proline, alanine, alanine,IgG4PAA)。临床前数据,可以有效激活T细胞(非NK细胞),杀伤原代多发性骨髓瘤病人细胞。Blood Adv . 2021T细胞效应分子,显著升高,包括TNF-α、IFN-γ、IL-2、颗粒酶B等。Blood Adv . 2021可以检索到7项多发性骨髓瘤临床实验在开展,包括单药治疗复发或难治性多发性骨髓瘤NCT04634552(2期),NCT03399799(1期)。今年ASCO上University Medical Center Utrecht的Monique C. Minnema报道了NCT03399799数据,ORR可达70%,PR 57%。国内目前驯鹿、启源等开展了GPRC5D CAR-T。02FLT3(急性髓系白血病)FLT3(FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3)分子量140-160KD,是一种1型跨膜蛋白,受体酪氨酸激酶。FLT3通过与其配体结合,促进造血细胞的增殖和分化。FLT3在急性髓系白血病(AML)中过表达,并在大约30%的AML患者中检测到其突变,导致AML患者预后不良。因为FLT3本身是酪氨酸激酶,所以小分子抑制剂是开发重点,全球有几十个药物在开发,安斯泰来制药吉瑞替尼片国内已经上市。礼来的LY3012218(IMC-EB10)是一种靶向FLT3的人单抗,因为缺乏活性,已经停止开发。AMG427AMG427,是Amgen的CD3/FLT3双抗,目前在AML的1期临床(NCT03541369)CLN-049 CLN-049 是CULLINAN ONCOLOGY(Nasdaq:CGEM)开发的CD3/FLT3双抗,目前在进行R/R-AML的1期临床(NCT05143996)。03CLEC12A(急性髓系白血病)CLEC12A(C-type lectin domain family 12 member A),是一种31kda髓系抑制受体,一种重要的炎症负调控因子。在AML中特异性表达,在约90%的AML患者中观察到,与AML患者预后不良密切相关但在正常的造血干细胞和祖细胞中不表达。MCLA-117Merus N.V.开发的CD3/CLEC12A,采用低亲和力CD3抗体臂和高亲和力CLEC12A抗体臂。Merus N.V官网临床前的数据显示可以有效激活并扩增病人T细胞,并有效杀伤病人AML细胞Merus N.V官网目前开展了一项AML临床(NCT03038230)。04CD123(急性髓系白血病)CD123是IL-3Rα,75KD的1型跨膜蛋白,它在白血病干细胞中过表达,但在正常造血干细胞中低表达或不表达。CD123与IL-3结合,可导致各种血液癌的生存和增殖,如AML、ALL和HL,在AML,CD123表达与病人不良预后相关。Flotuzumab (MGD-006)靶向CD123XCD3,采用MacroGenics的DART技术。目前开展了AML的2期临床(NCT04582864)。SAR440234(Sanofi-Aventis)CD123XCD3,2022年赛诺菲已经终止了AML临床研究(NCT03594955)JNJ-63709178杨森开发CD123 x CD3 DuoBody 双抗,NCT02715011在2021年完成,未继续。APVO436(Aptevo)靶向CD123XCD3,采用ADAPTIR Technology ,包含4个scFV,融合突变的Fc(没有ADCC和CDC活性)https://aptevotherapeutics.com/adaptir/NCT03647800,Study of APVO436 in Patients With AML or MDS,phase1,部分队列有CR。Vibecotamab/XmAb14045(Xencor)靶向CD123XCD3,采用scFv-Fab。目前在进行AML 和 MDS的2期临床(NCT05285813),与诺华的合作已经终止。05 CD33(急性髓系白血病)又名Siglec-3,调节免疫细胞功能,如吞噬、细胞因子的释放和凋亡,在急性髓系白血病中过表达。据报道,在接受化疗的AML患者中,CD33高表达患者的OS率为42.9%,而CD33低表达患者的OS率为67.5%。AMG330AMG330, 一个短效BiTE CD33/CD3双抗。不过目前Amgen已经终止了两项临床开发( NCT02520427,NCT04478695).AMG673Amgen的AMG673作为另外一个 CD33/CD3双抗,也被终止了临床开发(NCT03224819)JNJ-67371244杨森的JNJ-67371244,是基于Duobody的IgG样双抗,目前处于激活未招募状态。(NCT03915379)AMV564(Amphivena Therapeutics)CD33/CD3双抗,采用了Tandem技术,分子量106KD,半衰期8.72-19.2小时。对复发/难治性AML患者进行了1、3+3剂量爬坡研究。初步结果,19名患者持续静脉输液超过14天,未见DLTs或治疗相关等级≥3不良事件。在100μg/天的队列中,1例患者获得完全反应, 1例有PR,2例有稳定的疾病。huCD33-Bi Specific(Y-mAbs Therapeutics)Y-mAbs Therapeutics开发的CD33/CD3双抗,目前开始进行R/R-AML 1期临床研究 (NCT05077423)。