预约演示
更新于:2025-05-07
Acute Encephalitis
急性脑炎
更新于:2025-05-07
基本信息
别名 Acute encephalitis、Acute encephalitis (disorder)、acute encephalitis + [4] |
简介- |
关联
3
项与 急性脑炎 相关的临床试验NCT00000794
Phase II Randomized Open-Label Trial of Atovaquone Plus Pyrimethamine and Atovaquone Plus Sulfadiazine for the Treatment of Acute Toxoplasmic Encephalitis
To evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerance of atovaquone with either pyrimethamine or sulfadiazine in AIDS patients with toxoplasmic encephalitis.
AIDS patients with toxoplasmic encephalitis who receive the standard therapy combination of sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine experience a high frequency of severe toxicity. Atovaquone, an antibiotic that has demonstrated efficacy against toxoplasmosis in animal models and in preclinical testing has been well tolerated, is now available as a suspension, which is more readily absorbed than the tablet form of the drug. The efficacy and safety of atovaquone in combination with sulfadiazine or pyrimethamine will be studied.
AIDS patients with toxoplasmic encephalitis who receive the standard therapy combination of sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine experience a high frequency of severe toxicity. Atovaquone, an antibiotic that has demonstrated efficacy against toxoplasmosis in animal models and in preclinical testing has been well tolerated, is now available as a suspension, which is more readily absorbed than the tablet form of the drug. The efficacy and safety of atovaquone in combination with sulfadiazine or pyrimethamine will be studied.
NCT06674837
Diagnostics and Surveillance of Acute Meningo-encephalitis Among Children in Cambodia With a Focus on Japanese Encephalitis Virus
The primary objective of this study is to quantify the clinical burden of Japanese Encephalitis (JE) and the asymptomatic circulation of JEV among Cambodian children, through two pediatric cohorts: non-febrile children at recruitment and children hospitalized with febrile neurological syndrome (FNS). Secondary objectives include estimating anti-JEV seropositivity rates, identifying individual risk factors and living conditions associated with JEV infection, characterizing clinical and biological profiles related to disease severity, and evaluating the role of deficiencies in interferon (IFN) response in severe JEV infections.
开始日期2025-06-01 |
申办/合作机构- |
NCT04339205
Diffusion Imaging in Acute Auto-immune Encephalitis : a Cohort of 80 Patients
The aim of this non randomised retrospective study is to investigate the imaging (MRI) of auto-immune encephalitis at presentation, especially in diffusion-weighted sequences.
Indeed, few series describe the MRI aspect of auto-immune at their beginning. Recognize early MRI abnormalities seen in auto-immune encephalitis could help reduce the time to positive diagnosis and improve the therapeutic management.
Indeed, few series describe the MRI aspect of auto-immune at their beginning. Recognize early MRI abnormalities seen in auto-immune encephalitis could help reduce the time to positive diagnosis and improve the therapeutic management.
开始日期2020-02-01 |
申办/合作机构 |
100 项与 急性脑炎 相关的临床结果
登录后查看更多信息
100 项与 急性脑炎 相关的转化医学
登录后查看更多信息
0 项与 急性脑炎 相关的专利(医药)
登录后查看更多信息
1,389
项与 急性脑炎 相关的文献(医药)2025-05-01·Neurology Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation
Chronic Dengue Virus Encephalitis
Article
作者: Torres, Gabriel Saboia De Araújo ; da Costa, Daniel Lacerda ; Doi, André Mário ; Castro, Luiz H. ; Labello, Julia Haddad ; Dorlass, Erick Gustavo ; Casal, Yuri R. ; Allioni, Gabriela Abrahao ; de Souza, Gabriel Samir Martins ; Rebello Pinho, Joao Renato ; Peres Fernandes, Gustavo Bruniera ; Vieira, Germana Titoneli ; Guedes, Bruno Fukelmann ; Amgarten, Deyvid ; Duarte-Neto, Amaro Nunes ; Malta, Fernanda de Mello
2025-04-01·Movement Disorders
Movement Disorders after Dengue Virus Infection: A Scoping Review
Review
作者: Perez‐Lloret, Santiago ; Phokaewvarangkul, Onanong ; Sringean, Jirada ; Garg, Divyani ; Yadav, Ravi ; Desai, Soaham ; Holla, Vikram ; Rosca, Elena Cecilia ; Mohamed Ibrahim, Norlinah ; Pal, Pramod Kumar
