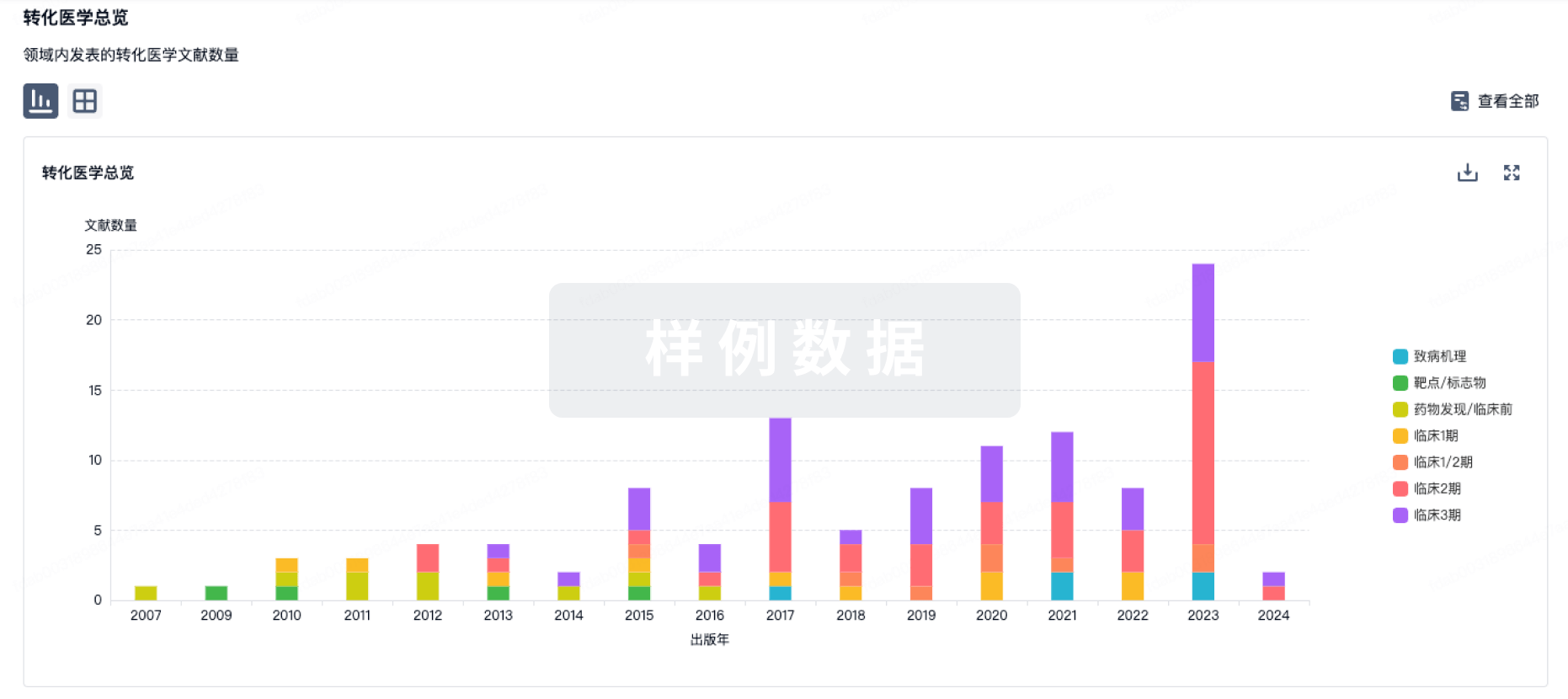
Our study had demonstrated that WW domain-binding protein 2 (WBP2) conferred chemoresistance in breast cancer (BC). However, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Herein, a decreased expression of itchy E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (ITCH) was observed in drug-resistant BC tissues which negatively regulated the expression of WBP2. However, ligase-deficient ITCH C830A mutant missed this function. WBP2 upregulation-initiated the chemoresistance to doxorubicin was reversed by exogenous ITCH, which was not affected by ITCH C830A mutant. In in vivo model, exogenous ITCH obstructed WBP2-mediated chemoresistance, which was destroyed by the proteasome inhibitor (MG132). Upon RNA sequencing, the excessive activations of angiomotin-like 2 (AMOTL2) and c-JUN (Jun proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit) were screened in WBP2-overexpressed BC cells. Additionally, AMOTL2 and endonuclear phosphorylated c-JUN were at a high level in chemoresistant BC tumors and WBP2-overexpressed BC cells. Mechanistically, exogenous ITCH transfection prevented the activation of AMOTL2/c-JUN induced by WBP2 overexpression, which was restored by MG132-mediated inhibition on ITCH activation. The increase of multiple drug-resistant proteins caused by WBP2 upregulation were restrained by AMOTL2 knockdown or c-JUN antagonist, respectively. Our findings present how ITCH/WBP2 signaling functions to link the intricate AMOTL2/c-JUN signaling networks in chemoresistant BC cells. Targeting WBP2 combined with c-JUN inhibitors may be a potential option to overcome chemoresistance in breast cancer patients.