06CD38(多发性骨髓瘤)CD38是45KD的2型跨膜蛋白,在多发性骨髓瘤细胞中过表达,但在正常淋巴细胞和髓系细胞中低表达。单抗达雷妥尤单抗注射液说明书已在国内上市,治疗单药治疗复发和难治性多发性骨髓瘤成年患者。ISB 1342Ichnos Sciences开发的CD38/CD3双抗,目前在1期临床NCT03309111 Study of ISB 1342, a CD38/CD3 Bispecific Antibody, in Subjects With Previously Treated Multiple Myeloma。XmAb968 (CD38 x CD3)Ichnos Sciences SA NCT03309111 Study of ISB 1342, a CD38/CD3 Bispecific Antibody, in Subjects With Previously Treated Multiple MyelomaY150武汉友之友开发的CD38/CD3双抗,目前开始多发性骨髓瘤1期临床,NCT05011097 A Phase I Clinical Trial of Y150 in the Treatment of Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma07 CD30(霍奇金淋巴瘤)CD30是一种120-kDa的I型跨膜蛋白,属于肿瘤坏死因子受体家族。它通过NF-κB和MAPK通路,在淋巴细胞活化和增殖中发挥关键作用,具有抗凋亡和促存活作用。它在造血系统恶性肿瘤中过表达,包括霍奇金淋巴瘤(HL)和NHL,并与这些细胞存活相关。目前Seagen的CD30-ADC药物Adcetris® (brentuximab vedotin),2011年批准上市。目前还没有TCE双抗开发。AFM13Affimed Therapeutics开发的NK细胞四价双特异性抗体(CD30/CD16A)。J Hematol Oncol . 2015 Aug 1;8:96.AACR 2022, MD Anderson Yago Nieto, MD, PhD报道了NCT04074746初步结果 89% ORR,62%CR。08 CD22(急性淋巴细胞白血病)CD22是一种140-kda的I型跨膜蛋白,是BCR的抑制性共受体,调节B细胞的过度刺激。CD22在多种B细胞淋巴瘤中过表达,如CLL、ALL和NHL,但在未成熟的B细胞和浆细胞上表达水平较低,是B细胞白血病良好的治疗靶点。2017年Pfizer/Wyeth的CD22-ADC药物Besponsa® (inotuzmab ozogamicin)获批上市,治疗复发/难治性(R/R)B细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病。JNJ-75348780杨森开发的CD22/CD3双抗,目前开始了CLL和NHL的1期临床(NCT04540796),同时也在国内开始了相关临床(JXSL2200017,JXSL2200016)09CD19( B 细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病和NHL)CD19是一种95kda的I型跨膜蛋白,是BCR的共受体,调节细胞生长。它在大多数B细胞恶性肿瘤中过表达,如ALL、非霍奇金淋巴瘤(NHL)和慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL)。CD19的过表达促进了这些B细胞恶性肿瘤的增殖和存活。博纳吐单抗(Blinatumomab)是第一个CD19/CD3单抗,2019年Amgen在中国上市了该产品,治疗成人复发或难治性前体 B 细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病。TNB-486TeneoTwo Inc开发,NCT04594642,A Study of TNB-486 in Subjects With Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma,Phase1GNR-084AO GENERIUM,NCT04601584,GNR-084 Safety and Pharmacological Characteristics in Refractory or Relapse B-cell Precursor ALL, Phase1/2CLN-978 (NexGem)Cullinan 开发的CD19 X CD3 X HSA trispecific抗体,在CD19/CD3 BiTE双抗前,加了一个Vhh HSA抗体。目前尚未进入临床。https://www.cullinanoncology.com/ui/uploads/2022/05/nexgem-aacr-2022-poster-final-revised.pdf10 BCMA(多发性骨髓瘤)B细胞成熟抗原(BCMA),随着传奇生物的Carvykti(西达基奥仑赛)上市,该靶点广为人知,是多发性骨髓瘤不可多得的优质靶点。BCMA是肿瘤坏死因子受体超家族成员17(TNFRSF17),是一种20kda的III型跨膜蛋白。BCMA与其配体结合,如增殖诱导配体和B细胞激活因子,促进B细胞的存活。成熟靶点,辉瑞、新基、杨森、再生元等均有布局,上海岸迈等国内企业也已进入临床阶段。Elranatamab (PF-06863135) Elranatamab 是辉瑞开发的CD3/BCMA双抗,目前在进行多发性骨髓瘤1期临床。