2025-03-19·Infectious Disorders - Drug Targets
Longitudinally Extensive Transverse Myelitis (LETM) and Meningoencephalitis Following Acute Epstein-barr Virus Infection in an Immunocompetent Male: Case Report and Review Literature
Article
作者: Sinha, Anshika ; Kumar, Nilesh ; Singh, Jitendra ; Dinkar, Anju ; Kumar, Kailash ; Daga, Rohit
4
项与 急性脑炎 相关的新闻(医药)2024-06-15
摘要:疫苗用于控制动物的传染病。与其他类型的疫苗接种(如活疫苗、减毒或灭活疫苗)相比,基于mRNA的疫苗具有显著优势。由于只使用病原体遗传物质的一小部分,且mRNA疫苗的剂量率低,病原体逆转自身的可能性最小。为了传递mRNA疫苗,需要一种载体或运输工具来保护mRNA疫苗免受宿主细胞RNases的侵害。临床试验表明,mRNA疫苗在对抗影响动物的各种传染病(包括病毒性和寄生虫性)方面有效,能够诱导细胞介导的免疫反应和体液免疫反应,这些疾病包括狂犬病、口蹄疫、弓形虫病、寨卡病毒、利什曼病和COVID-19。当前的综述旨在强调mRNA疫苗在动物病毒性和寄生虫性疾病中的应用。
1.引言
疫苗用于控制和预防动物传染病的出现。由于疫苗的广泛使用,一些疾病如天花和小反刍兽疫已从世界中完全根除,许多其他疾病的发病率在全球范围内大幅降低。通过疫苗接种,天花和小反刍兽疫等疾病已从世界中根除,这是疫苗接种成功的故事。传统疫苗开发方法为动物的许多传染病和人畜共患病提供了持久的保护,此类疫苗的例子包括灭活疫苗、活减毒疫苗、灭活疫苗或亚单位疫苗。然而,通过这些传统方法未能预防或充分控制的疾病需要新的方法来开发疫苗,特别是针对那些更能欺骗和逃避宿主适应性免疫反应的病原体。对于病毒疫苗的开发,主要障碍是快速开发和大规模制剂及其部署,而不是传统方法的有效性。同样,传统疫苗开发方法对于非传染病(如癌症)也不适用。由于这个原因,迫切需要开发更有效和广泛适用的疫苗平台。
传统疫苗方法的有希望和有效的替代方法是使用mRNA疫苗。目前,许多技术和研究发明使mRNA疫苗成为预防和控制动物工业中许多病毒和寄生虫疾病的有效工具。使用mRNA疫苗有几个好处,如(i)安全性;感染逆转和插入突变的潜在风险最小,是一种非整合性和非感染性方法。抗原修饰减少了mRNA的免疫原性并增强了其安全性。(ii)有效性;mRNA疫苗的稳定性和翻译可以被修改,从而通过将mRNA分子制剂到载体分子中,可以实现mRNA在宿主细胞质中的快速吸收和表达。由于其最小的遗传物质,mRNA可以避免抗载体免疫,并且可以重复接种。(iii)生产;mRNA疫苗可以快速大规模生产。
细胞质含有RNases(酶),这些酶迅速降解裸露的mRNA。因此,也开发并使用了一种转染试剂用于mRNA疫苗,它保护疫苗遗传物质免受RNases的侵害,并促进mRNA被细胞吸收。一旦进入宿主体内,当mRNA到达细胞质时,核糖体(细胞翻译机制)开始从mRNA产生蛋白质,翻译后,这些新合成的蛋白质经历翻译后修饰,从而产生完全功能性和正确折叠的蛋白质(图1,使用Biorender创建)。这种mRNA药理机制使其对需要跨膜或细胞质蛋白的疫苗和蛋白质替代疗法有利。必须将这些蛋白质正确地输送到其功能位点。完成工作后,这些mRNA被宿主细胞的正常生理机制降解。
图 1. mRNA疫苗(纳米颗粒)在宿主细胞中的呈现和抗原翻译
通过动物中自我复制的纳米颗粒RNA疫苗的免疫接种,可以引起对各种传染病的强烈免疫反应(T细胞和B细胞)。在体内,mRNA的载体包括含有可离子化的氨基脂质的纳米颗粒,这些被认为是此目的的最佳选择。含脂质mRNA疫苗的最佳解剖部位是皮内途径,因为皮肤中存在大量异质免疫细胞。这种含脂质mRNA纳米颗粒疫苗的特性优于其他形式的疫苗。
2.mRNA疫苗引起的免疫反应
在过去疫苗开发过程中,各种形式(灭活或活减毒)疫苗的作用机制是未知的。然而,通过活减毒疫苗在动物、细胞系或不利生长条件下的开发,以及灭活或灭活疫苗在控制动物(牛瘟、猪瘟和马传染性贫血)和人类(麻疹、腮腺炎、天花、脊髓灰质炎和风疹)的传染病方面取得了成功。分子生物学理论和技术的进步导致了对疫苗机制的广泛了解,例如灭活疫苗产生抗原特异性抗体,而活减毒疫苗引起宿主的体液免疫反应,这对根除细胞内病原体是必要的。RNA基非病毒疫苗的免疫接种刺激了滤泡辅助T细胞和生发中心B细胞的产生(图2,使用Biorender创建)。这些疫苗模仿活微生物的疫苗接种或感染。
图2. mRNA疫苗接种引发的先天和适应性免疫反应。(1) 当mRNA疫苗被接种时,RNA感受器识别疫苗颗粒并激活先天免疫反应,导致干扰素和细胞因子的产生。(2) 这些干扰素和细胞因子促进树突状细胞的成熟,这些细胞迁移到淋巴结以呈现感兴趣的抗原。(3) 在淋巴结中,由树突状细胞启动T细胞和B细胞。树突状细胞激活T细胞。辅助性T细胞促进产生抗体的浆细胞的成熟。辅助性T细胞和细胞因子共同促进B细胞分化为记忆B细胞。(4) 细胞免疫和体液免疫被激活,免疫细胞向感染的组织或细胞移动。(5) 被病毒感染的细胞受到抗原特异性T细胞的攻击。(6) 通过抗体中和病毒。
mRNA疫苗引起的免疫反应机制仍需进一步阐述。mRNA疫苗被细胞受体感知和激活细胞受体的过程尚不清楚。细胞内有两种受体参与识别和诱导免疫反应,即内体性Toll样受体(TLRs)和视黄酸诱导基因I(RIG-I)样受体(RLRs)。TLRs进一步细分为TLR-3、TLR-7、TLR-8和TLR-9,它们存在于单核细胞、巨噬细胞和树突状细胞中。TLR-3参与识别包括由单链RNA(ssRNA)产生的45个以上碱基对的双链RNA(dsRNA),而富含鸟苷、尿苷或多尿苷的RNA由TLR-7和TLR-8激活。TLR-8只能与ssRNA结合,而TLR-7可以与ssRNA和dsRNA结合,并增强抗原呈递、细胞因子分泌和B细胞免疫反应刺激。内体TLR-9受体参与抗原呈递细胞,并作用于激发宿主的免疫反应。
RIG-I样受体作为模式识别受体,RLR家族的其他成员包括黑色素瘤分化相关蛋白5(MDA5)和遗传学和生理学实验室2(LGP2)。RIG-1参与识别ssRNA和dsRNA,最终导致干扰素的产生,而MDA5存在于细胞质中,参与识别病毒RNA复制期间产生的长dsRNA。mRNA疫苗刺激了先天免疫。
mRNA疫苗接种激活了先天免疫系统和适应性免疫系统。mRNA疫苗激活宿主适应性免疫反应,增强了细胞因子和干扰素的产生,这些因子参与了免疫防御细胞的招募,即自然杀伤细胞、巨噬细胞和树突状细胞。先天免疫系统损害了抗原的表达,从而降低了疫苗的有效性。有一份报告指出,当IFN拮抗剂与mRNA疫苗一起使用时,观察到疫苗的相当大的效果。因此,为了避免先天免疫系统(例如mRNA的修饰)的过度反应,必须共同给予拮抗剂,以维持疫苗的有效性。
3.动物传染病的mRNA疫苗开发
疫苗被认为是控制和预防人类和动物传染病最成功的预防性和治疗性工具(见表1和表2)。疫苗可以挽救成千上万的动物和人的生命,并节省资金。由于疫苗接种,麻疹、脊髓灰质炎和小天花等严重传染病已被根除或接近根除,许多其他疾病的发病率和死亡率也大幅降低。
3.1.口蹄疫
口蹄疫是一种由口蹄疫病毒(FMDV)引起的有蹄动物的传染性病毒疾病,在发展中国家和不发达国家尤为常见。根据抗原和遗传属性,FMDV有O、A、C、Asia1、SAT1、SAT2和SAT3七个血清型。尽管口蹄疫的死亡率很低,但FMD的爆发会导致严重的经济损失,并对活体动物及其产品的国内外贸易产生负面影响。病毒的传播方式是通过气溶胶、直接接触感染动物、通过污染物、人类和其他非敏感动物。无口蹄疫国家通过严格的检疫和限制从口蹄疫流行国家进口敏感动物及其产品来维持这一状态。在控制家畜(牛、水牛、绵羊和山羊)中的FMD方面,最有效的方法是限制感染动物及其产品从其所在地向健康易感动物的流动,屠宰暴露和感染的动物,消毒受污染的地方和设备,以及接种疫苗。
表1:针对传染病的mRNA疫苗
表2:mRNA疫苗对动物和人类传染病的免疫反应
目前用于控制和预防FMD的传统疫苗通过激活先天免疫反应和适应性免疫反应来诱导保护。这些疫苗不提供长期保护,需要多次加强剂量来维持群体中足够的免疫水平。这些传统疫苗也有一些缺点,如基因毒性潜力、较低的细胞免疫、较短的保护期限,以及在接种和感染动物之间难以进行血清学区分。为了克服所有这些问题并在过去十年中开发更安全的下一代FMD疫苗,进行了许多尝试。2010年,进行了一项研究,阐述了在小鼠中由mRNA FMDV(基因工程)诱导的免疫,并证明它可以在实验室动物中引起强烈的免疫反应。这为开发基于mRNA的疫苗提供了可能性,以实现对动物自然感染的长期保护。口蹄疫病毒对干扰素(IFN)敏感。因此,Rodriguez-Pulido及其同事进行了一项研究,表明FMDV的dsRNA可以在IBRS-2(猪肾细胞系)和新生小鼠中引起免疫反应,并且体外转录RNA对预防FMD的有效性。结果表明,3'非编码区的dsRNA在SK-6细胞系中诱导了强大的IFN alpha/beta激活。进一步,这种dsRNA在新生小鼠体内也证实了自然免疫反应的诱导。这认识到dsRNA具有开发针对动物FMDV疫苗的潜力。同一组研究了对应于内部核糖体进入位点的非感染性RNA作为FMD疫苗设计的佐剂的潜力,当它与常规疫苗一起增强了小鼠对FMDV挑战的免疫反应时。此外,Rodriguez-Pulido及其同事分析了合成非感染性RNA在猪中的免疫调节效应。这项研究证明了这些RNA分子与常规疫苗共同给予可以增强针对FMDV的特异性抗体滴度。此外,FDMV能够与宿主细胞发生突变和重组。病毒与宿主细胞的重组可能比单独的非活性病毒引起更强的免疫反应。宿主细胞中存在的酶(RNAses)在它们进入细胞后如果不适当修饰和/或通过封装(加帽)保护,会迅速降解裸露的RNA。同样,在反向遗传过程中,体外合成的RNA也会被酶降解。Semkum及其同事建立了一个DNA载体pKLS3(FMDV的小型基因组),它最小化了RNAses对合成mRNA的降解。它可以用来驱动FMDV感兴趣的基因的转录,因为它包含转录和翻译病毒所需的最小顺式作用组分。用于生产疫苗的mRNA是在体外转录的,编码特定的抗原。pKLS3有潜力用作转录系统,用于表达mRNA,可能在生产基于mRNA的疫苗中有用。对于FMD疫苗(基于mRNA)的开发,现有信息提供了一个有希望的途径。
