预约演示
更新于:2025-09-27
CAN-xx
更新于:2025-09-27
概要
基本信息
原研机构 |
在研机构 |
非在研机构- |
权益机构- |
最高研发阶段药物发现 |
首次获批日期- |
最高研发阶段(中国)- |
特殊审评- |
关联
100 项与 CAN-xx 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 CAN-xx 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 CAN-xx 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
11
项与 CAN-xx 相关的文献(医药)2017-05-01·Biosensors & bioelectronics1区 · 工程技术
Development of a colloidal gold immunochromatographic strip for rapid detection of Streptococcus agalactiae in tilapia
1区 · 工程技术
Article
作者: Fu-Yan, Chen ; Wen-de, Wu ; Ming, Chen ; Rui, Wang ; Min, Li ; Han-Zhong, Chen ; Hai-Lan, Chen ; Qiang, Mi ; Wan-Wen, Liang ; Li-Ping, Li
A colloidal gold immunochromatographic strip was developed for rapid detection of Streptococcus agalactiae (S. agalactiae) infection in tilapia. The monoclonal antibodies (mAb) 4C12 and 3A9 were used to target S. agalactiae as colloidal gold-mAb conjugate and captured antibody, respectively. The colloidal gold immunochromatographic strip was assembled via routine procedures. Optimal pH and minimum antibody levels in the reaction system for gold colloidal-mAb 4C12 conjugation were pH 7.4 and 18μg/mL, respectively. Optimal concentrations of the captured antibody 3A9 and goat anti-mouse antibody were 0.6mg/mL and 2mg/mL, respectively. The sensitivity of the strip for detecting S. agalactiae was 1.5×105 colony forming units (CFU). No cross-reaction was observed with other commonly encountered bacteria, including Pseudomonas fluorescens, Aeromonas hydrophila, Vibrio anguillarum and Streptococcus iniae. The assay time for S. agalactiae was less than 15min. Tilapia samples artificially infected with S. agalactiae were tested using the newly developed strip. The results indicated that blood, brain, kidney, spleen, metanephros and intestine specimens of infected fish can be used for S. agalactiae detection. The validity of the strip was maintained for 6 months at 4°C. These findings suggested that the immunochromatographic strip was effective for spot and rapid detection of S. agalactiae infected tilapia.
2016-10-01·Archives of virology4区 · 医学
Identification of a linear B-cell epitope on the avian leukosis virus P27 protein using monoclonal antibodies
4区 · 医学
Article
作者: Gao, Yadong ; Zhu, Haibo ; Qi, Xiaole ; Wang, Yongqiang ; Li, Xiaofei ; Cui, Xuezhi ; Qin, Liting ; Gao, Honglei ; Gao, Yulong ; Sun, Yingjun ; Wang, Xiaomei
Avian leukosis virus (ALV) is an avian oncogenic retrovirus that can induce various clinical tumors. The capsid protein P27 is the group-specific antigen of ALV and has many viral antigen sites that are easy to detect. In this study, we produced a monoclonal antibody (mAb), 3A9, that is specific for the P27 protein. A series of partially overlapping peptides were screened to define (181)PPSAR(185) as the minimal linear epitope recognized by mAb 3A9. The identified epitope could be recognized by chicken anti-ALV and mouse anti-ALV P27 sera. The epitope was highly conserved among a number of ALV-A, ALV-B and ALV-J strains. MAb 3A9 might be a valuable tool for the development of new immunodiagnostic approaches for ALV, and the defined linear epitope might help further our understanding of the antigenic structure of the P27 protein.
2008-11-01·Molecular immunology3区 · 医学
Structural analysis of the adenovirus type 2 E3/19K protein using mutagenesis and a panel of conformation-sensitive monoclonal antibodies
3区 · 医学
Article
作者: Martina Sester ; Hans-Gerhard Burgert ; Ralf Schmid ; Katja Koebernick ; Beatrice Menz
The E3/19K protein of human adenovirus type 2 (Ad2) was the first viral protein shown to interfere with antigen presentation. This 25 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein binds to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), thereby preventing transport of newly synthesized peptide-MHC complexes to the cell surface and consequently T cell recognition. Recent data suggest that E3/19K also sequesters MHC class I like ligands intracellularly to suppress natural killer (NK) cell recognition. While the mechanism of ER retention is well understood, the structure of E3/19K remains elusive. To further dissect the structural and antigenic topography of E3/19K we carried out site-directed mutagenesis and raised monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against a recombinant version of Ad2 E3/19K comprising the lumenal domain followed by a C-terminal histidine tag. Using peptide scanning, the epitopes of three mAbs were mapped to different regions of the lumenal domain, comprising amino acids 3-13, 15-21 and 41-45, respectively. Interestingly, mAb 3F4 reacted only weakly with wild-type E3/19K, but showed drastically increased binding to mutant E3/19K molecules, e.g. those with disrupted disulfide bonds, suggesting that 3F4 can sense unfolding of the protein. MAb 10A2 binds to an epitope apparently buried within E3/19K while that of 3A9 is exposed. Secondary structure prediction suggests that the lumenal domain contains six beta-strands and an alpha-helix adjacent to the transmembrane domain. Interestingly, all mAbs bind to non-structured loops. Using a large panel of E3/19K mutants the structural alterations of the mutations were determined. With this knowledge the panel of mAbs will be valuable tools to further dissect structure/function relationships of E3/19K regarding down regulation of MHC class I and MHC class I like molecules and its effect on both T cell and NK cell recognition.
1
项与 CAN-xx 相关的新闻(医药)2022-08-19
·美中药源
今天诺华宣布其IL-1 beta抗体canakinumab在一个叫做CANOPY-A 的三期临床未能达到主要终点DFS。这个试验招募1382位2、3A、3B期经手术和铂类药物治疗后的NSCLC患者,比较200毫克 Q3W的Cana与安慰剂比较对DFS的影响。此前Cana与多西他赛联用在转移NSCLC、与K药联用在手术前用药已经失败两个晚期临床。受此消息影响开发同类药物的Cantargia下滑5%。
一个治疗罕见病的细胞因子抗体、不远万里来治疗肺癌,这是什么精神?原来Cana本是作为一个抗炎药物开发,因为能降低hcCRP所以可能降低心血管事件。诺华做了一个万人CANTOS试验证明cana确实作为心血管二级预防药物降低心血管事件风险,但因为安全性问题并未获得这个标签。后来对CANTOS试验结果进行全面回顾性分析显示cana降低77%的肺癌发病率,这是CANOPY系列临床试验的缘起。
临床观察是新药发现的重要途径、但是这个模式也有它的局限,主要是意外观测因为没有严格的逻辑框架很容易把噪音当作信号、这是为什么临床试验终点要预设的原因。当然临床观测也产生不少著名药物,如伟哥。CANTOS试验的另一个重要发现是cana降低高尿酸患者50-60%的痛风发作风险,这个观测后来在对照试验中就得到验证。为降低风险通常需要回头建立完整证据链,如临床前机理研究和早期临床数据积累。炎症与肿瘤发生确实有一定关联,但IL1b这个具体免疫因子与肺癌这个具体肿瘤的关系还是比较模糊。
CANTOS招募的是心脏病患者、患者入组前无肿瘤诊断,看到的信号是预防肿瘤的发生。且不说这种钓鱼式回顾性分析看到的结果是否真实还存疑,即使cana能真正预防心脏病患者得肺癌用它来治疗已经发生、并经过几种疗法治疗过的复杂疾病如肺癌还是一个较大的逻辑跳跃。虽然心脏病与肺癌关系未知,但这显然是个经过一定筛选的人群(没心脏病的人群被排除)、跳到所有肺癌患者有个稀释过程。预防与治疗也是不同的任务,比如新冠疫苗虽然激活新冠病毒免疫反应、但只能用于预防新冠转为重症,对新毒株连感染风险都无法降低,治疗只在极特殊的情况下如免疫缺陷患者有零星报导。肿瘤形成后在自身繁殖能力、抑制免疫系统、打造TME对外防御等方面都已经有了质的飞跃,与肿瘤发生时的一穷二白不可同日而语。
虽然诺华根据CANOS试验的意外发现就开始多个NSCLC的晚期临床试验有点冒进,但我们也要看到整个IO 领域本来就成功率较低。IDO、TIM3、TIGIT这些科班出身的抗肿瘤新药也在晚期试验中已经失败或还在挣扎,所以不能因为cana的失败就否定临床线索作为立项根据的策略。IL-1b是NLRP3炎症小体激活后释放的最终炎症信号之一,炎症小体过度活跃与人间几乎所有疾苦都有一定关联、但cana只在病理相对清晰的罕见病CAPS获得批准,这本身应该是个危险信号。在NSCLC找出一个最可能应答的人群而不是直接全面开战可能是更可控的一个策略,这个人群如果成功可以有序扩大战果、如果失败可以及时止损。本垒打永远是个诱惑、除非你能意识到击中来球有多么困难。
内容来源于网络,如有侵权,请联系删除。
临床结果
100 项与 CAN-xx 相关的药物交易
登录后查看更多信息
研发状态
10 条进展最快的记录, 后查看更多信息
登录
| 适应症 | 最高研发状态 | 国家/地区 | 公司 | 日期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肿瘤 | 药物发现 | 瑞典 | - |
登录后查看更多信息
临床结果
临床结果
适应症
分期
评价
查看全部结果
| 研究 | 分期 | 人群特征 | 评价人数 | 分组 | 结果 | 评价 | 发布日期 |
|---|
No Data | |||||||
登录后查看更多信息
转化医学
使用我们的转化医学数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

