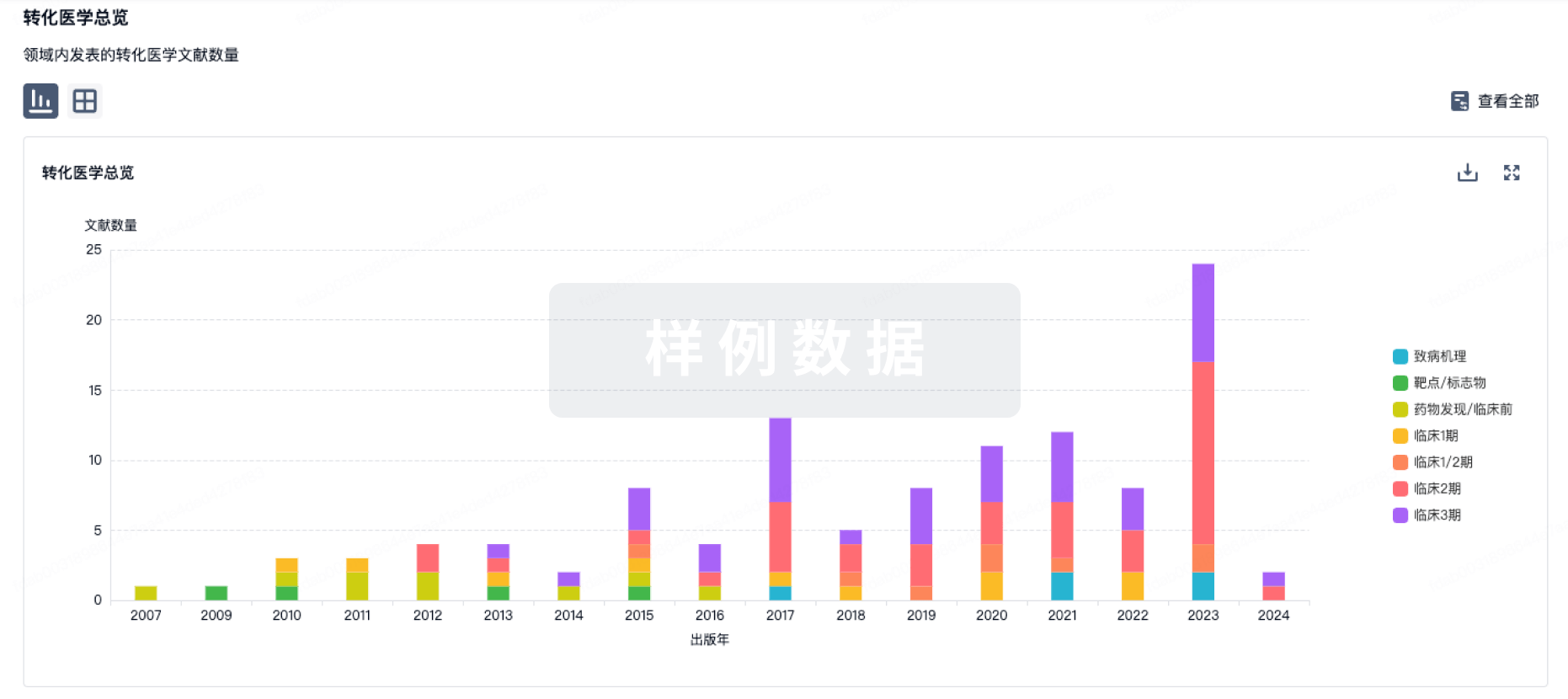
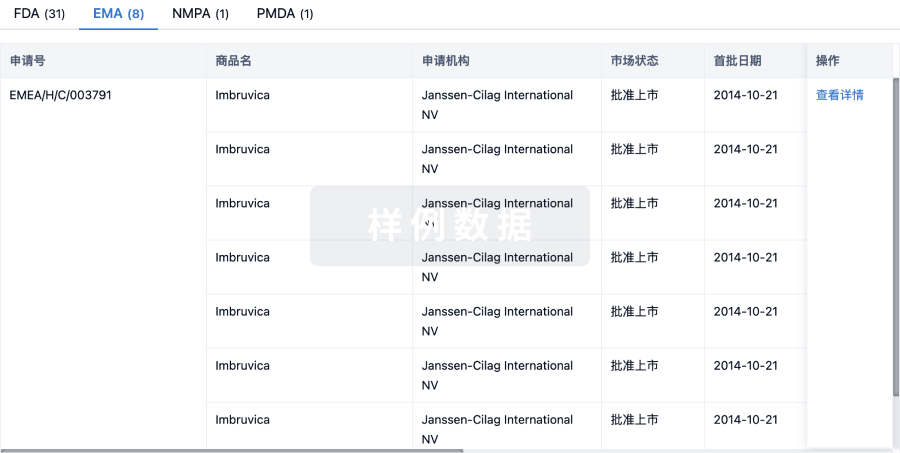
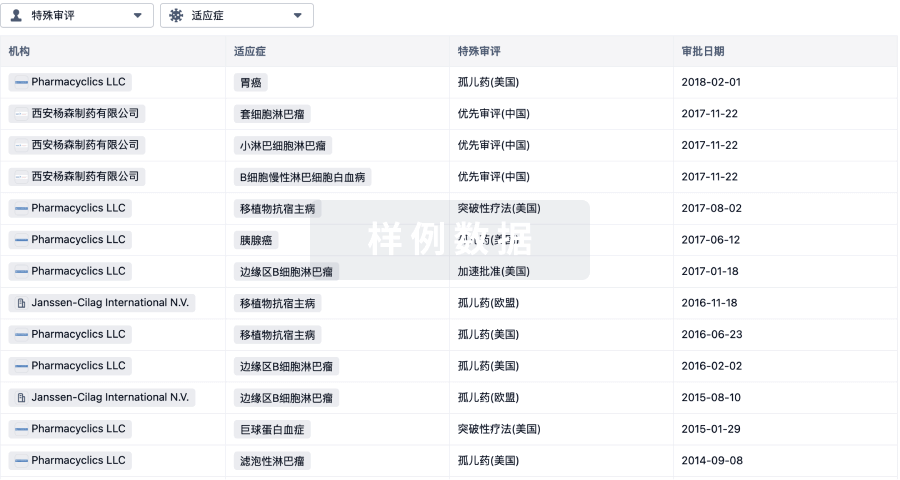
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are a rapidly expanding class of anticancer therapeutics, with 14 ADCs already approved worldwide. We developed unique linker technologies for the bioconjugation of drug molecules with controlled-release applications. We synthesized cathepsin-cleavable ADCs using a dimeric prodrug system based on a self-immolative dendritic scaffold, resulting in a high drug-antibody ratio (DAR) with the potential to reach 16 payloads due to its dendritic structure, increased stability in the circulation and efficient release profile of a highly cytotoxic payload at the targeted site. Using our novel cleavable linker technologies, we conjugated the anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (anti-HER2) antibody, trastuzumab, with topoisomerase I inhibitors, exatecan or belotecan. The newly synthesized ADCs were tested in vitro on mammary carcinoma cells overexpressing human HER2, demonstrating a substantial inhibitory effect on the proliferation of HER2-positive cells. Importantly, a single dose of our trastuzumab-based ADCs administered in vivo to mice bearing HER2-positive tumors, showed a dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth and survival benefit, with the most potent antitumor effects observed at 10 mg/kg, which resulted in complete tumor regression and survival of 100% of the mice. Overall, our novel dendritic technologies using the protease-cleavable Val-Cit linker present an opportunity for the development of highly selective and potent controlled-released therapeutic payloads. This strategy could potentially lead to the development of novel and effective ADC technologies for patients diagnosed with HER2-positive cancers. Moreover, our proposed ADC linker technology can be implemented in additional medical conditions such as other malignancies as well as autoimmune diseases that overexpress targets, other than HER2.