3.2.狂犬病
狂犬病是由狂犬病病毒引起的病毒性疾病,可以感染所有温血动物,包括人类。它是一种人畜共患病,每年大约有60,000人因狂犬病病毒感染而死亡。超过95%的狂犬病病例是由狂犬动物的咬伤引起的,特别是狂犬狗的咬伤。这是一种严重的病毒性疾病,以急性脑炎为特征,通过狂犬动物的咬伤或通过与狂犬动物的唾液接触粘膜从狂犬动物传播给人类和其他易感动物。病毒通过表面糖蛋白(狂犬病病毒糖蛋白)附着在其细胞受体上,并沿着周围神经传播到大脑。为了预防狂犬病,早期疫苗是在哺乳动物的神经组织中生产的,但后来被胚胎蛋和组织培养中开发的疫苗所取代。全世界都需要一种负担得起且有效的狂犬病疫苗,因为目前可用的疫苗由于某些限制(如生产能力、储存要求、成本和接种时间表)无法满足需求。以前为了开发狂犬病疫苗,使用了多种不同的病毒疫苗生产方法。CureVac®应用的新概念是使用mRNA编码主要的狂犬病病毒抗原狂犬病病毒糖蛋白(RABV-G)。在研究mRNA疫苗对狂犬病的免疫反应的第一阶段临床试验中,选择了疫苗候选物(CV7201)。CV7201证明可以诱导保护性免疫反应,这受到疫苗剂量和接种途径的影响。阳离子蛋白鱼精蛋白被用作CV7201中编码狂犬病病毒糖蛋白抗原的热稳定mRNA的稳定剂。与传统的商业灭活狂犬病病毒疫苗相比,mRNA疫苗诱导了更好的免疫反应,通过促进合成病毒中和抗体,这些抗体对保护是必要的。在第一阶段试验中,发现需要高剂量的狂犬病mRNA疫苗才能提供显著的抗体滴度以保护。为了降低狂犬病疫苗(CV7201)的剂量率,采用了一种新方法,即使用脂质纳米颗粒(LNPs)包裹mRNA抗原。这项临床试验表明,mRNA疫苗是安全的,其反应原性概况可能是可以接受的,这种技术形式比传统疫苗提供了许多优势。同样,在接种编码RABV-G的mRNA的家猪和老鼠中确认了中和抗体的产生。RABV-G mRNA疫苗诱导了CD4+和CD8+的产生,并提供了对脑内致死性感染挑战的保护。这项研究表明,编码RABV-G的基于mRNA的疫苗在小型和大型动物中是可行的,并且可能是控制动物病原体疾病的有希望的方法。
3.3.利什曼病
利什曼病是由雌性白蛉沙蝇叮咬传播的一种寄生虫性人畜共患病。引起该病的病原体是利什曼属(L.)的原生动物寄生虫。该病有不同形式,最常见的包括由不同种类引起的内脏利什曼病、皮肤利什曼病和粘膜皮肤利什曼病,如L. donovani、L. chagasi、L. infantum、L. braziziliensis、L. maxicana和/或L. archibaldi。狗是宿主,而人类是偶然宿主。第一代和第二代疫苗都是为了预防人类疾病而开发的,但缺乏完全保护。为了更好地提供保护,正在考虑基于mRNA的疫苗。Savar等人设计了两种组合的融合蛋白(LmSTI1-PpSP15和PpSP15-LmSTI1)用于疫苗开发。融合蛋白包括L. major的应激诱导蛋白1(LmSTI1)和来自白蛉沙蝇(PpSP15)的SP15。这种组合还基于alphavirus-derived self-amplifying mRNA以病毒复制子粒子的形式在in silico研究中设计。in silico分析显示了抗原组合的有效性。后来使用基于自复制mRNA(SAM)的疫苗在细胞系Baby Hamster Kidney成纤维细胞(BHK-21细胞)中表达了融合蛋白。结果表明,使用SAM载体的PpSP15-LmSTI1表达水平很高。同样,研究了其他融合重组抗原(LEISH-F2和LEISHF3+)对L. donovani的影响,采用异源主要增强方案进行免疫。C57BL/6和TLR7−/−小鼠接种了表达LEISH-F2抗原的RNA基疫苗,随后接种了亚单位疫苗。结果表明,单独使用RNA基疫苗的免疫(同源免疫)没有提供显著的保护。然而,当小鼠使用异源方案的增强剂免疫时,产生了强大的抗原特异性T细胞反应(CD4和CD8),并对细胞内寄生虫提供了显著的保护。需要进一步研究以识别新抗原并开发有效的针对利什曼病的基于mRNA的疫苗。
3.4.弓形虫病
弓形虫是一种专性细胞内原生动物,负责所有温血动物的弓形虫病。它的复杂生命周期包括在确定宿主(猫科动物)中的性繁殖和在中间宿主(猫和其他温血动物)中的无性繁殖。全球大约有一半的人类被弓形虫感染,但这种感染的流行率在不同国家之间变化,从10%到80%不等。人类可以通过食用未煮熟的肉类中的组织囊肿或污染食物中的卵囊偶然获得这种感染。主要为了保护免受弓形虫感染,免疫依赖于由CD4+和CD8+介导的细胞免疫反应,并最终刺激细胞因子(伽马干扰素)的分泌。除此之外,体液免疫也在限制弓形虫病方面发挥重要作用,通过抗弓形虫抗体抵抗寄生虫的入侵,通过调理作用促进寄生虫的吞噬作用,并最终激活经典补体途径。Chahal等人最近开发了一种完全合成的树突状纳米颗粒疫苗,其中包含封装的mRNA复制子编码抗原,这些抗原能够引发免疫反应并提供对弓形虫感染的保护。这种mRNA复制子同时编码六种抗原,如密集颗粒蛋白6(GRA6)、棘蛋白18(ROP18)、棘蛋白2A(ROP2A)、表面抗原1(SAG1)、顶端膜抗原1(AMA1)和表面抗原2A(SAG2A)。这是一种完全保护性的单剂量mRNA疫苗(mRNA复制子纳米颗粒),用于预防和控制弓形虫。尽管如此,它可能需要时间才能商业化。Luo等人分析了小鼠中针对弓形虫挑战的自复制RNA疫苗的活性,该疫苗编码核苷酸三磷酸水解酶-II(NTPase-II)。进一步,他们评估了疫苗与脂质纳米颗粒的联合效应。小鼠的免疫接种结果产生了强大的免疫反应。细胞和体液免疫反应都被激发,产生了高特异性抗弓形虫抗体和IFN-γ。与对照组相比,接种疫苗的小鼠大脑囊肿减少了62.1%,并显著延长了动物的存活时间。现有信息为生产预防弓形虫病的mRNA疫苗提供了一个有希望的途径。
3.5.寨卡病毒病
寨卡病毒最初是在1947年从乌干达寨卡森林的一只哨兵恒河猴的血液中分离出来的。该病毒通过蚊子(埃及伊蚊)的叮咬传播。它具有人畜共患的重要性,是神经和胎儿异常(如脑钙化、小头症、听力和视力丧失)的罪魁祸首。最初,它与轻微的发热症状相关。然而,它传播到美洲和太平洋岛屿,导致严重的后果,如吉兰-巴雷综合征、先天性寨卡综合征和自然流产。最近,它已成为一种流行病,因此,需要开发一种有效且安全的疫苗。已表明有多种类型的疫苗可以保护非人灵长类动物和小鼠,如灭活疫苗、亚单位疫苗和/或基于腺病毒的疫苗。然而,开发一种针对寨卡病毒的有效且安全疫苗仍然是必要的。Essink及其同事评估了两种先前开发的基于mRNA的疫苗mRNA-1325和mRNA-1893在人类中的安全性和免疫原性。mRNA-1325脂质纳米颗粒包裹是第一代疫苗,编码来自2007年密克罗尼西亚寨卡病毒分离株的前膜(prM)和包膜E结构蛋白,即prME。而mRNA-1893是第二代疫苗,编码来自寨卡病毒(RIO-U1)分离株的相同蛋白prME。RIO-U1寨卡病毒是从巴西感染寨卡病毒的孕妇尿液中分离出来的。mRNA-1325和mRNA-1893疫苗的prME中分别有一个和五个氨基酸残基的差异。在小鼠的临床前研究中,编码prME的修饰mRNA疫苗显示出有希望的结果,并保护小鼠免受寨卡病毒挑战。在成年人类的第一阶段临床试验中,研究了两种mRNA疫苗的不同剂量反应。两种疫苗都被所有健康志愿者很好地耐受,并且没有向疫苗传达严重的不良反应。由于只有一个氨基酸残基,mRNA-1325的寨卡病毒特异性中和抗体(nAb)反应较差。另一方面,由于五个氨基酸残基,mRNA-1893疫苗以较小的剂量引起了强大的nAb反应,与mRNA-1325相比。所获得的结果是有希望的,Essink及其同事向第二阶段临床试验迈进。然而,为了检查疫苗的有效性,将需要第三阶段的临床试验。
3.6.冠状病毒病
许多动物种类,包括人类,都可能被冠状病毒感染。对兽医重要的冠状病毒包括猪传染性胃肠炎病毒、牛冠状病毒和禽传染性支气管炎病毒。目前,冠状病毒被认为是一种新兴病原体,负责动物和人类的急性和慢性感染,包括肠道、呼吸和中枢神经系统。2003年,由于严重急性呼吸综合征冠状病毒(SARS-CoV)在人类中爆发,震惊了世界。2012年至2016年,在阿拉伯半岛,由于名为中东呼吸综合征冠状病毒(MERS-CoV)的冠状病毒,人类中报告了几次爆发。该病毒在中东和非洲的骆驼中流行。近年来,全球大流行感染了呼吸系统的冠状病毒病2019(COVID-19),由一种名为严重急性呼吸综合征冠状病毒2(SARS-CoV-2)的传染性病原体引起,它起源于蝙蝠。世界卫生组织宣布COVID-19是重大的公共卫生紧急情况。对于鸡来说,为了预防由传染性支气管炎病毒引起的传染性支气管炎病,有许可的疫苗可用。然而,对于预防其他动物的冠状病毒病,开发一种安全有效的疫苗是一个未满足的需求。对于COVID-19疫苗的开发,采用了几种方法,如灭活病毒、活减毒、重组蛋白、腺病毒载体、流感病毒载体、DNA和mRNA疫苗。mRNA疫苗方法是COVID-19预防的一场变革。一种编码刺突蛋白的自复制mRNA疫苗在小鼠中提供了针对SARS-CoV-2的保护。编码刺突蛋白三聚体受体结合域的RNA疫苗针对几种SARS-CoV-2变体在恒河猴和小鼠中显示出显著的保护。BioNTech和辉瑞合作开发了一种基于mRNA的SARS-CoV-2疫苗。BNT162b2编码病毒刺突糖蛋白的全长。这是美国FDA批准的疫苗,在16岁及以上的人中两剂间隔21天的效力为95%,在随后的六个月,其效力变为91.3%。Moderna还开发了一种基于mRNA的疫苗(mRNA-1273),编码病毒融合刺突蛋白的全长。在18岁及以上的个体中,两剂间隔28天的第三阶段临床试验的效力为94.1%。