药物交易
使用我们的药物交易数据加速您的研究。
登录
或

核心专利
使用我们的核心专利数据促进您的研究。
登录
或

临床分析
紧跟全球注册中心的最新临床试验。
登录
或

批准
利用最新的监管批准信息加速您的研究。
登录
或

生物类似药
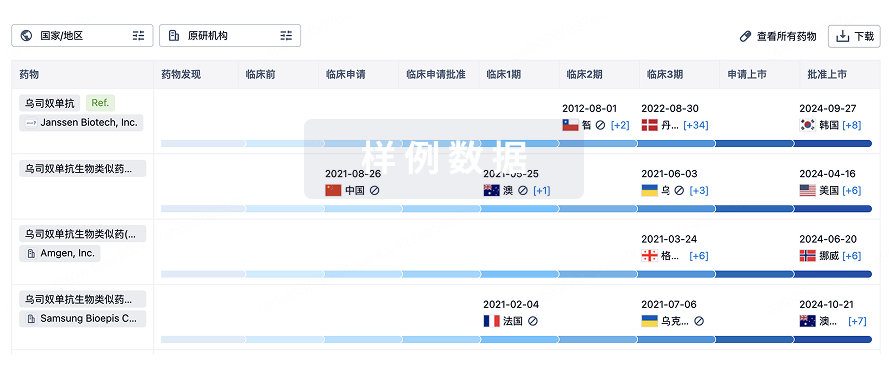
生物类似药在不同国家/地区的竞争态势。请注意临床1/2期并入临床2期,临床2/3期并入临床3期
登录
或
特殊审评
只需点击几下即可了解关键药物信息。
登录
或

Eureka LS:
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用