NCT05228470 Study Of Elranatamab (PF-06863135) Monotherapy in Chinese Participants With Refractory Multiple MyelomaCC-93269 Celgene 开发,NCT03486067 Study of CC-93269, a BCMA x CD3 T Cell Engaging Antibody, in Participants With Relapsed and Refractory Multiple MyelomaTeclistamab Janssen开发, NCT03145181 Dose Escalation Study of Teclistamab, a Humanized BCMA*CD3 Bispecific Antibody, in Participants With Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (MajesTEC-1)REGN5458Regeneron开发,NCT03761108 First in Human (FIH) Study of REGN5458 in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Multiple MyelomaTNB-383BTeneoOne Inc.开发,NCT03933735 A Study of TNB-383B in Participants With Relapsed or Refractory Multiple MyelomaEMB-06 上海岸迈开发, NCT04735575 A Ph1/2 Study of EMB-06 in Participants With Relapsed or Refractory Myeloma参考资料 Roche官网新闻:https://www.roche.com/media/releases/med-cor-2022-06-08临床实验进展:https://clinicaltrials.gov/Christie P M Verkleij et al,Preclinical activity and determinants of response of the GPRC5DxCD3 bispecific antibody talquetamab in multiple myeloma,Blood Adv . 2021 Apr 27;5(8):2196-2215.https://merus.nl/app/uploads/2019/02/MCLA-117-Merus-SITC2016.pdfMichael J. Slade, Geoffrey Uy,CD123 bi-specific antibodies in development in AML: What do we know so far?Best Practice & Research Clinical Haematology (2020)Jingjing Wu et al,AFM13: a first-in-class tetravalent bispecific anti-CD30/CD16A antibody for NK cell-mediated immunotherapy,J Hematol Oncol . 2015 Aug 1;8:96佰傲谷知识周边
抗体AACR会议抗体药物偶联物免疫疗法ASCO会议
100 项与 GNR-084 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 前体B细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病 | 临床2期 | 俄罗斯 | 2020-10-15 | |
| 难治性 B 细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病 | 临床2期 | 俄罗斯 | 2020-10-15 | |
| 急性髓性白血病 | 临床1期 | 俄罗斯 | - |
登录后查看更多信息
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
No Data | |||||||
登录后查看更多信息
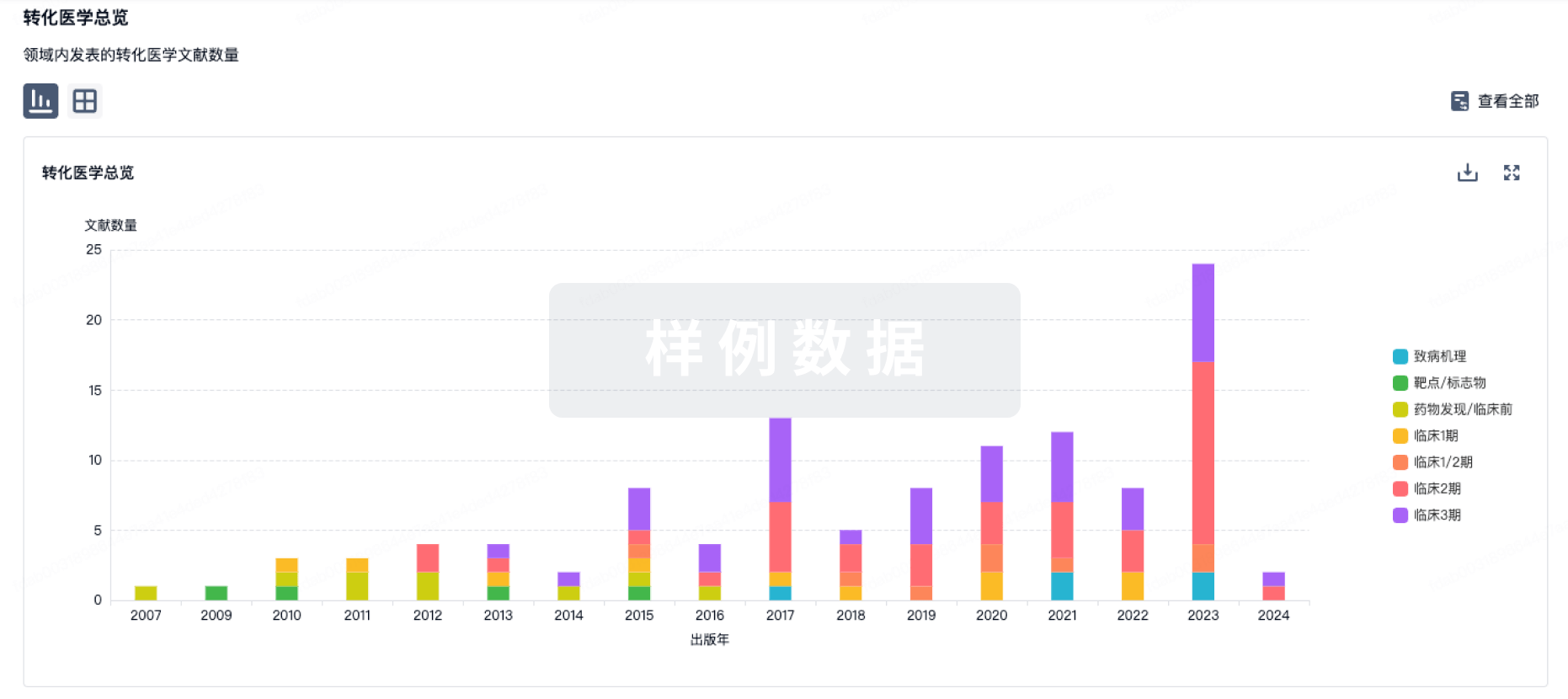
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或
核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或
临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或

批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或
生物类似药
生物类似药在不同国家/地区的竞争态势。请注意临床1/2期并入临床2期,临床2/3期并入临床3期
登录
或
特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或
Eureka LS:
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用