4.mRNA疫苗的类型
中心法则表明,mRNA在翻译(DNA编码蛋白)和由细胞质中的核糖体合成蛋白之间处于中心位置。目前,有两种主要类型的mRNA用于mRNA疫苗的开发,即自复制mRNA或复制体mRNA疫苗和非复制mRNA或非复制mRNA。在自复制mRNA疫苗开发方法中,mRNA编码抗原以及病毒RNA的复制机制保持不变,这使得mRNA可以在细胞内自我复制,从而实现丰富的蛋白表达。而在非复制mRNA疫苗开发方法中,mRNA仅编码感兴趣的基因,其中包含5'和3'的非翻译区。
4.1.自复制mRNA疫苗
在自复制mRNA疫苗中,感兴趣的抗原取代了阿尔法病毒基因组的结构蛋白,但RNA的复制机制保持不变。通过使用自复制mRNA,可以通过最小剂量的抗原编码RNA翻译,向宿主细胞传递大量的抗原。当自复制mRNA进入细胞质时,它与宿主核糖体结合产生非结构蛋白1(nsP1)、nsP2、nsP3和nsP4。它们是依赖核糖核苷酸的RNA聚合酶的组成部分。病毒蛋白酶(nsP2)进一步将这些蛋白质调节成单个蛋白质。这些蛋白质发挥许多重要作用,例如nsP1在建立RNA复制复合体和质膜复制复合体之间的联系方面的作用,nsP2作为蛋白酶和解旋酶,nsP3介导宿主-病毒与蛋白质的相互作用,nsP4是一种依赖RNA的RNA聚合酶。在编码区域基因组中,生成病毒RNA,表达病毒蛋白,并包装病毒基因组。自复制mRNA疫苗具有许多优点,包括由于能够自我复制而具有高表达水平,缺乏结构病毒蛋白基因,以及能够持续长达两个月。除了它们更大的尺寸和无法耐受各种合成修饰之外,还有一些缺点。
4.2.非复制mRNA疫苗
非复制mRNA疫苗包含编码感兴趣的蛋白,而不是像自复制mRNA疫苗那样需要mRNA复制的蛋白。非复制mRNA的基本结构与天然mRNA相同,包括5'帽子、聚(A)尾部、5'不饱和区、3'不饱和区,以及编码感兴趣基因的区域。5'和3'不饱和区元素在mRNA分子的稳定性和复制中起着至关重要的调节作用。5'是mRNA稳定性的重要元素,促进蛋白合成。聚(A)尾部具有保护功能,防止mRNA分子被RNases外切核糖酸酶降解。非复制mRNA疫苗的优点包括相对较小的尺寸(大约2-3 kb),与自复制mRNA疫苗(10 kb)相比,只携带所需的感兴趣基因,防止了任何其他可能导致宿主内不需要的免疫反应的蛋白表达,并且其构建容易。而缺点包括不稳定、半衰期短和表达水平低。
5.mRNA疫苗的配方和传递
mRNA疫苗的配方和传递系统决定了宿主细胞内抗原的表达效果和持续时间,以及它们引起的免疫反应的效力。mRNA分子的物理化学性质,如负电荷和大尺寸,使它们(裸露的mRNA)难以穿过细胞的质膜。模式识别受体可以轻易识别外源mRNA,并通过干扰素导致裸露mRNA的降解。因此,为了增强mRNA的细胞摄取和它们对核酸酶降解的抵抗力,需要一个传递载体。用于mRNA管理的传递载体包括树突细胞(体外)、电穿孔和基因枪(物理传递)、基于聚合物的传递和基于纳米颗粒的传递工具(LNPs)。LNPs是其中最有效和广泛使用的传递载体。
在体外,转录系统可以用来生产合成mRNA。这个转录系统由编码mRNA的DNA模板、噬菌体RNA聚合酶、RNA和合成帽子类似物组成。在某些情况下,也可以使用来自癌细胞的完整RNA用于疫苗。体外提取的mRNA或从肿瘤细胞获得的mRNA可以裸露或与载体一起管理。mRNA疫苗携带编码抗原的转录物进入宿主细胞,在那里使用宿主的翻译机制来产生抗原,然后刺激宿主的免疫系统。mRNA的细胞内稳定性和翻译效率很大程度上受其结构的影响。合成mRNA的设计基于真核RNA蓝图,在5'端有一个帽子,在3'端有一个聚A尾部。通过添加3'和5'非翻译区,可以进一步增强其稳定性和效力。这些非翻译区包含调节元素。
当mRNA疫苗被配制在脂质纳米颗粒中时,可以增强免疫反应,这也保护了mRNA免受细胞质RNases的侵害。由于其某些好处,如易于准备、毒性较小,以及能够被宿主细胞机制降解,脂质纳米颗粒长期以来被用作药物载体。脂质纳米颗粒有四个组成部分,如阳离子脂质(可离子化)、辅助磷脂、胆固醇和聚乙二醇。由于RNA是带负电荷的分子,它与带正电荷的阳离子脂质颗粒形成复合物。脂质颗粒的可离子化特性使复合物无毒,并在宿主生理pH下保持中性或轻微带正电荷的表面。这种特性还通过最小化非特异性细胞表面脂质和蛋白质之间的相互作用,促进mRNA释放到细胞质中。还有许多其他mRNA传递系统,如精蛋白、脂质复合物、多聚体纳米颗粒、胶束复合物纳米颗粒、脂多聚体,以及阳离子纳米乳液。
6.未来展望
在人类中接种mRNA疫苗所取得的成功结果为mRNA基础疫苗在兽医医学中的发展打开了大门。目前,只有少数mRNA疫苗在动物中针对其自然宿主的特定传染病进行了研究。全球寄生虫和病毒感染对动物健康和工业家畜生产构成重大威胁。全球最严重的病毒感染缺乏适当的预防策略,包括牛病毒性腹泻病毒(BVDV)、口蹄疫病毒(FMDV)、疙瘩皮肤病病毒(LSDV)、牛白血病病毒(BLV)、小反刍兽疫病毒(PPRV)、猪繁殖与呼吸综合征病毒(PRRSV)、非洲猪瘟病毒(ASFV)、猪流行性腹泻病毒(PEDV)、新城疫病毒(NDV)、禽流感病毒(AIV)等。传统疫苗对上述许多疾病安全有效,但仍需要研究以更好地预防疾病。对于传染病疫苗的开发,mRNA有潜力解决疫苗学中出现的许多挑战。在未来,疫苗不仅用于预防措施,还用于预防、控制和治疗动物和人类的癌症和肿瘤。
非洲猪瘟病毒是导致猪的高死亡率和出血的原因。中国是最大的猪肉生产国,由于缺乏有效的策略,这种疾病传播到许多其他国家,导致2019年约有七百万头猪死亡。目前,使用活减毒疫苗进行控制。活减毒疫苗的开发需要猪骨髓细胞或肺泡巨噬细胞,这既耗时又成本高昂。作为这种方法的替代方案,最近通过iVAX(计算疫苗设计平台)识别了非洲猪瘟病毒编码蛋白中的T细胞表位。在细胞免疫反应中,T细胞执行重要功能,参与在识别病毒的T细胞表位后直接杀死病毒感染的细胞。因此,为了充分利用T细胞表位的潜力,需要进一步调查以促进mRNA疫苗(针对T细胞)的开发。
猪繁殖与呼吸综合征病毒是导致母猪繁殖失败和仔猪呼吸道疾病的原因,影响猪农经济。PRRSV有两种抗原上不同的基因型。目前,使用活减毒或灭活疫苗预防性地控制疾病,但这些疫苗仅对同源菌株提供保护,对异源菌株的效力为零或部分。2019年,显示具有PRRSV GP5-Mosaic(糖蛋白5)序列的DNA疫苗候选物是免疫原性的,并对猪的病毒感染提供保护。借助in silico算法,可以组装不同PRRSV菌株的片段,这些片段诱导免疫反应,使用mRNA疫苗平台制作单一疫苗。这样的疫苗可以为两种类型的菌株提供广泛和有效的免疫,无论是同源还是异源菌株。
冠状病毒引起许多新兴大流行疾病,如严重急性呼吸综合征、中东呼吸综合征和新型冠状病毒病,感染了牛、水牛、猫、狗和猪等各种动物。抗体通过与冠状病毒的刺突(S)糖蛋白结合来中和病毒,该蛋白由S1和S2亚基组成。受体结合域(RBD)位于S1亚基中,参与特异性受体结合,而S2亚基参与宿主和病毒细胞膜的融合。随着对动物冠状病毒(猪急性腹泻综合征冠状病毒、牛冠状病毒、传染性胃肠炎病毒和猪流行性腹泻病毒)的细胞表面受体和新型受体结合域的研究进展,基于RBD的mRNA疫苗似乎是限制动物冠状病毒疾病出现和再现的有效策略。
在兽医领域经济上重要的 Pestiviruses,如牛病毒性腹泻病毒、经典猪瘟病毒和边缘病病毒。Pestiviruses 编码的三种糖蛋白包括 E1、E2 和 Erns(E 核糖核酸酶)。E2 是中和抗体的主要靶标。用作疫苗的 E2 亚基激活了体液免疫反应和细胞介导的免疫反应,因此基于 E2 的 mRNA 疫苗可以提供有效的保护。需要进一步评估 mRNA 疫苗,以评估在自然动物宿主中疫苗管理后发生的过敏反应。用于动物的疫苗必须是经济实惠且易于获得的,以便兽医可以访问它们。在未来,mRNA 疫苗在动物中的使用似乎是一种非常有效的方法,用于控制各种病原体疾病,由于上述讨论的许多优点。
7.结论
目前,科学家们对基于RNA的方法在疫苗开发中的兴趣日益增加,这些疫苗可用于预防和控制疾病。mRNA疫苗在用于临床前和临床试验的动物模型中激发了安全且持久的免疫反应。它在兽医领域对动物传染病有很强的潜力,并且比其他形式的疫苗具有某些优势,如感染风险消失、无逆转为毒力的风险,并且可以在一种疫苗中组装多种抗原,同时对多种病原体进行免疫,易于准备且处理和储存非常方便。mRNA疫苗为预防传染病提供了显著的保护性免疫来源,这一点已经通过COVID-19疫苗的成功应用得到证实。这一成功为预防一系列传统疫苗方法具有挑战性的传染病开辟了新的可能性。由于疫苗的快速发展,它可能是应对新兴传染病的一个有希望的平台。然而,要充分利用mRNA疫苗在未来的潜力,必须解决某些挑战,如配方、疫苗犹豫和广泛获取。
识别微信二维码,添加生物制品圈小编,符合条件者即可加入
生物制品微信群!
请注明:姓名+研究方向!
版
权
声
明
本公众号所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源和作者,不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系(cbplib@163.com),我们将立即进行删除处理。所有文章仅代表作者观点,不代表本站立场。
信使RNA疫苗
2023-08-01
·医药观澜
▎药明康德内容团队编辑根据中国国家药监局药品审评中心(CDE)官网公示信息,在刚刚过去的7月,又有许多1类新药在中国获得临床试验默示许可,其中有超70款新药为首次在中国获批临床。通过梳理发现,这些新药涵盖了单抗、双抗、纳米抗体、放射性核素疗法、反义寡核苷酸(ASO)疗法、CAR-T产品、基因治疗药物、肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(TIL)药物、siRNA药物、分子胶等等。本文将节选其中部分1类新药作介绍,仅供读者参阅(排名不分先后)。(向《医药观澜》微信号回复“7月”即可下载2023年7月首次在中国获得临床试验默示许可的1类新药PDF文件)图片来源:123RF罗氏(Roche):RO7434656注射液作用机制:新型ASO疗法适应症:IgA肾病根据罗氏公开资料,RO7434656是一种新型反义寡核苷酸(ASO)疗法,拟开发治疗免疫球蛋白A(IgA)肾病。该药可以降低炎症水平,保护原发性IgA肾病患者的肾脏免受长期损害。该产品正在海外开展治疗IgA肾病的3期临床研究。百济神州:BGB-24714胶囊作用机制:口服IAP拮抗剂适应症:恶性肿瘤根据百济神州公开资料,BGB-24714为一款在研的第二线粒体来源的半胱氨酸蛋白酶激活剂(SMAC)模拟物,也是一款新型口服IAP拮抗剂。IAP是细胞凋亡的重要调控因子,它的高表达促进了肿瘤发生和肿瘤转移。SMAC模拟物是一类新型的细胞凋亡诱导剂,可以有效模拟由线粒体释放的第二信使SMAC产生的生物效应,即结合并中和凋亡蛋白抑制因子(IAP)。本次BGB-24714获批临床的适应症为恶性肿瘤,包括但不限于肺癌、食管癌、乳腺癌、卵巢癌、头颈鳞癌等。荣昌生物:RC148注射液作用机制:双抗适应症:实体瘤患者根据荣昌生物新闻稿,RC148是该公司自研的新型双特异性抗体,也是该公司首款获批临床的双抗。该药本次获批的是一项1期临床研究,入组人群主要为经标准治疗后疾病进展,或对标准治疗不耐受,或不存在标准治疗的局部晚期不可切除或转移性恶性实体肿瘤。翰森制药:HS-10518胶囊作用机制:GnRH受体拮抗剂适应症:子宫内膜异位症相关中重度疼痛等HS-10518(又被称为TU2670)是一种口服非肽类GnRH受体拮抗剂。翰森制药于2022年与TiumBio公司达成约1.7亿美元合作,从而获得中国的独家许可,开发并商业化TU2670用于子宫内膜异位症和子宫肌瘤及其它潜在适应症的治疗。该药本次在中国获批临床,拟用于治疗子宫内膜异位症相关中重度疼痛、子宫肌瘤相关月经过多。信达生物:IBI354作用机制:靶向HER2的抗体偶联药物(ADC)适应症:晚期实体瘤根据信达生物公开资料,IBI354为一款注射用重组抗HER2单克隆抗体-喜树碱衍生物偶联物,本次获批临床的适应症为晚期实体瘤。根据ClinicalTrials官网,该药正在海外开展针对局部晚期不可切除或转移性实体瘤患者的1/2期临床研究。博锐生物:注射用BRY812作用机制:靶向LIV-1的ADC适应症:晚期恶性肿瘤根据博锐生物新闻稿,BRY812为该公司研发的靶向锌转运蛋白(LIV-1)的创新型ADC,拟定适应症为晚期恶性肿瘤。LIV-1是一种多次跨膜蛋白,与上皮-间质细胞转化有关,并在多种癌症中表达异常,对肿瘤的转移起到关键作用。BRY812通过CysLink不可逆化学偶联平台和高度稳定的连接子,将靶向LIV-1的抗体与小分子毒素偶联。该药在临床前研究中表现出明显的肿瘤生长抑制效果。福沃药业:FWD1802片作用机制:第三代口服选择性雌激素受体降解剂适应症:乳腺癌根据福沃药业公开资料,FWD1802是第三代口服选择性雌激素受体(ER)降解剂(SERD),它兼具ER降解和拮抗的双重作用,具有较强的体内、体外药效,并且对于上一代用药后产生的突变同样有效。同时,该药在临床上可以采用更加便捷的口服用药。该产品获批临床的适应症为:ER+/HER2-不可切除的局部晚期或转移性乳腺癌。英矽智能/复星医药:ISM8207胶囊作用机制:靶向QPCTL的小分子抑制剂适应症:晚期恶性肿瘤根据英矽智能早先招股书资料,ISM8207胶囊(又称ISM004-1057D)是其与复星医药合作开发的靶向QPCTL(CD47-SIRPα轴的调节剂)的口服小分子抑制剂,用作癌症免疫治疗。QPCTL这一修饰是CD47与配体SIRPα相互作用所必需的,对CD47上焦谷氨酸的形成起着关键作用。QPCTL抑制剂可模拟CD47抗体的治疗效果,通过阻断该信号来达到抗肿瘤效果。根据复星医药早先新闻稿介绍,ISM8207不仅具有较高的肿瘤渗透性,还能降低血液学毒副作用、避免抗原沉没,而这正是目前大多数CD47抗体药物较为常见的副作用。图片来源:123RF星浩澎博医药:XH-S003胶囊作用机制:补体系统小分子抑制剂适应症:肾小球疾病根据复星医药公告,XH-S003为其控股子公司星浩澎博医药自主研发的小分子抑制剂,拟用于治疗补体异常激活相关的疾病。该新药通过抑制补体系统的异常激活,进而抑制疾病病理表型中常见的补体蛋白复合物的生成。临床前研究显示,其可以显著降低因补体激活导致的炎性损伤,改善靶器官功能,且表现出良好的安全性。该药本次获批临床,拟用于治疗IgA肾病等补体异常激活相关的肾小球疾病。赛神医药:SNP201注射液作用机制:α-突触核蛋白抑制剂适应症:帕金森病根据赛神医药早先新闻稿,SNP201注射液为一款α-突触核蛋白(帕金森病的关键驱动因素)抑制剂。赛神医药于2021年与礼来(Eli Lilly and Company)达成协议,在大中华区(包括中国大陆、香港、澳门和台湾地区)开发和商业化这款靶向抗体疗法。α-突触核蛋白是一种由140个氨基酸组成的蛋白质,它被认为参与调控突触活动和细胞内运输,与帕金森病有着密切关联的路易小体结构便是由α-突触核蛋白的异常纤维化聚集形成的。对于患者来说,降低该蛋白的水平有望延缓或停止帕金森病的病程进展。百极优棠:BPYT-01胶囊作用机制:口服小分子促肠GLP-1分泌剂适应症:2型糖尿病根据百极优棠新闻稿,BPYT-01为一款口服小分子促肠GLP-1分泌剂,由百极优棠、中国科学院上海药物研究所、西双版纳热带植物园合作开发。临床前研究结果表明,BPYT-01口服给药后选择性分布于肠道组织,通过全新作用机制直接促进肠L细胞分泌GLP-1,提高内源性GLP-1水平,显示出与多肽类GLP-1受体激动剂作用类似的作用。该药本次获批临床的适应症为2型糖尿病。宇耀生物:YY201片作用机制:双功能磷酸化位点靶向抑制剂适应症:晚期实体瘤和恶性血液肿瘤根据宇耀生物新闻稿,YY201片是该公司自主研发的STAT3双功能磷酸化位点靶向抑制剂,本次获批针对晚期实体瘤和复发难治性恶性血液肿瘤开展1期临床研究。STAT3(信号转导和转录激活因子3)为“难成药靶点”,其靶点界面相对平坦,无法提供小分子特异性结合的“口袋”结构。YY201具有纳摩尔级别活性,可与STAT3直接结合,抑制其Tyr705和Ser727双位点磷酸化,从而抑制STAT3功能和阻断下游信号传递,发挥抑制肿瘤作用。该药在多种体内模型中表现出显著的抗肿瘤作用,极低剂量下可致肿瘤完全消退。天泽云泰:VGM-R02b作用机制:基因替代疗法适应症:戊二酸血症I型根据天泽云泰公开资料,VGM-R02b用于治疗戊二酸血症I型(GA-I),为该公司基因替代疗法产品管线中的一员。该药属于儿童专用创新药,为防止婴幼儿及儿童期戊二酸血症造成严重或危及生命的疾病进展的潜在治疗方法。GA-I是一种罕见的常染色体隐性遗传性神经代谢性疾病,会引起以神经系统为主的多脏器损害。GA-I多在婴幼儿期发病,常在感染、高蛋白饮食或预防接种等应激刺激后诱发急性脑病危象,通常危及生命。图片来源:123RF天玑济世:TJ0113胶囊作用机制:线粒体自噬诱导剂小分子化合物适应症:Alport综合征根据天玑济世新闻稿,TJ0113为该公司开发的线粒体自噬诱导剂小分子化合物,拟开发治疗Alport综合征。这是一种遗传性肾脏胶原病,基因突变导致肾小球基底膜病变,从而引起肾脏进行性病变。线粒体自噬是细胞中重要的线粒体质量控制过程,即细胞通过自噬机制选择性地包裹并降解线粒体,从而保持线粒体和细胞内稳态。研究表明,激活线粒体自噬可以通过清除受损的线粒体和维持线粒体稳态来逆转受伤肾脏和心脏的病理变化。艾美斐生物:IPG11406片作用机制:新型GPCR小分子拮抗剂适应症:系统性红斑狼疮等根据艾美斐生物新闻稿,IPG11406是一款新型GPCR小分子拮抗剂。相较于目前的治疗药物,IPG11406可以根除炎症部位的免疫细胞浸润,从而避免疾病反复发作。此外,该产品的安全窗口超过150倍,具有较高的安全性。该药本次获批临床,针对的适应症包括系统性红斑狼疮、类风湿关节炎、多发性硬化、炎症性肠病等一系列疾病。普祺医药:PG-018片作用机制:JAK1抑制剂适应症:膜性肾病根据普祺医药新闻稿,PG-018是该公司研发的一款全新高选择性JAK1抑制剂,在非临床研究中表现出良好的靶点特异性和对肾脏病变的显著修复作用,同时避免了非选择性JAK激酶抑制导致的毒副作用,安全性较高。普祺医药计划在临床研究中确证PG-018片治疗膜性肾病的临床疗效和安全性。膜性肾病又被称为膜性肾小球肾炎,是一种抗体介导的自身免疫性肾小球疾病。海正药业:HS329片作用机制:FXIa抑制剂适应症:血栓栓塞性疾病根据海正药业公告,HS329片是该公司研发的通过抑制FXIa来预防和治疗血栓事件的口服抗凝剂,拟用于治疗血栓栓塞性疾病。公开资料显示,凝血因子XIa(FXIa)抑制剂能够降低静脉血栓的发病率而对出血并没有明显影响,是一种新型的抗血栓药物。晟斯生物:注射用培重组人凝血因子IX-Fc融合蛋白作用机制:长效重组九因子适应症:血友病B根据晟斯生物新闻稿,注射用培重组人凝血因子IX-Fc融合蛋白(SS327)是一款长效重组九因子,通过独创的PEG融合与Fc融合技术,大幅延长了九因子的体内半衰期。该产品本次获批临床,即将在12岁以上青少年和成年血友病B(先天性凝血因子IX缺乏症)患者中开展临床研究,用于患者控制出血和常规预防。图片来源:123RF上海医药:SPH7050颗粒作用机制:肠道限制性的免疫调节剂适应症:溃疡性结肠炎根据上海医药公告介绍,SPH7050颗粒(又称I039)是其自主研发的一款肠道限制性的免疫调节剂,能抑制胃肠道的炎症反应和激活胃肠道的调节反应。临床前研究显示该药能改善肠炎动物模型的肠道炎症的症状。该药本次获批临床的适应症为溃疡性结肠炎。恒润达生:HR010作用机制:抗人CD70 CAR-T产品适应症:晚期/转移性肾癌根据恒润达生新闻稿,HR010是该公司首个获批临床的实体瘤CAR-T细胞治疗药物,为一款抗人CD70 T细胞注射液,拟开发治疗晚期/转移性肾癌。恒润达生通过纳米抗体库筛选的全新CD70抗体序列,优化并验证了HR010的CAR结构和功能。在动物模型上,HR010已显示出良好的药效,达到完全清除肿瘤的效果。先博生物:靶向CD19的嵌合抗原受体基因修饰的NK细胞注射液作用机制:通用型NK细胞治疗产品适应症:大B细胞淋巴瘤根据先博生物新闻稿,本次获批临床的产品为该公司自主研发的通用型NK细胞治疗产品,采用了创新设计的CAR结构,临床前研究中展示出了优效的抗肿瘤活性。在前期研究者发起的临床研究(IIT)中,最长获益的患者已实现超过1年的完全缓解。舒泰神:STSA-1201皮下注射液作用机制:抗TSLP单抗适应症:哮喘根据舒泰神公告,STSA-1201皮下注射液由该公司自主研发,是一种靶向人TSLP的全人源单克隆抗体,可通过特异性结合并阻断TSLP与其受体的结合,阻断其生物学功能,如树突细胞的激活、Th2细胞因子和趋化因子的释放、嗜酸性粒细胞浸润和IgE的产生,以及气道高反应等,从而达到治疗哮喘的目的。该产品获批临床的适应症为哮喘。倍特药业:BPR-101胶囊作用机制:阴道用微生态活菌制剂适应症:细菌性阴道病根据倍特药业新闻稿,BPR-101是该公司首个获批临床试验的生物药,拟用于治疗细菌性阴道病。BPR-101属于阴道用微生态活菌制剂,采用乳杆菌及其代谢物的复方制剂,预期在临床上可以快速杀灭病原微生物,为患者本底乳杆菌腾出生长空间,促进其增殖恢复到健康状态;若患者已经缺失该益生菌,BPR-101的活菌亦可快速补充,达到恢复健康阴道微生态,实现治疗目的。中国科学院上海药物研究所、致本医药:ZB-001干混悬剂作用机制:细菌拓扑异构酶抑制剂适应症:单纯性淋病根据致本医药新闻稿,ZB-001是该公司与中国科学院上海药物研究所联合研发的新型抗菌药物,拟用于治疗单纯性淋病等多种细菌感染疾病。ZB-001是新结构、新机制的细菌拓扑异构酶抑制剂。临床前研究表明,该产品抗菌谱覆盖敏感、耐药的淋球菌和几乎所有主要的革兰氏阳性致病菌,以及苛养的革兰氏阴性菌。此外,该产品杀菌作用呈现浓度依赖特征,在药效动力学上表现较好,对单纯性淋病适应症有可能实现较低剂量单次口服“治愈”。图片来源:123RF阿斯利康(AstraZeneca):AZD5863、eplontersen注射液作用机制:CLDN18.2 x CD3双特异性抗体、ASO疗法适应症:实体瘤、转甲状腺素蛋白淀粉样变性心肌病AZD5863(HBM7022)是一款CLDN18.2 x CD3双特异性抗体,为阿斯利康以3.5亿美元合作引进自和铂医药。该产品采用二价高亲和力抗CLDN18.2和单价低亲和力抗CD3的结构,在保证高杀伤活性的同时,降低了产生细胞因子风暴的风险。本次该药获批临床的适应症为晚期或转移性实体瘤。Eplontersen注射液为阿斯利康超35亿美元合作开发的一款反义寡核苷酸(ASO)疗法。它被设计为一月一次,可由患者自己皮下注射,可抑制转甲状腺素蛋白(TTR)的生产。该药本次获批临床的适应症为治疗遗传型和野生型转甲状腺素蛋白淀粉样变性心肌病(ATTR-CM)成人患者。赛诺菲(Sanofi):注射用SAR444200作用机制:抗GPC3/TCR纳米抗体适应症:GPC3阳性晚期实体瘤SAR444200是赛诺菲基于Nanobody技术开发的一款抗GPC3/TCR纳米抗体(VHH)。据赛诺菲官网介绍,大多数抗体只能结合到一个靶标上,然而通过连接Nanobody分子片段,就像串珠一样,可以创建新的化合物(称为“多价”纳米体分子),可一次结合多个不同的靶点。本次该药在中国获批临床,拟开发适应症为GPC3阳性晚期实体瘤。葛兰素史克(GSK):GSK3858279注射液作用机制:抗CCL17抗体适应症:糖尿病周围神经痛、膝骨关节炎所致的中度至重度疼痛葛兰素史克GSK3858279注射液获批临床,拟适用于成人慢性糖尿病周围神经痛(DPNP)以及成人膝骨关节炎所致的中度至重度疼痛。公开资料显示,这是GSK在研的一款抗CCL17抗体。CCL17是一种趋化因子,它通过激活其受体CCR4,可能引起炎症细胞和免疫细胞的聚集,释放炎症介质,从而导致神经损伤和疼痛感受的增加。曙方医药、Santhera公司:vamorolone口服混悬液作用机制:创新类固醇药物适应症:杜氏肌营养不良公开资料显示,vamorolone口服混悬液是曙方医药1.24亿美元自Santhera Pharmaceuticals引进的一款罕见病新药。这是一种创新类固醇药物,能够选择性地激活类固醇的某些信号通路,在引发抗炎症效果的同时,具有一定潜力避免传统类固醇所带来的安全性顾虑与副作用。该药本次在中国获批临床,拟开发治疗2岁及以上患者的杜氏肌营养不良(DMD)。该药已在美国递交用于治疗DMD的新药上市申请。Bellus Health公司:BLU-5937片作用机制:P2X3受体拮抗剂适应症:难治性慢性咳嗽BLU-5937(camlipixant)是Bellus Health公司研发的一款选择性口服P2X3受体拮抗剂,葛兰素史克于今年6月以总额约为20亿美元完成对Bellus Health的收购,从而囊获这款在研疗法。P2X3受体拮抗剂通过拮抗位于初级传入神经的P2X3受体,降低传入神经兴奋性以抑制咳嗽,并有望在没有中枢神经系统影响的情况下实现镇咳的效果。该药本次获批临床的适应症为难治性慢性咳嗽。除了上述产品,还有其它1类新药也在中国首次获得临床试验默示许可,比如:英矽智能“合成致死”新靶点药物USP1小分子抑制剂、信念医药AAV基因治疗药物、沙砾生物表达膜结合细胞因子的基因编辑型TIL产品、启函生物基因编辑iPSC来源的细胞治疗产品、邦耀生物通用型异体CAR-T制剂、迈威生物分别靶向Trop-2以及B7-H3的ADC产品、康弘药业抗抑郁症新药GABAA受体正向变构调节剂、先声药业自身免疫候选药物IL-2突变融合蛋白、贝达药业多靶点酪氨酸激酶抑制剂伏罗尼布的新型玻璃体内植入剂、晶核生物靶向PSMA的放射性核素疗法等等。限于篇幅,本文不再一一介绍。希望这些在研疗法后续进展顺利,早日惠及患者。向《医药观澜》微信号回复“7月”,即可下载2023年7月首次在中国获得临床试验默示许可的1类新药PDF文件。参考资料:[1]中国国家药监局药品审评中心(CDE)官网.Retrieved July 31,2023, From https://www.cde.org.cn/main/xxgk/listpage/4b5255eb0a84820cef4ca3e8b6bbe20c[2]各公司官网及公开资料本文来自药明康德内容团队,欢迎个人转发至朋友圈,谢绝媒体或机构未经授权以任何形式转载至其他平台。转载授权请在「医药观澜」微信公众号留言联系我们。其他合作需求,请联系wuxi_media@wuxiapptec.com。免责声明:药明康德内容团队专注介绍全球生物医药健康研究进展。本文仅作信息交流之目的,文中观点不代表药明康德立场,亦不代表药明康德支持或反对文中观点。本文也不是治疗方案推荐。如需获得治疗方案指导,请前往正规医院就诊。
临床1期临床3期siRNA引进/卖出免疫疗法
2023-06-20
药物研发进展
1.维健医药引进!口服用苯丁酸甘油酯在中国获批上市
6月19日,香港维健医药集团(以下简称“维健医药”)宣布中国国家药品监督管理局(NMPA)正式批准口服用苯丁酸甘油酯(瑞维安,英文名:Glycerol Phenylbutyrate Oral Liquid)上市,用于不能通过限制蛋白质的摄入和/或单纯补充氨基酸控制的尿素循环障碍(UCDs)患者的长期治疗,包括氨甲酰磷酸合成酶I缺乏、鸟氨酸氨甲酰基转移酶缺乏、瓜氨酸血症1型、精氨琥珀酸尿症、精氨酸血症和HHH[高鸟氨酸血症-高氨血症-同型瓜氨酸尿症]综合征。UCDs是指一组罕见的遗传代谢疾病,由于尿素循环中所需酶或转运蛋白降低或缺乏而导致氨合成尿素发生障碍,造成过量的氨蓄积体内,形成高氨血症。临床以急、慢性血氨升高引起的神经和消化系统症状为主要症状表现,死亡率高、致残率高、症状反复且需长期管理;急性高氨血症可能引起恶心、呕吐、意识障碍等急性脑病症状;长期高氨血症可能会引起生长发育迟滞、认知功能障碍等。研究显示,口服用苯丁酸甘油酯可以维持正常血氨水平、减少高氨危象发生率、改善患者认知功能和生长发育水平,并凭借无色无味的口感提升患者服药体验,显著提高患者依从性和生活质量。2020年12月,维健医药和Immedica Pharma公司宣布双方签署协议,获得了口服用苯丁酸甘油酯在大中华区、韩国、新加坡、越南、印度尼西亚、马来西亚、菲律宾和泰国的独家商业化权益。维健医药成立于2006年,是一家立足中国、面向全球的创新型生物医药公司,致力于为患有罕见病和其他未满足医疗需求的患者提供创新疗法。该公司已建立多元化的产品组合,并拥有多个已上市和处于临床后期阶段的产品,包括孤儿药及专科药品。
2.齐鲁制药伊布替尼片剂仿制药申报上市
6月19日,CDE官网显示,齐鲁制药伊布替尼伊布片上市申请获得受理。这是国内首款申报上市的伊布替尼片剂仿制药。伊布替尼(Imbruvica,商品名:亿珂)是全球首个获批上市的BTK抑制剂。伊布替尼可与BTK的ATP结合结构域的活性位点上的半胱氨酸残基(Cys481)共价结合形成共价键,从而抑制激酶活性,阻断B细胞受体信号传导,从而减少B细胞生长、增殖、存活、黏附和迁移。同时伊布替尼还可通过减少分泌细胞趋化因子及促炎细胞因子,下调抗凋亡蛋白bcl-2家族的表达水平,抑制肿瘤细胞的生长、黏附、侵袭和迁移,并促进其凋亡,从而起到良好的抗肿瘤作用。2013年11月,伊布替尼胶囊(70mg和140mg)获得FDA批准上市,用于治疗套细胞淋巴瘤(MCL)。套细胞淋巴瘤诊断与治疗中国专家共识(2016年版)中指出,对于复发患者尚无统一的治疗推荐,需综合考虑选择与之前治疗方案非交叉耐药的方案,条件允许的情况下可考虑新药联合化疗。复发难治MCL的新药选择包括伊布替尼、硼替佐米、来那度胺和西罗莫司,其中伊布替尼的总反应率(ORR)和完全缓解(CR)率最高,中位缓解持续时间(DOR)、中位无进展时间(PFE)和总生存(OS)时间最长。2015年3月,艾伯维斥资210亿美元重金收购Pharmacyclics,获得了伊布替尼美国市场的商业权利,而强生拥有全球其它国家的商业权利。2018年2月,艾伯维和强生推出了伊布替尼片剂版本,规格包括140mg、280mg和420mg。此前,2022年10月14日,先声药业伊布替尼胶囊获国家药监局批准上市,这是国内首个获批的伊布替尼胶囊剂仿制药。
3.显著缓解溃疡性结肠炎!艾伯维IL-23抗体3期试验达主要终点
近日,艾伯维(AbbVie)公布COMMAND临床3期维持试验的积极顶线结果,数据显示Skyrizi(risankizumab)在治疗中重度溃疡性结肠炎(UC)的成年患者52周时达主要终点(即根据调整后Mayo评分的临床缓解)以及关键次要终点。溃疡性结肠炎是一种慢性、特发性、免疫介导的炎症性肠病(IBD),可引起从直肠延伸至更近端结肠不同程度的持续性粘膜炎症。溃疡性结肠炎的标志性体征和症状包括直肠出血、腹痛、血性腹泻、里急后重(压迫感)、尿急和大便失禁。溃疡性结肠炎的病程因患者而异,在某些情况下可能会引起并发症(包括癌症和死亡)或导致患者需要进行手术。该病症状的严重程度和病程的不可预测性给患者带来了沉重的负担,甚至常常会致残。Risankizumab是一种人源化、IgG1亚型的单克隆抗体,可以借由与IL-23的p19亚基结合而选择性地拮抗IL-23。IL-23是一种与炎症有关的细胞因子,被认为与许多慢性免疫疾病有关。目前,Skyrizi已获得3项FDA批准的适应症,包括克罗恩病、中重度斑块状银屑病,以及成人活跃银屑病关节炎。在COMMAND维持试验中,来自INSPIRE临床2b/3期试验中对诱导治疗产生应答的患者被重新随机分配,接受180 mg、360 mg risankizumab的皮下注射,或着停止risankizumab的治疗。其中约75%的患者在过去对至少一种溃疡性结肠炎疗法(生物制剂,JAK抑制剂和/或S1P受体调节剂)治疗失败。分析显示,接受180 mg、360 mg risankizumab治疗的患者中,有显著更高比例在52周时达到临床缓解:分别为40%和38%,此数值在对照组中为25%(p<0.01)。
4.进击一线疗法!辉瑞启动ER PROTAC第二项III期临床研究
6月19日,辉瑞启动了vepdegestrant(ARV-471/PF-07850327)的第2项全球性III期临床试验(VERITAC-3),旨在评估vepdegestrant联合哌柏西利对比标准治疗(来曲唑+哌柏西利)一线治疗雌激素受体阳性(ER+)、人表皮生长因子受体阴性(HER2-)局部晚期或转移性乳腺癌患者的优效性和安全性。研究的主要终点为无进展生存期(PFS)。该研究拟纳入1180例既往未接受过任何治疗的乳腺癌患者,预计将于2023年6月28日启动并于2030年7月26日完成。在研究正式开始之前,存在一个研究诱导期(Study Lead-In,SLI),将在50例患者中评估两种剂量vepdegestrant的治疗效果,以确定III期推荐剂量(R3PD)。此前,辉瑞已于2022年12月16日启动了vepdegestrant的第一项III期临床试验VERITAC-2,旨在评估vepdegestrant对比氟维司群二线治疗ER+/HER2-晚期乳腺癌患者的有效性和安全性。Vepdegestrant是Arvinas开发的一款可口服、靶向ER的蛋白降解剂(PROTAC),可诱导野生型和突变型ER的降解。在临床前研究中,vepdegestrant在肿瘤细胞中显示出高达97%的ER降解,在多种ER驱动的异种移植模型中作为单一药物给药时诱导肿瘤缩小,并且与标准治疗药物fulvestrant相比,无论是作为单一药物还是与CDK4/6抑制剂联合使用,都显示出更高的抗肿瘤活性。2021年7月,Arvinas宣布与辉瑞达成全球合作,共同开发和共同商业化vepdegestrant,Arvinas和辉瑞将平均分担全球开发成本、商业化费用和利润。
5.安进启动纳武利尤单抗生物类似药III期临床
6月19日,clinicaltrials.gov网站上登记了安进开展的一项III期临床试验,其旨在评估ABP206与纳武利尤单抗(Opdivo,O药)在黑色素瘤患者中的药代动力学(PK)相似性、有效性、安全性和免疫原性。该研究是一项随机、双盲临床试验,拟纳入249例未接受过抗癌药物治疗的III期或IV期黑色素瘤患者,患者将按1:1:1随机分配接受ABP206或FDA批准的O药或欧盟批准的O药治疗。研究的主要终点为28天内的血清浓度-时间曲线下面积(AUC0-28d)和第17-21周稳态给药间隔期内的血清浓度-时间曲线下面积(AUCtau_SS)。预计该研究将于2023年7月启动并于2025年7月完成。根据安进研发管线以往的生物类似药产品编号,ABP206大概率是O药的生物类似药。纳武利尤单抗(欧狄沃)是一种PD-1免疫检查点抑制剂,它通过与免疫细胞上的PD-1结合,阻止PD-1与PD-L1结合,进而重新激活患者自身免疫细胞来杀伤肿瘤目前,全球内共8款在研O药生物类似药,其中仅3款处于临床阶段,而安进ABP206进展最快。其它两款临床在研产品来自博安生物(LY01015)和迈博太科/百迈博(CMAB819)。O药的竞争对手帕博利珠单抗(K药),也在面临生物类似药的潜在威胁,10款相关在研产品,最快的也已进入III期阶段(MB12,Laboratorio ELEA)。
6.百时美施贵宝首次披露Breyanzi研究数据
6月17日,百时美施贵宝公司宣布首次披露靶向CD19的CAR-T细胞疗法Breyanzi的两项关键性研究的主要分析结果,分别是:治疗复发性或难治性滤泡性淋巴瘤(FL)患者的全球多中心2期TRANSCEND FL试验,以及多中心1期TRANSCEND NHL 001试验的复发或难治性套细胞淋巴瘤(MCL)队列。这些数据在近日举行的2023年国际恶性淋巴瘤会议(ICML)上以口头报告形式公布。最新临床数据显示,Breyanzi在滤泡淋巴瘤和套细胞淋巴瘤中产生了深刻且持久的反应,两项试验中总缓解率(ORR)分别达到97%和86.5%。Breyanzi(lisocabtagene maraleucel; liso-cel)是一款靶向CD19的CAR-T细胞疗法,具有4-1BB共刺激结构域,可增强CAR-T细胞的扩增和持久性。该产品于2021年2月获美国FDA批准,用于治疗接受过两种或以上系统治疗的复发/难治性大B细胞淋巴瘤(LBCL)成人患者。公开资料显示,Breyanzi的独特之处在于CAR-T疗法中CD8阳性和CD4阳性T细胞的比例得到控制,从而可以更好地控制细胞疗法的毒副作用。套细胞淋巴瘤(MCL)是一种侵袭性的、罕见的非霍奇金淋巴瘤(NHL),约占所有NHL病例的3%。在MCL中,初始治疗后复发较为常见,对于大多数人来说,疾病最终会进展或复发。MD安德森癌症中心(MD Anderson Cancer Center)癌症医学部淋巴瘤和骨髓瘤系首席研究员兼教授Michael Wang博士说,尽管治疗取得了进展,但对高风险、侵袭性复发或难治性套细胞淋巴瘤患者提供深度和持久反应的额外治疗仍然是一个关键的未满足需求。Breyanzi提供了一次性输注完全缓解的潜力和可管理的安全性,代表了这些患者潜在的新治疗选择。
7.天广实口头报告抗CD20抗体膜性肾病2期临床数据
6月19日,天广实宣布在第60届欧洲肾脏协会(ERA)大会期间以口头报告形式公布了第三代抗CD20抗体(MIL62)在膜性肾病治疗领域的2期临床研究数据,汇报人为北京大学第一医院崔昭教授。数据显示,MIL62单药治疗24周肾脏总体缓解率达到62.7%,明显由于对照组(34.8%)。原发性膜性肾病(pMN)是成人肾病综合征的主要病理类型,临床表现为不同程度的蛋白尿,约60%表现为肾病综合征,可伴血尿、肾小球滤过率下降、高血压等临床表现。该病病情缓慢,部分患者可自行缓解,多数患者对治疗反应不佳,且易复发,心血管事件或肾脏疾病的进展风险很高,部分病例在10~15年或更长的时间可发展为终末期肾脏病。公开资料显示,目前有糖皮质激素、环孢素和环磷酰胺在中国获批用于肾病综合症的治疗,但这类产品毒副作用较大,其它如他克莫司和利妥昔单抗则属于适应症外用药。因此,原发性膜性肾病患者在中国存在亟需解决的临床需求。MIL62为天广实研发的一种创新型的II型抗CD20重组人源化单克隆抗体,采用了岩藻糖全敲除技术增强抗体抗体依赖细胞介导(ADCC)。在临床前体外及体内研究中,与第一代抗CD20抗体相比,该产品表现出更强的ADCC活性和清除体内异常激活B细胞的能力。MIL62已经开展了多项临床2/3期试验,涵盖淋巴瘤与自身免疫性疾病的多个细分治疗领域,其中治疗原发性膜性肾病的3期临床试验正在进行中。
8.奥赛康子公司口头报告抗CLDN18.2单抗最新数据
近日,奥赛康药业子公司AskGene在研抗CLDN18.2单抗ASKB589用于实体瘤患者的1/2期多中心试验最新研究成果,在第十五届国际胃癌大会(IGCC)上由北京大学肿瘤医院沈琳教授以口头汇报形式公布。2期扩组研究数据显示,ASKB589联合CAPOX(一种包括卡培他滨和奥沙利铂的联合化疗方案)治疗,经研究者确认的客观缓解率(cORR)为79.2%,疾病控制率(DCR)达95.8%。ASKB589注射液是AskGene公司研发的一款抗CLDN18.2人源化单克隆抗体。临床前研究结果显示,该产品对CLDN18.2的亲和力和特异性高,且均转化为更强的抗体依赖细胞介导(ADCC)和补体依赖的细胞毒性作用(CDC)。该公司已于2022年完成了ASKB589单药和联合CAPOX化疗方案治疗实体瘤受试者的剂量递增阶段的病人入组,目前正在进一步探索该产品联合CAPOX方案以及联合化疗和抗PD-1单抗一线治疗CLDN18.2阳性胃癌或胃食管交界处腺癌的剂量扩展研究。此次在大会上展示的是一项在晚期实体瘤患者中进行的首次人体研究,旨在评价ASKB589单药和联合化疗治疗的安全性及耐受性、药代动力学、免疫原性和初步疗效,包括ASKB589单药剂量递增和扩展研究(Part A)及ASKB589联合化疗剂量递增和扩展研究(Part B)。根据研究人员得出的结论,ASKB589联合CAPOX方案一线治疗CLDN18.2阳性胃癌或胃食管交界处腺癌患者在≥6mg/kg的剂量水平下表现出较好的抗肿瘤活性,且安全性和耐受性良好。本研究证明了其作为下一代抗CLDN18.2抗体的潜质,同时数据进一步支持该产品未来的注册性临床3期研究。
9.葛兰素史克RSV疫苗在中国获批临床
6月19日,中国国家药监局药品审评中心(CDE)官网公示,葛兰素史克(GSK)申报的重组呼吸道合胞病毒(RSV)疫苗(AS01E佐剂系统)获得临床试验默示许可,适用于主动免疫,以预防由呼吸道合胞病毒RSV-A和RSV-B亚型导致的60岁及以上成人的下呼吸道疾病。RSV是一种常见的、具有传染性的病毒,可导致潜在的严重呼吸道疾病。当感染RSV后,老年人群患严重疾病的风险很高,部分原因是与年龄相关的免疫力下降,其中有基础疾病(如呼吸系统和心脏疾病,以及糖尿病)的老年人患上严重疾病的风险更大。RSV还会加重其他疾病,包括慢性阻塞性肺疾病、哮喘和慢性心力衰竭,并可导致重度并发症(如肺炎、住院和死亡)。Arexvy为GSK开发的一款针对老年人的RSV疫苗,它由RSV融合前(prefusion)F糖蛋白(RSVPreF3)与GSK专有的佐剂AS01E组合而成。此融合前F糖蛋白为RSV病毒进入人体细胞所需。美国FDA已于今年5月批准Arexvy上市,用于预防60岁及以上人群因RSV引起的下呼吸道疾病(LRTD)。根据GSK此前新闻稿,FDA批准Arexvy是基于AReSVi-006(成人呼吸道合胞病毒)关键性3期试验积极结果。在试验中,该疫苗对60岁及以上成人的RSV-LRTD的保护效力为82.6%(疫苗组7/12,466人;对照组40/12,494人),具有显著的统计学和临床意义,达到临床试验主要终点。
行业资讯
恒瑞医药终止与天广实MIL62的合作及股权投资
近日,江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司与北京天广实生物技术股份有限公司协商一致,决定终止有关MIL62 产品的相关合作以及终止达成的初步股权投资意向,并签署了终止协议。原合作协议于 2021 年 9 月由恒瑞医药与天广实生物达成。一、合作终止的原因:因市场环境变化等因素,经双方友好协商,决定终止有关 MIL62 产品的相关合作,并终止达成的初步股权投资意向。二、合作的进展情况:截至2023年6月16日,恒瑞医药已获得 YY-20394 联合 MIL62 治疗复发难治 B 细胞非霍奇金淋巴瘤的临床试验批件,暂未就股权投资事项与天广实生物签订正式的股权投资协议。合作终止后,恒瑞医药将不再开展 MIL62与公司产品联用的临床研究,双方 仍将履行保密义务,互不负有债权债务,不存在任何纠纷或争议。三、终止合作对恒瑞医药的影响:此次与天广实生物终止合作后,恒瑞医药不再拥有MIL62在大中华地区内的商业化权益,且不再开展 MIL62 与公司产品联用的临床研究。本次终止合作不会对财务状况及经营成果构成重大影响。MIL62是天广实生物研发的糖基化改造人源化II型抗CD20单抗。2021年4月,天广实获得国家药品监督管理局批准进行难治性滤泡性淋巴瘤患者III期注册试验,成为中国首款进入III期临床试验阶段的由国内药企开发的第三代抗CD20抗体。MIL62单抗可通过抗体依赖的细胞毒作用、补体依赖的细胞毒作用和与CD20分子结合引起直接效应来杀伤B细胞来源的肿瘤,拟用于多种血液肿瘤和自身免疫疾病的治疗。

临床研究疫苗免疫疗法
分析
对领域进行一次全面的分析。
登录
或
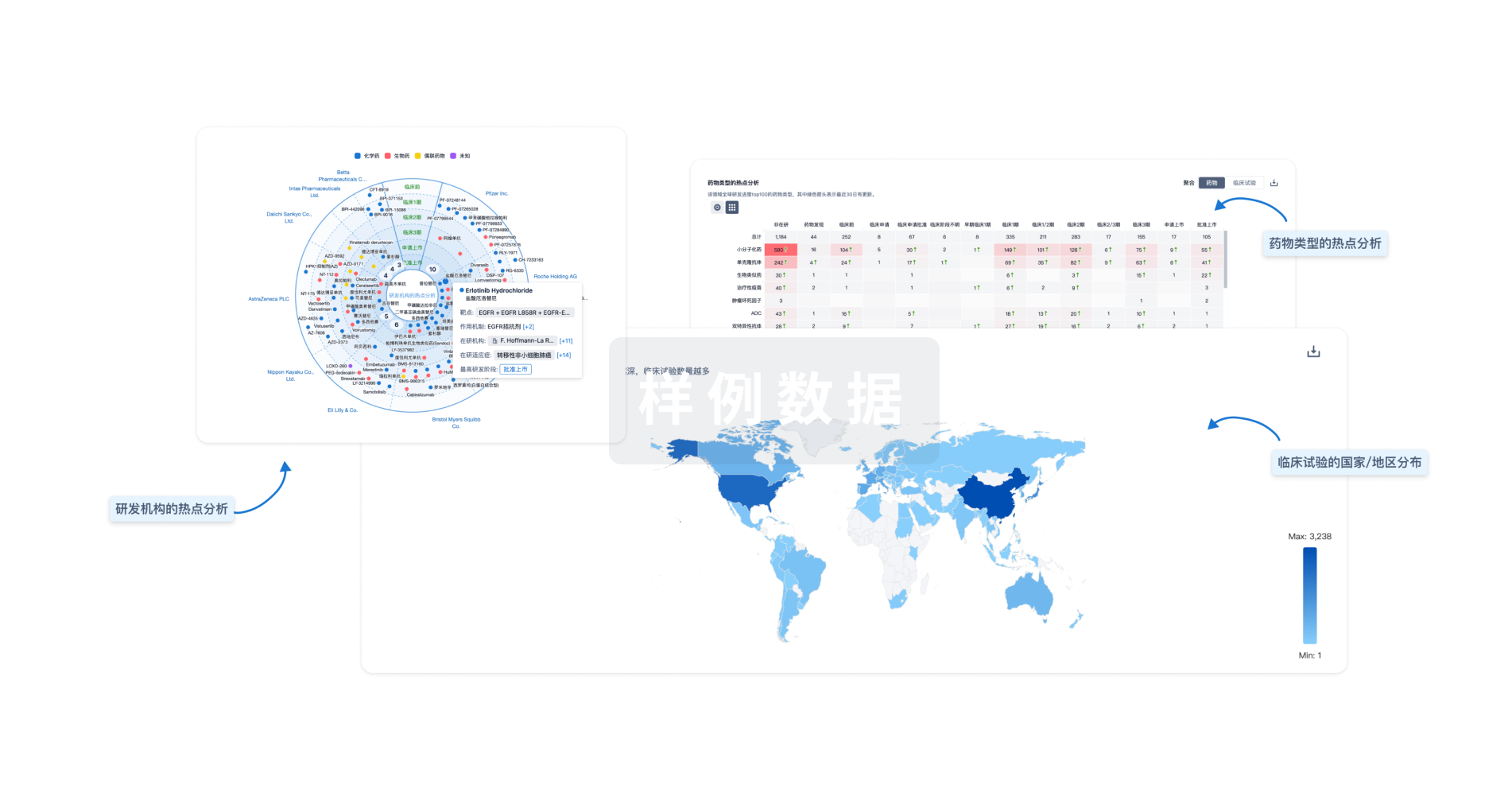
Eureka LS:
全新生物医药AI Agent 覆盖科研全链路,让突破性发现快人一步
立即开始免费试用!
智慧芽新药情报库是智慧芽专为生命科学人士构建的基于AI的创新药情报平台,助您全方位提升您的研发与决策效率。
立即开始数据试用!
智慧芽新药库数据也通过智慧芽数据服务平台,以API或者数据包形式对外开放,助您更加充分利用智慧芽新药情报信息。
生物序列数据库
生物药研发创新
免费使用
化学结构数据库
小分子化药研发创新
免费使用
